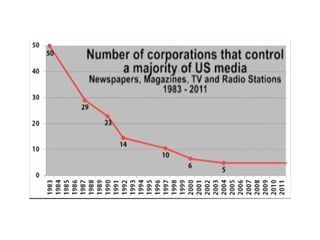
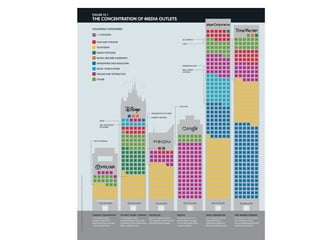
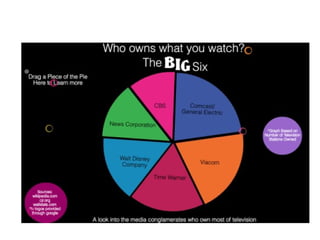
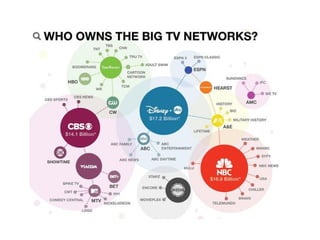
This document provides information on media mogul Rupert Murdoch and his acquisition of numerous newspapers, television stations, and film studios over several decades to build a massive media empire. It also summarizes key concepts in media economics like monopoly, oligopoly, deregulation, and trends in business practices such as outsourcing, wage gaps, and media consolidation.