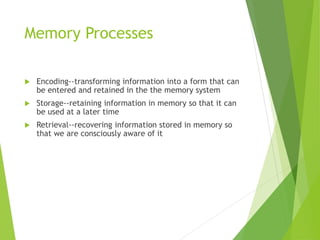
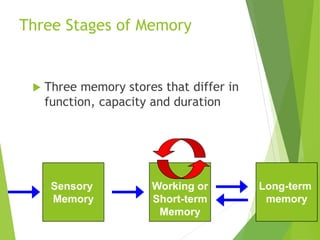
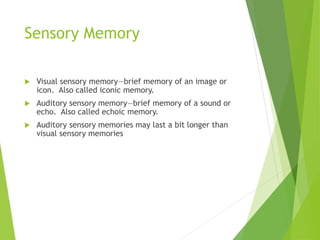
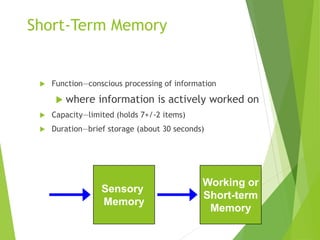
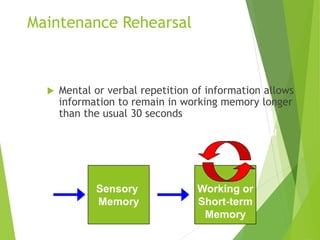
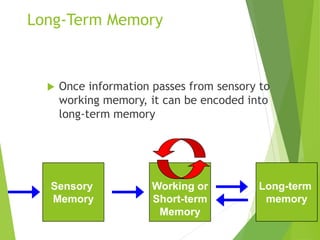
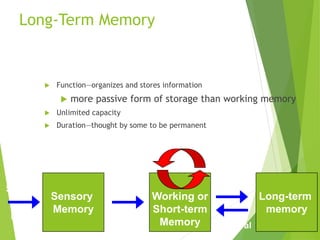
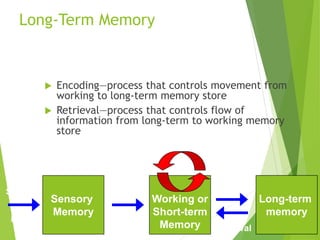
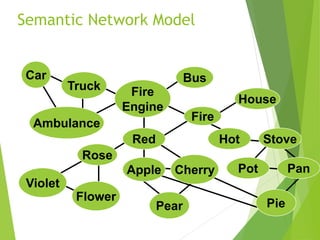
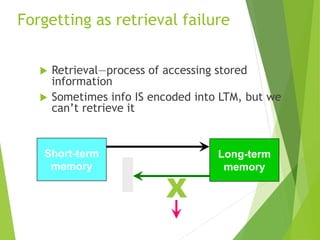
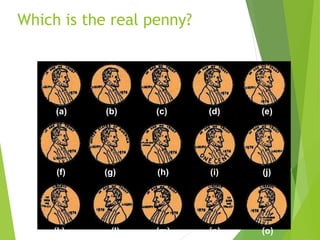
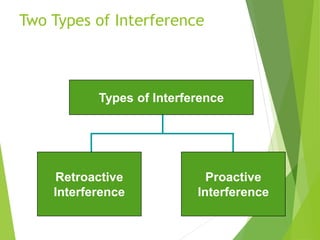
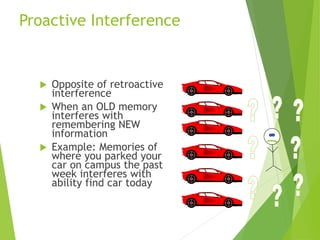
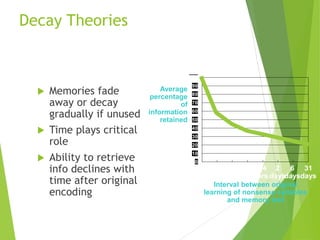
There are three main stages of memory: sensory memory, short-term/working memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory briefly stores sensory information, short-term memory actively processes information over seconds to minutes, and long-term memory stores information indefinitely. Information is encoded, stored, and retrieved between these memory systems. While long-term memory has unlimited capacity, we can forget due to encoding failures, interference, motivated forgetting, or decay over time if memories are not reinforced.