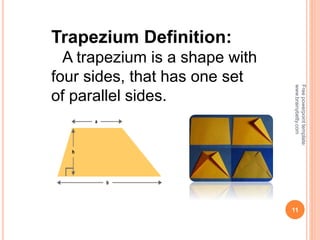
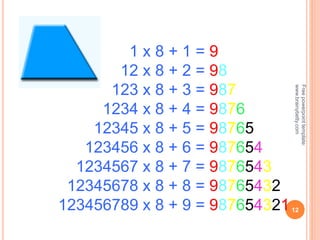
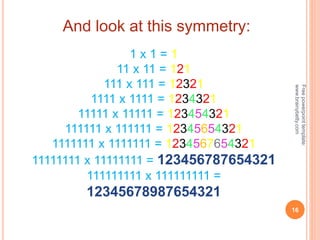
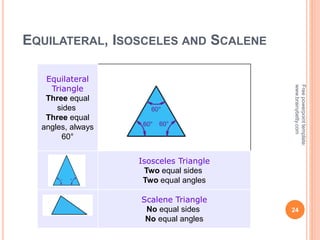
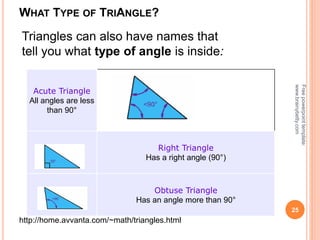
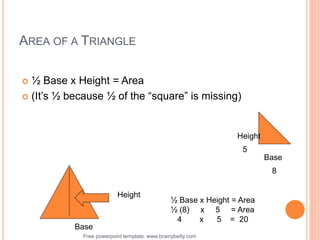
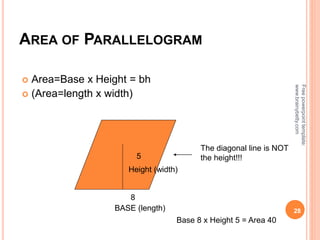
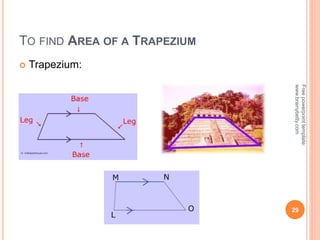
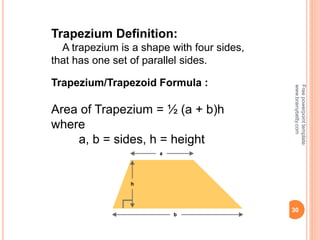
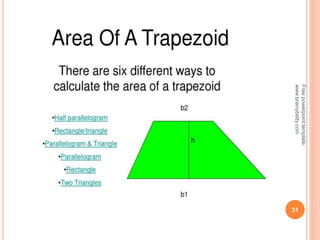
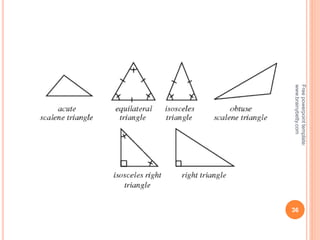
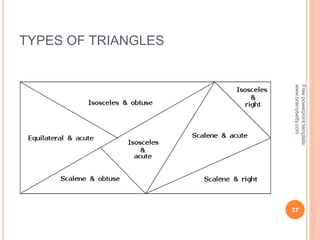
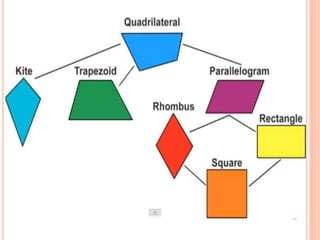
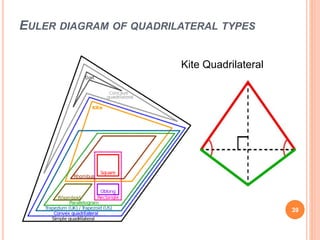
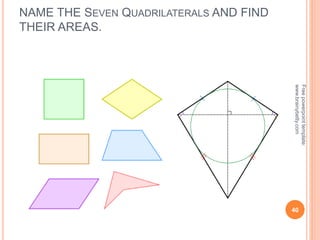
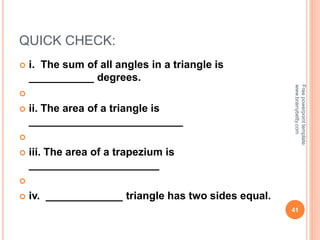
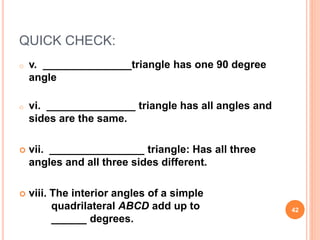
This document discusses the topic of mensuration, which is the measurement of quantities such as perimeter, area, volume, and length of geometrical figures. It begins by explaining that mensuration is important for tasks like building houses or planning gardens, as it allows one to calculate the space occupied by different shapes. The document then provides definitions and examples of plane mensuration, which deals with 2D figures, and solid mensuration, which involves 3D solids. Specific shapes discussed include triangles, rectangles, circles, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Formulas are presented for calculating the areas of common shapes like triangles, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids.