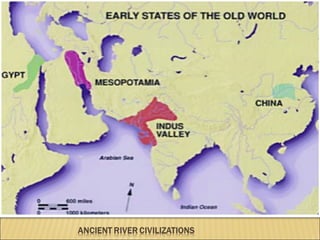
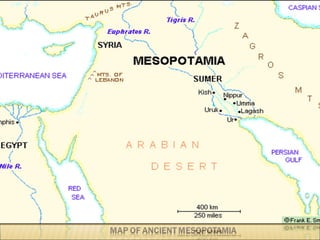
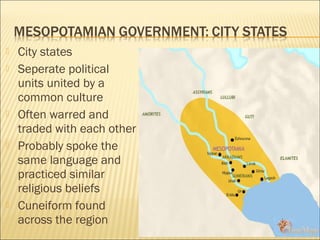
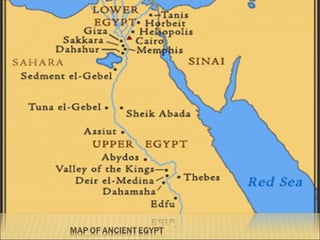
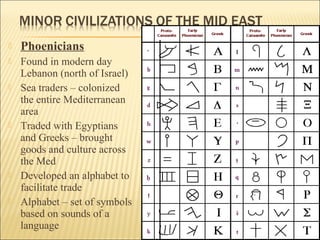
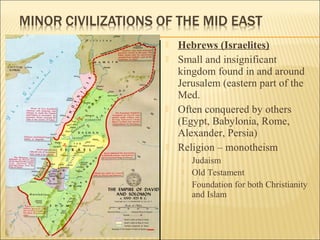
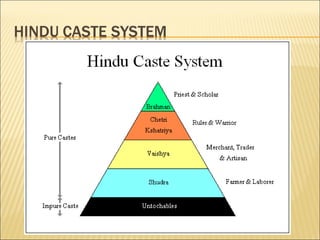
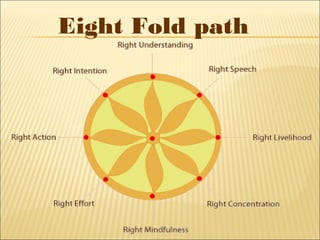
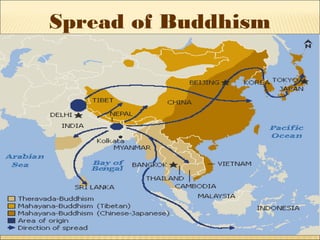
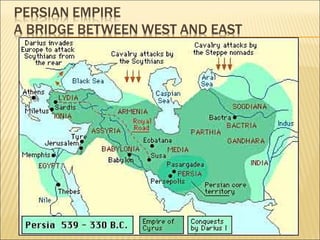
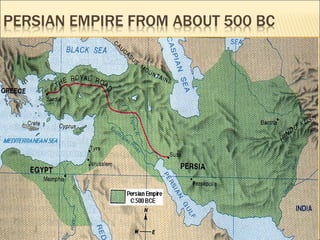
The document provides background information on early civilizations that developed writing systems. It discusses the earliest civilizations along major river valleys in Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China. The oldest writing system was cuneiform developed by the Sumerians in Mesopotamia around 3500 BCE. Other early writing systems included hieroglyphics in Egypt and an alphabet developed by the Phoenicians. Major religions also originated in these early civilizations like Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, and Confucianism. The Persian Empire was also discussed as a powerful empire that stretched from India to Greece in the 6th-4th centuries BCE.