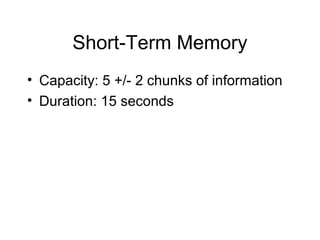
The document discusses different aspects of human memory such as encoding, storage, retrieval, and forgetting. It summarizes classic memory models proposed by Atkinson and Shiffrin in 1968 that describe sensory memory, short-term memory and long-term memory. It also references studies on memory capacity like George Miller's finding that short-term memory can hold 7 plus or minus 2 chunks of information. Finally, the document outlines Ebbinghaus' forgetting curve which showed that the more times one practices information, the fewer times it needs to be repeated to be relearned.