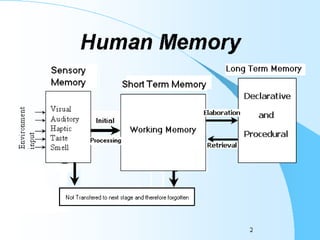
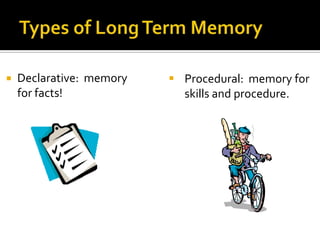
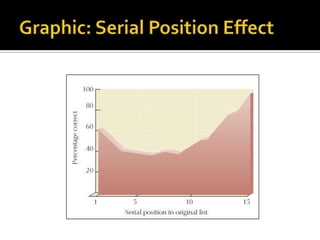
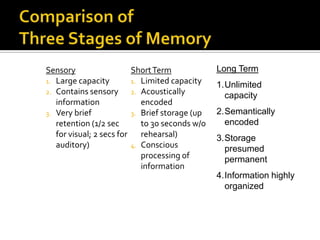
The document discusses various aspects of long-term memory, including its types (declarative, procedural, semantic, episodic, emotional) and factors affecting memory formation and recall. It explains different amnesia types, memory retrieval methods (recall, recognition, relearning), and theories of forgetting like encoding failure, decay, and interference. Additionally, it highlights techniques for enhancing memory retention, such as mnemonics, spaced practice, and the importance of physiological factors.