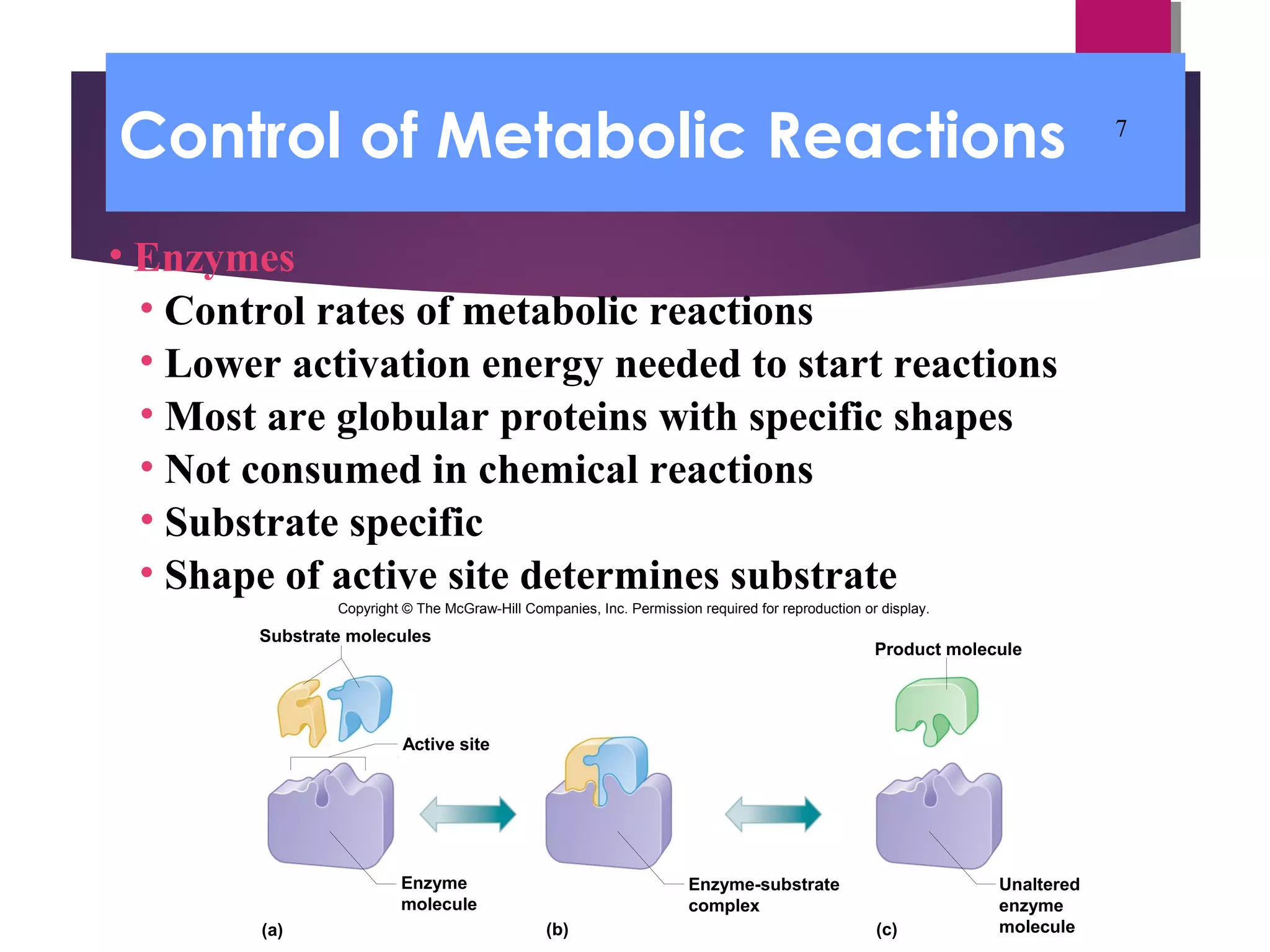
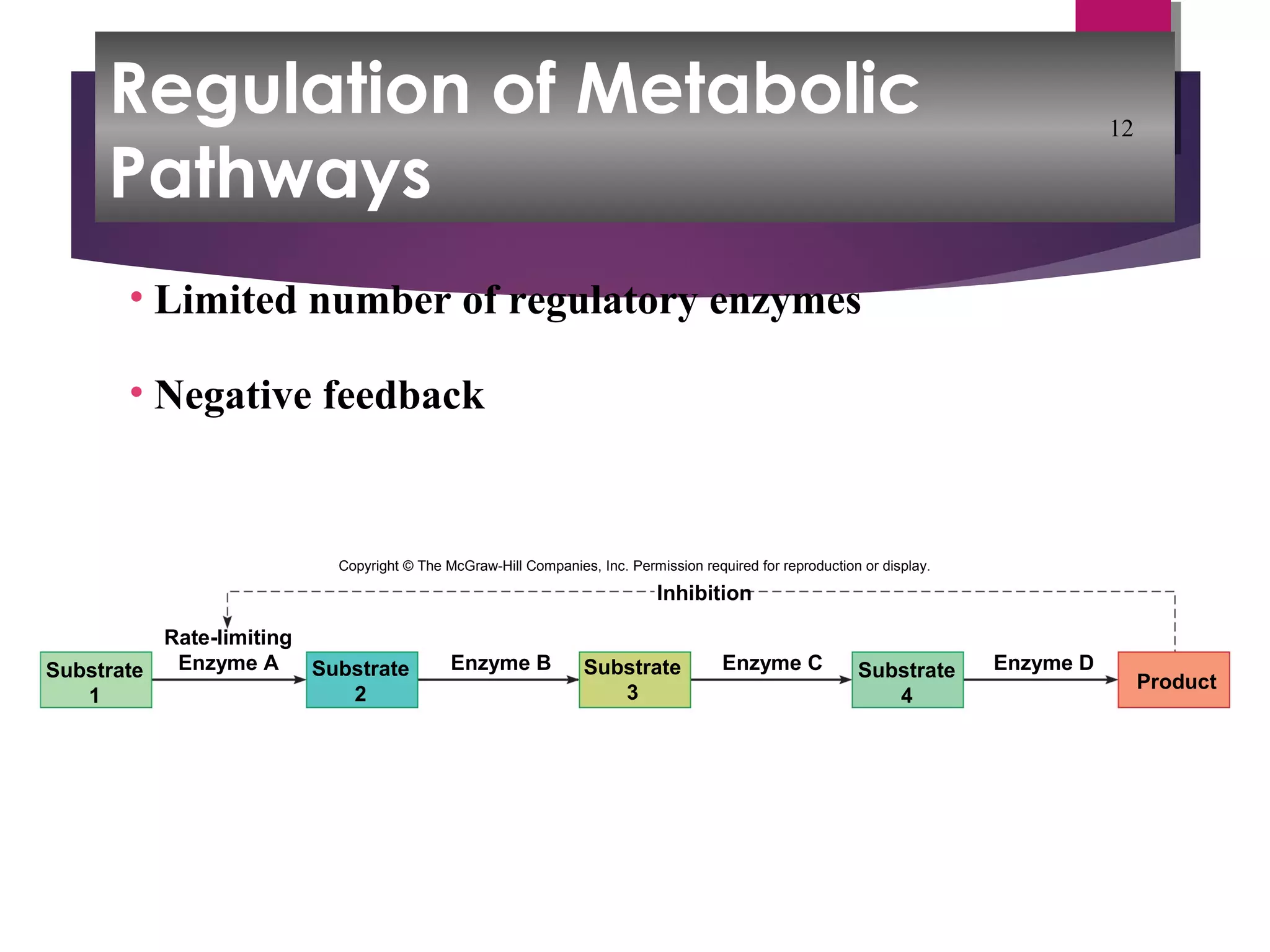
Metabolic processes are the chemical reactions that occur in the body and include both anabolism and catabolism. Anabolism involves building larger molecules from smaller ones and requires energy, while catabolism breaks down larger molecules into smaller ones and releases energy. Enzymes control the rates of metabolic reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for the reactions and are specific to certain substrates due to the shape of their active sites.