The document discusses meningitis, an inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, detailing its global incidence, etiology caused primarily by microorganisms, and clinical manifestations such as headache and fever. It outlines diagnostic evaluations and management strategies for bacterial and viral meningitis, including the use of antibiotics for bacterial infections and supportive care for viral cases. Prevention measures, including vaccination recommendations, and nursing management practices are also highlighted.
![PRESENTED BY :
Ms. Yasmeen MK
2nd
year B.sc nursing
BBC College Of Nursing Gangavathi
SUPERVISED BY:
Mr.Geroge.D.Honnali M.Sc.[N]
HOD . Dept of Medical Surgical Nursing
BBC College Of Nursing Gangavathi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meningitispresentation-240903161142-298f148d/75/Meningitis-1-2048.jpg)


![ETIOLOGY :
Meningitis is mostly caused by microorganisms like
• Bacteria[Neisseria meningitidis & Hemophilus influenza]
• Viruses[mumps, herpes simplex virus]
• parasites[Naegleria fowleri(brain eating amoeba)]
• fungi [Cryptococcus]
These microorganisms infect blood and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
non-infectious causes:
including certain diseases like AIDS
• cancer
• diabetes
• physical injury
• certain drugs that weaken the body's immune system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meningitispresentation-240903161142-298f148d/85/Meningitis-5-320.jpg)
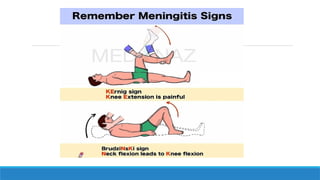
![CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS:
Meningitis signs and symptoms may develop over several hours or over 1 or 2 days and in
anyone over the age of 2, typically include
• Headache
• Sudden high fever
• Altered mental status
• Confusion or altered consciousness
• Vomiting
• Inability to tolerate light[ photophobia] or loud noises[ phonophobia]
• Irritability, and drowsiness
• Signs of meningeal irritations
• Nuchal rigidity[neck stiffness] associated with fever
• Positive Brudzinski signs
• Positive kerning signs
• Signs of increased ICP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meningitispresentation-240903161142-298f148d/85/Meningitis-7-320.jpg)

![BLOOD CULTURE CHEST X-RAY
[Neisseria meningitidis] [Tubercular meningitis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meningitispresentation-240903161142-298f148d/85/Meningitis-10-320.jpg)
![CSF examination for cell count,
glucose, and protein
CT scan of the head
[BACTERIAL MENINGITIS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meningitispresentation-240903161142-298f148d/85/Meningitis-11-320.jpg)