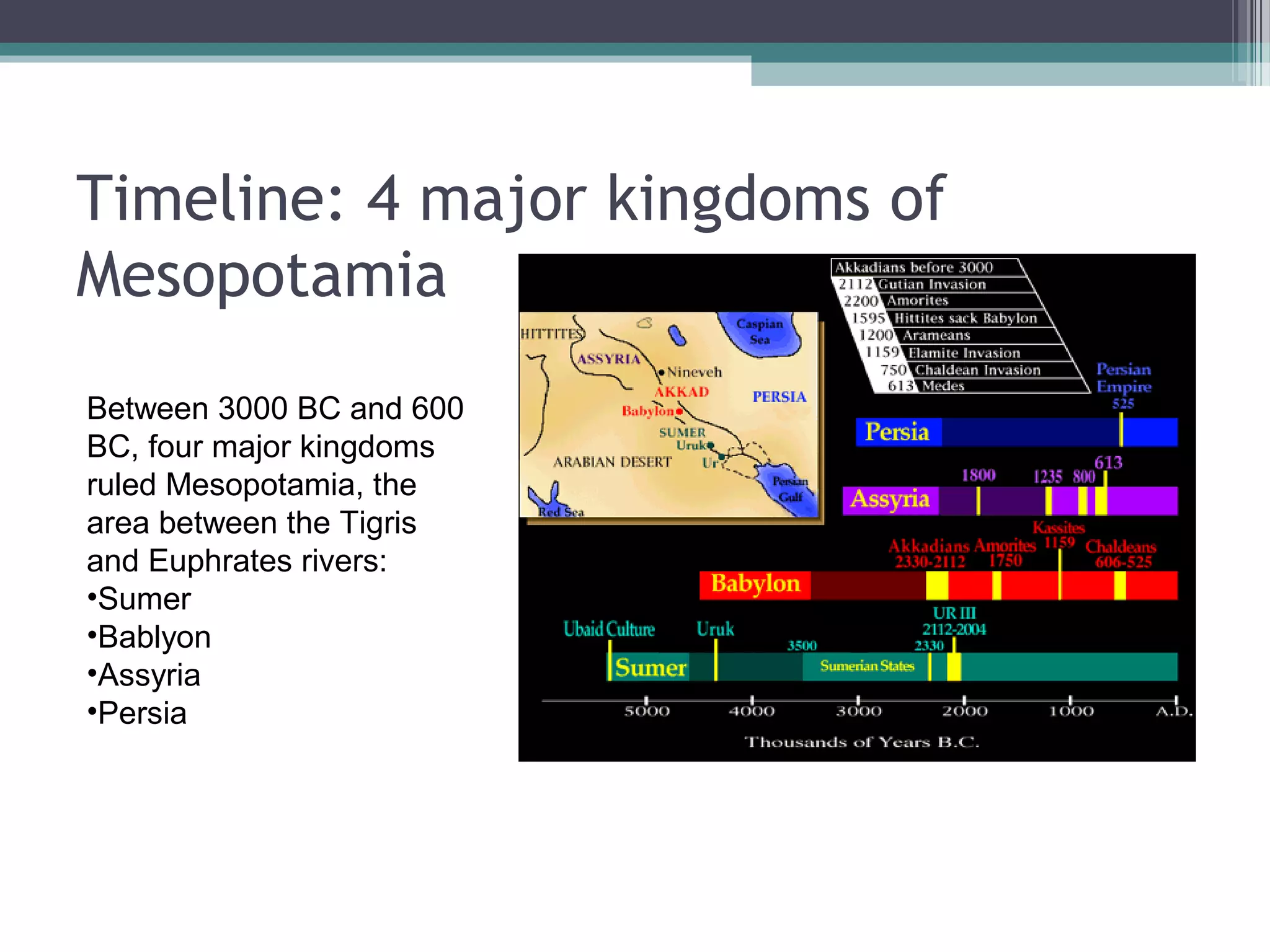
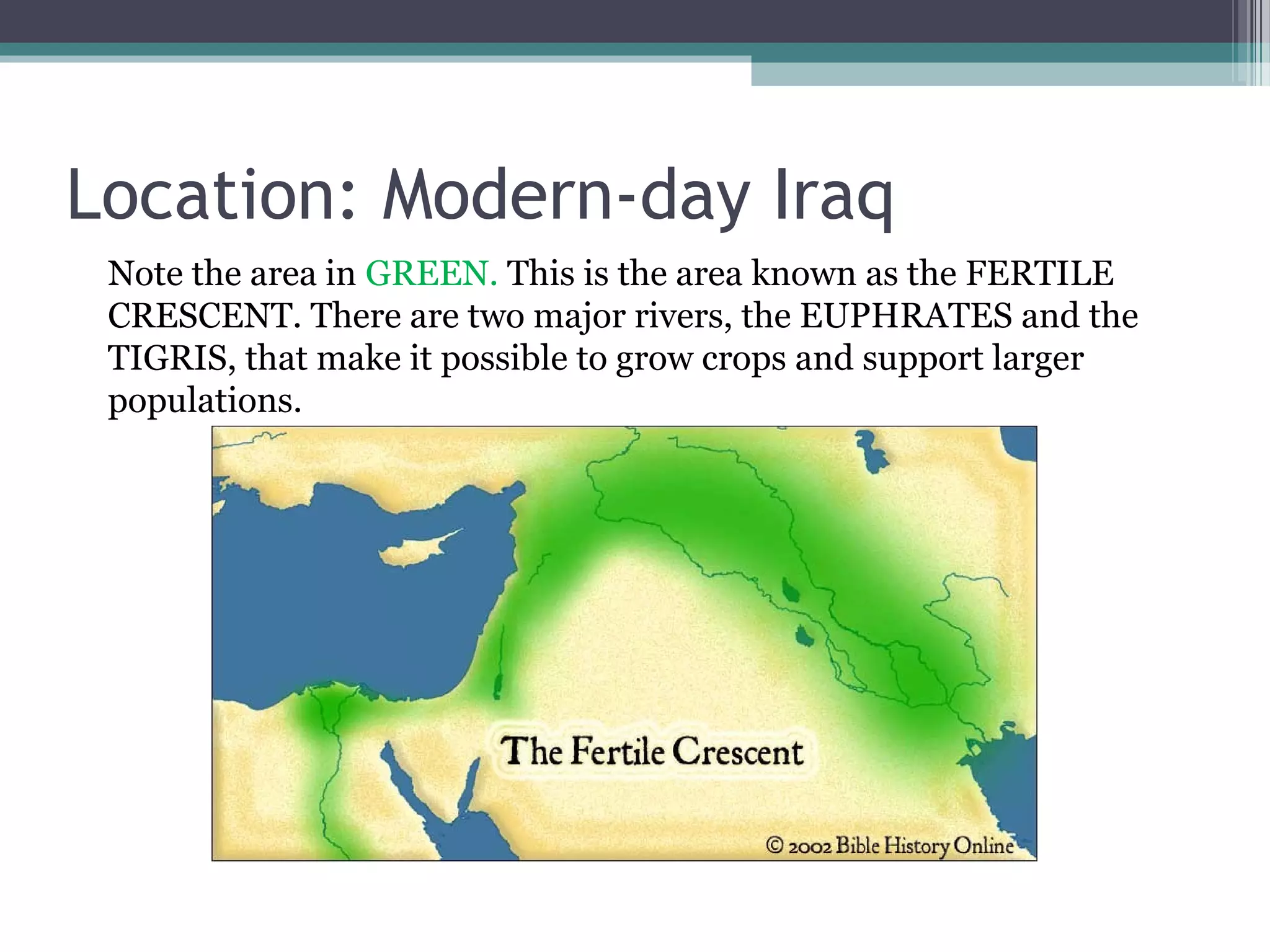
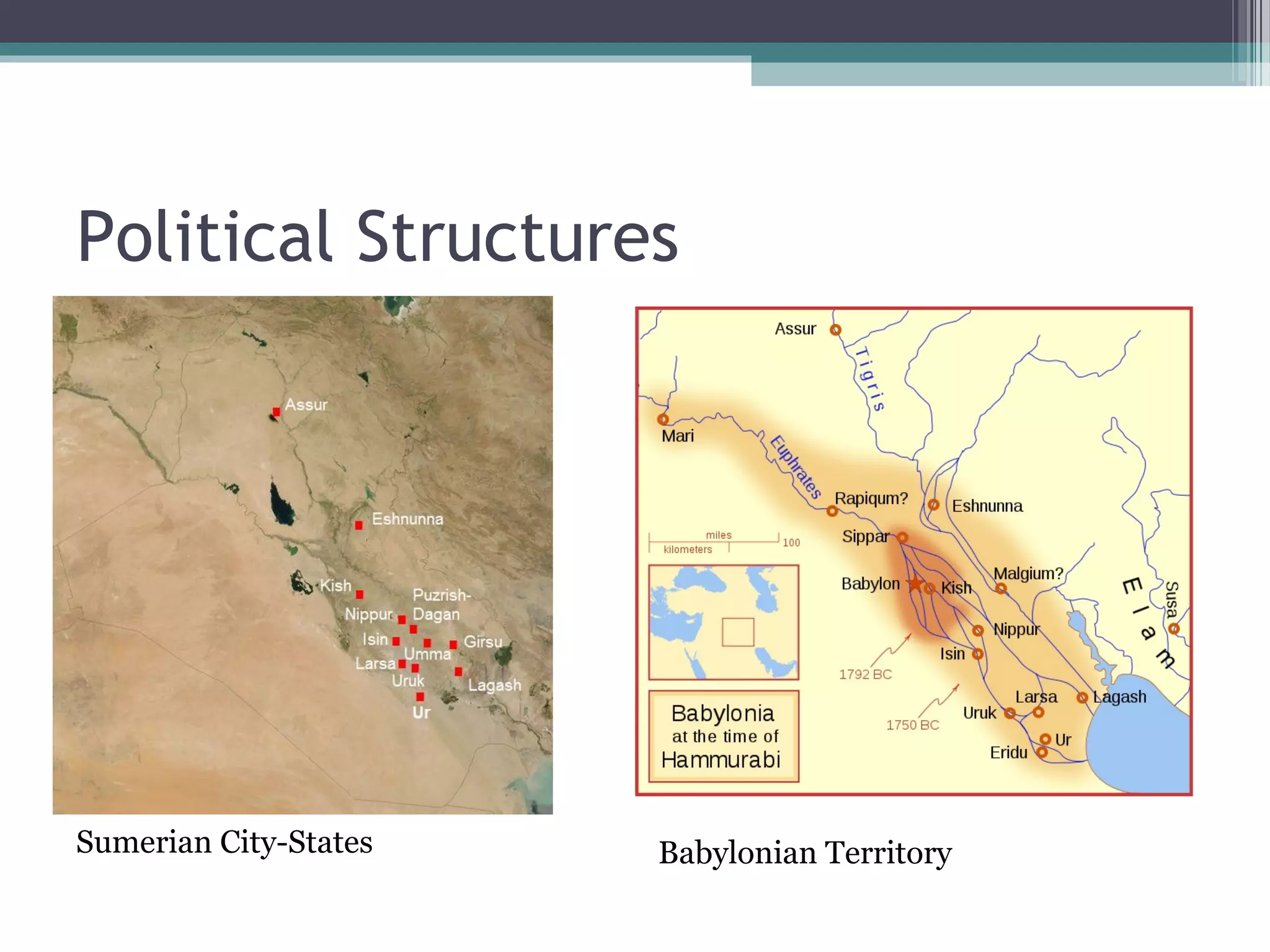
Mesopotamia was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern-day Iraq. Several ancient civilizations flourished there between 5000 BCE and 600 BCE, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. The region had a desert climate but the rivers provided fertile land for agriculture. City-states dominated the political structures, each ruled by a king, and empires like Babylon and Assyria later united the region through conquest. The Mesopotamian economy was based on agriculture and trade of crops and resources. Religion, science, and the arts also developed significantly.