Mental retardation, also known as intellectual disability, is a developmental disability characterized by limitations in intellectual functioning (IQ under 70-75) and adaptive behaviors that are diagnosed before age 18. It occurs in approximately 2-3% of the population and can be caused by genetic, prenatal, childhood, and environmental factors. Mental retardation is classified by severity into four categories: mild, moderate, severe, and profound. Treatment focuses on education, life skills training, supportive living, and family therapy.






![Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
mental
[men´tal]
1. pertaining to the mind.
2. pertaining to the chin.
mental disorder any clinically significant behavioral or psychological syndrome characterized by distressi
ng symptoms,significant impairment of functioning, or significantly increased risk of death, pain, or other d
isability. Mental disorders areassumed to result from some behavioral, psychological, or biological dysfun
ction in the individual. The concept does notinclude deviant behavior, disturbances that are essentially co
nflicts between the individual and society, or expected andculturally sanctioned responses to particular ev
ents.
mental retardation less than average general intellectual functioning that brings with it some degree of i
mpairedadaptation in learning, social adjustment, or maturation, or in all three areas; it is now classified a
s a DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITY.
Mental retardation is a relative term. Its meaning depends on what society demands of the individual in le
arning, skills,and social responsibility. Many people who are considered developmentally challenged in th
e complex modern worldwould get along normally in a simpler society.
Diagnosis: There is no absolute measurement for retardation. At one time the different types were classifi
ed onlyaccording to the apparent severity of the retardation. Since the most practical standard was intellig
ence, the degree ofretardation was based on the score of the patient on INTELLIGENCE
TESTS such as the INTELLIGENCE
QUOTIENT (IQ). The averageperson is considered to have an IQ of between 90 and 110, and those who sc
ore below 70 are considered mentallyretarded.
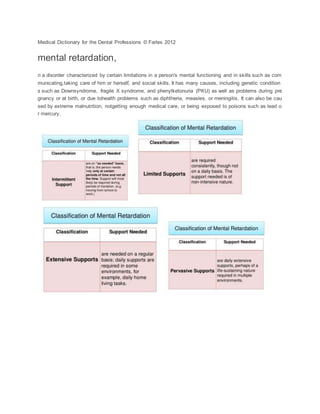
In the past, the different groupings were classified in terms such as feebleminded, idiot, imbecile, and mor
on. Today,most health care providers use the following classifications: for IQ's from 50 to 70, mild; 35 to 5
0, moderate; 20 to 35,severe; under 20, profound. Whatever classifications are used, it is agreed that IQ
measurements are only one part ofthe factors to be considered in determining mental retardation. Others,
such as the patient's adaptability to surroundings,the services and training available, and the amount of c
ontrol shown over his or her emotions, are also very important.
About 85 per cent of patients considered mentally retarded are in the least severe, or mild, group. Those i
n this group donot usually have obvious physical defects and thus are not always easy to identify as ment
ally retarded while they arestill infants. Sometimes such a child's mental defects do not show up until the t
ime of entering school, when the childhas difficulty learning and keeping up with others in the same age g
roup. Many persons who are in the mild category, asadults can find employment or a place in society suit
able to their abilities, so that they are no longer identified asmentally retarded.
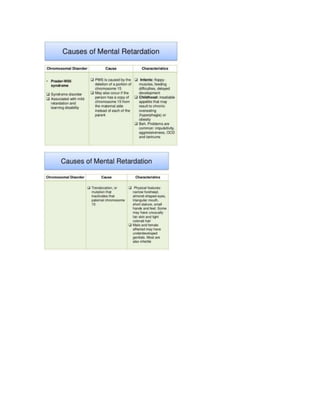
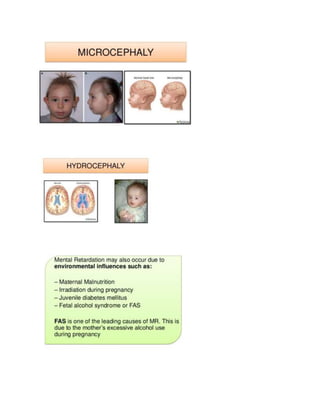
Cause: The cause of mental retardation is often unidentifiable; known ones are classified as either geneti](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/document1-160420102937/85/Document1-7-320.jpg)
![c or acquired.Genetic conditions include chromosomal abnormalities such as DOWN
SYNDROME and KLINEFELTER'S
SYNDROME and errors ofmetabolism such as PHENYLKETONURIA, HYPOTHYROIDISM, and TAY-SACHS
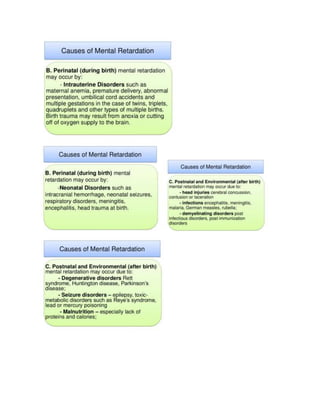
DISEASE. Acquired conditions may be prenatal, perinatal,or postnatal. Prenatal conditions include RUBELLA
and other viral infections, toxins, placental insufficiency, and blood typeincompatibility. Perinatal causes a
re anoxia, birth injury, and prematurity. Postnatal causes may include infections,poisons, poor nutrition, tr
auma, and sociocultural factors such as deprivation.
Many conditions that can cause severe retardation can be diagnosed during pregnancy, and in some cas
es propertreatment can lessen or even prevent retardation. Proper care for the mother during pregnancy
and for the baby in thefirst months of life is also important.
retardation
[re″tahr-da´shun]
delay; hindrance; delayed development.
mental retardation subnormal general intellectual development, associated with impairment of either lear
ning and socialadjustment, maturation, or both; see also MENTAL RETARDATION.
psychomotor retardation a generalized slowing of physical and emotional reaction, such as that seen in
majorDEPRESSION and in catatonic SCHIZOPHRENIA.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. ©
2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
men·tal re·tar·da·tion
subaverage general intellectual functioning that originates during the developmental period and is associa
ted withimpairment in adaptive behavior. The American Association on Mental Deficiency lists eight medic
al classificationsand five psychological classifications; the latter five replace the three former classification
s of moron, imbecile, andidiot. Mental retardation classification requires assignment of an index for perfor
mance relative to a person's peers ontwo interrelated criteria: measured intelligence (IQ) and overall soci
oadaptive behavior (a judgmental rating of theperson's relative level of performance in school, at work, at
home, and in the community). In general an IQ of 70 orless indicates mental retardation (mild = 50/55-
70; moderate = 35/40-50/55; severe = 20/25-35/40; profound = below20/25); an IQ of 70-
85 signifies borderline intellectual functioning.
Synonym(s): amentia (1) , mental deficiency, oligophrenia
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
mental retardation
n. Often Offensive
Intellectual disability.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/document1-160420102937/85/Document1-8-320.jpg)