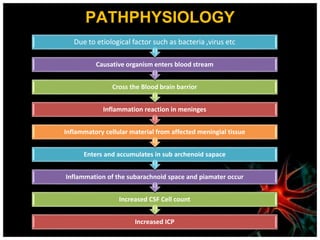
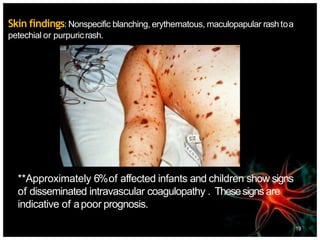
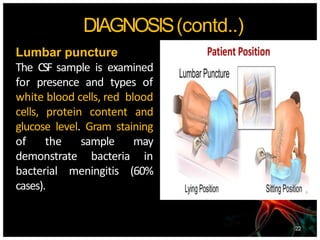
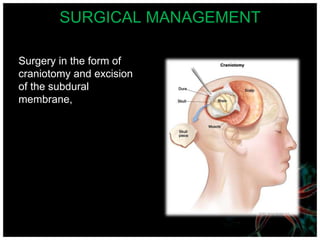
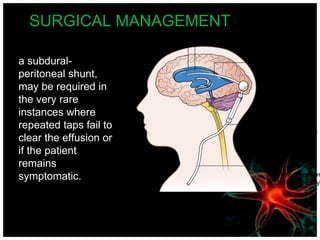
Meningitis is an acute inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, often caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It is a medical emergency due to its potential life-threatening complications, with significant annual mortality rates. Diagnosis involves examining cerebrospinal fluid, and management includes antibiotics, supportive care, and preventive vaccinations.