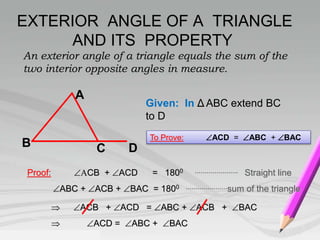
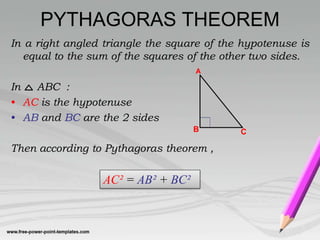
This document discusses various properties of triangles, including:
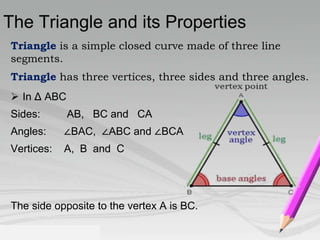
- Triangles have three sides, three vertices, and three angles.
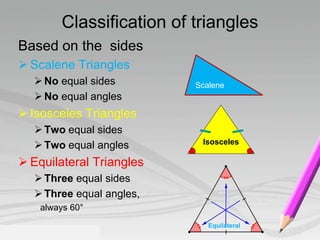
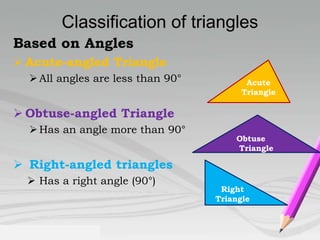
- Triangles can be classified based on sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral) and angles (acute, obtuse, right).
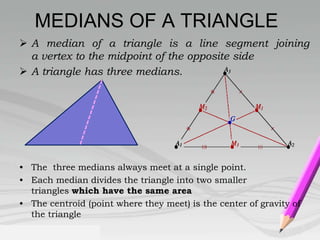
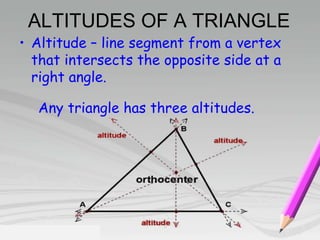
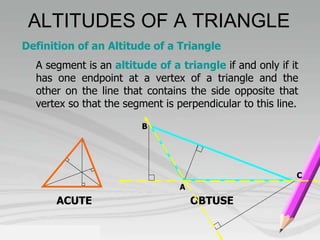
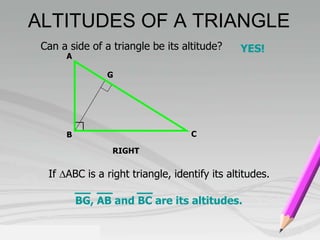
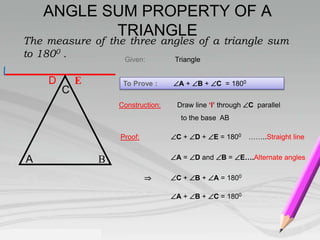
- Key properties include: a triangle's three medians intersect at the centroid; a triangle has three altitudes drawn from each vertex to the opposite side; the measure of a triangle's three angles sum to 180 degrees.