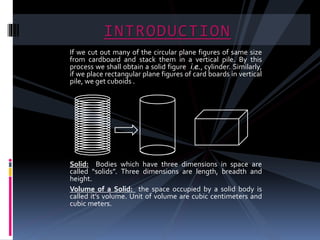
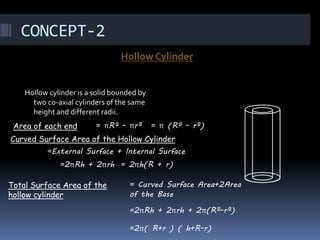
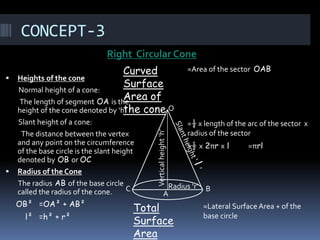
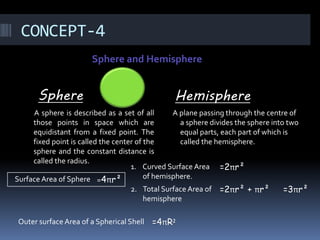
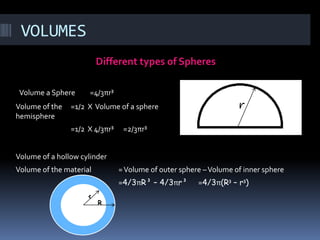
The document discusses different geometry concepts related to mensuration including cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres and hemispheres. It defines key terms like total surface area, lateral surface area and volume. Formulas are provided to calculate surface areas and volumes of cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres and hemispheres. Examples are given to illustrate concepts like hollow cylinders and spherical shells.