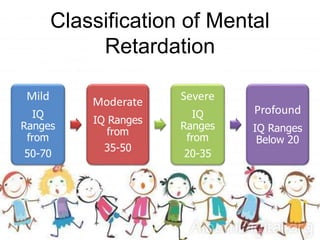
This document discusses mental retardation, including its definition as a developmental disability marked by below-average intelligence and limited daily living skills. It describes the classification of mental retardation as mild, moderate, severe or profound based on IQ ranges. The types are then defined in more detail, outlining common characteristics. Causes of mental retardation are also listed, such as genetic abnormalities, problems during pregnancy or birth, infections, and exposure to diseases or toxins. Finally, some specific types of mental retardation are named, like Down's syndrome, Fragile X syndrome, Microcephaly and Hydrocephalus.