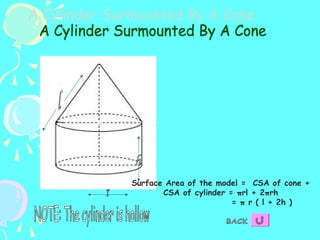
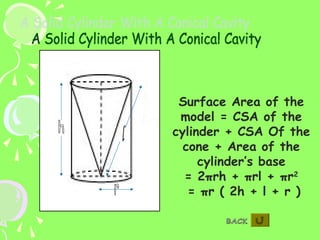
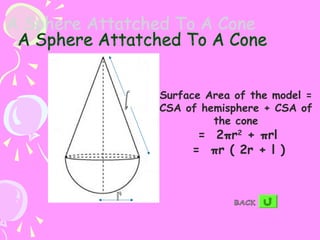
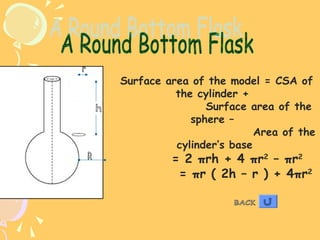
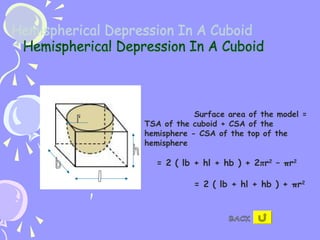
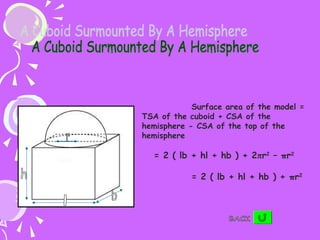
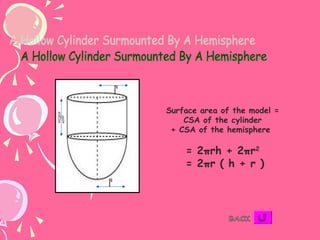
The document provides formulas for calculating the surface area of various 3D geometric shapes like cubes, cuboids, spheres, cylinders, cones, and combinations of shapes. The key information summarized is:
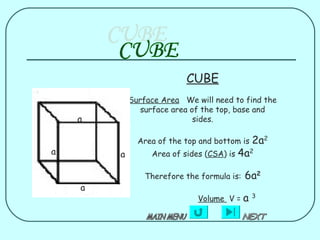
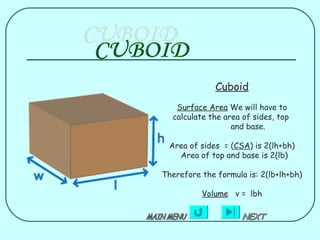
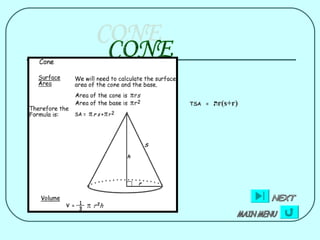
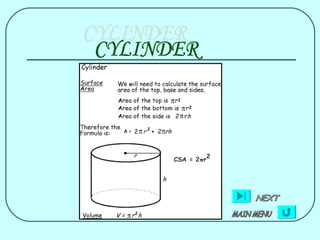
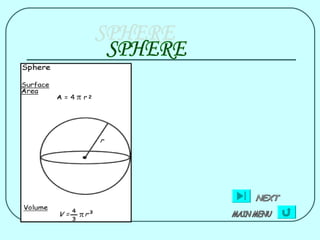
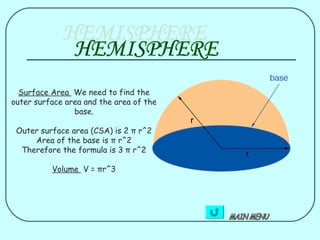
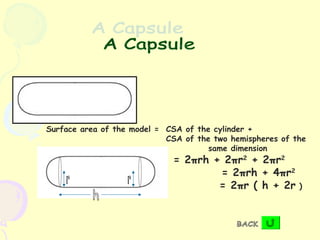
1) Formulas are given for surface area of individual shapes like cubes (6a^2), cuboids (2(lb+lh+bh)), spheres (4πr^2), cylinders (2πrh+2πr^2), and cones (πr(l+2h)).
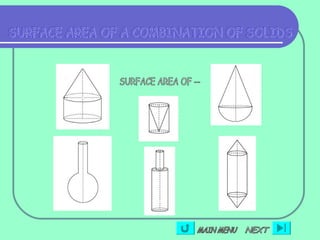
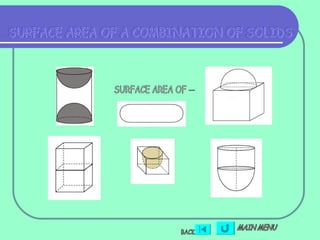
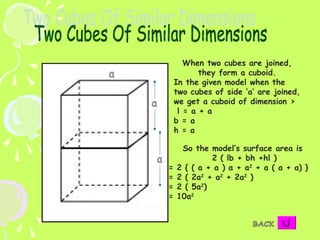
2) Formulas are also provided for combinations of shapes, for example when two cubes are joined to form a cuboid the surface area is 10a^2.
3) In general,