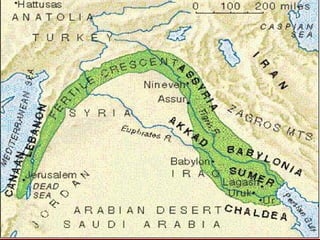
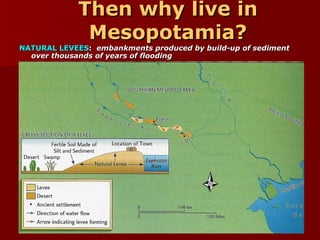
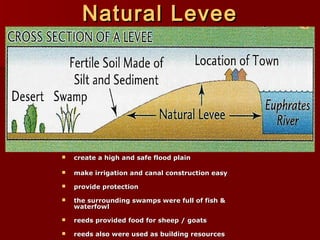
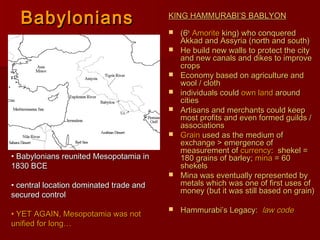
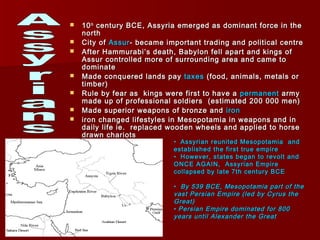
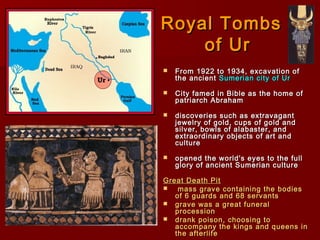
Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in present-day Iraq, was the site of some of the earliest civilizations. The Sumerians established cities around 3500 BCE and developed irrigation systems, writing, mathematics, and metalworking. Later, the Akkadians and Babylonians ruled parts of Mesopotamia. King Hammurabi of Babylon unified the region in the 18th century BCE and established the famous Code of Hammurabi, one of the earliest known legal codes. Despite periods of unity, Mesopotamia saw rule by many different peoples and independent states over 3000 years, establishing it as the "Cradle of Civilization."