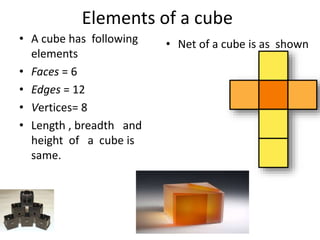
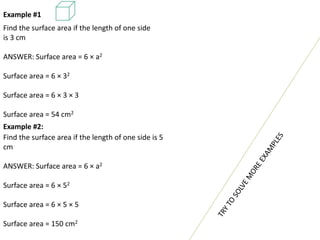
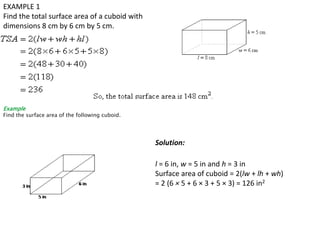
The document provides detailed information about three-dimensional shapes: cubes, cuboids, and cylinders. It includes definitions, properties, surface area and volume formulas, and examples for each shape. Key formulas include the surface area of a cube as 6a², volume as s³, for a cuboid as 2(length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height), and for a cylinder as 2πrh + 2πr².