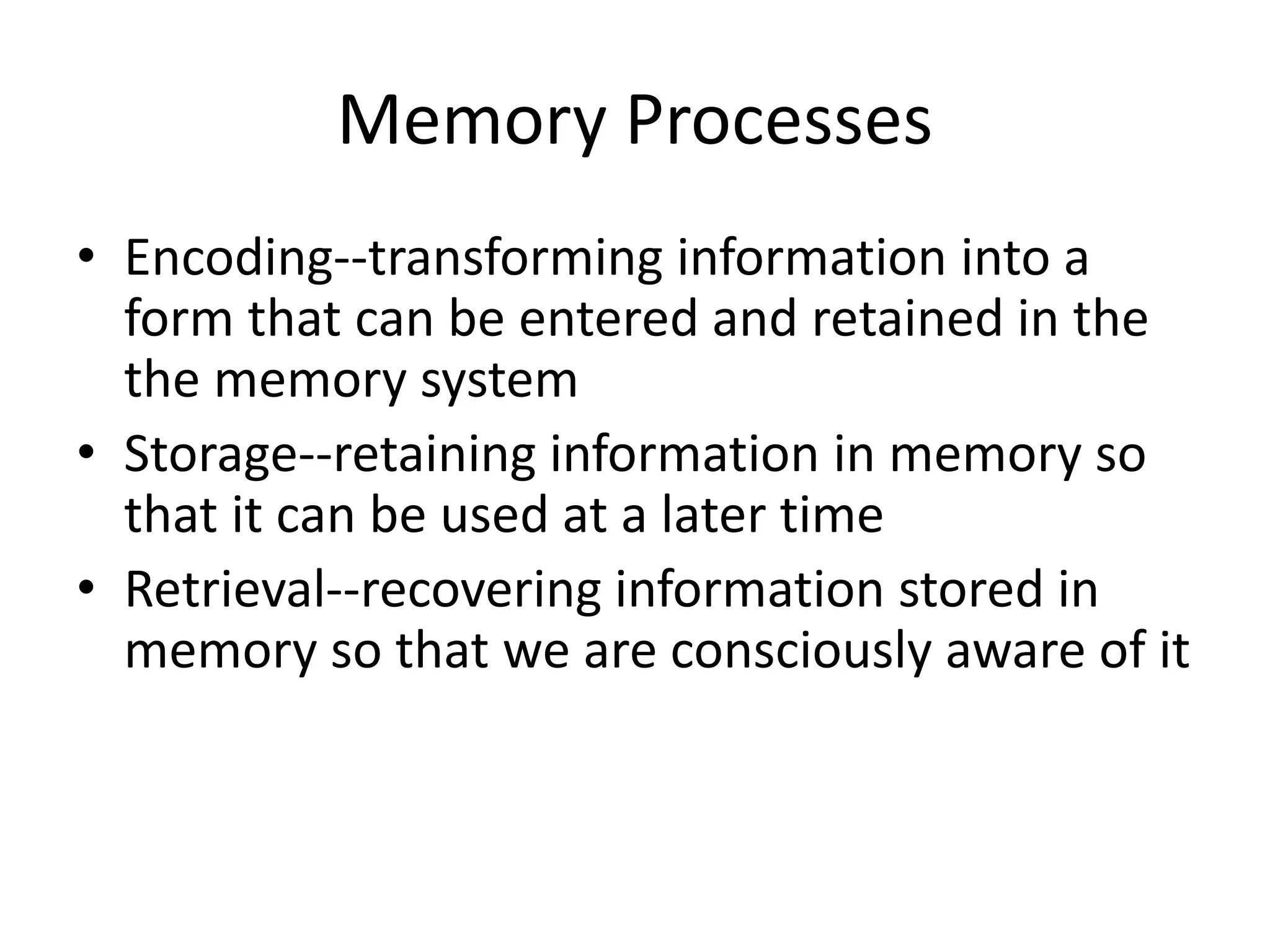
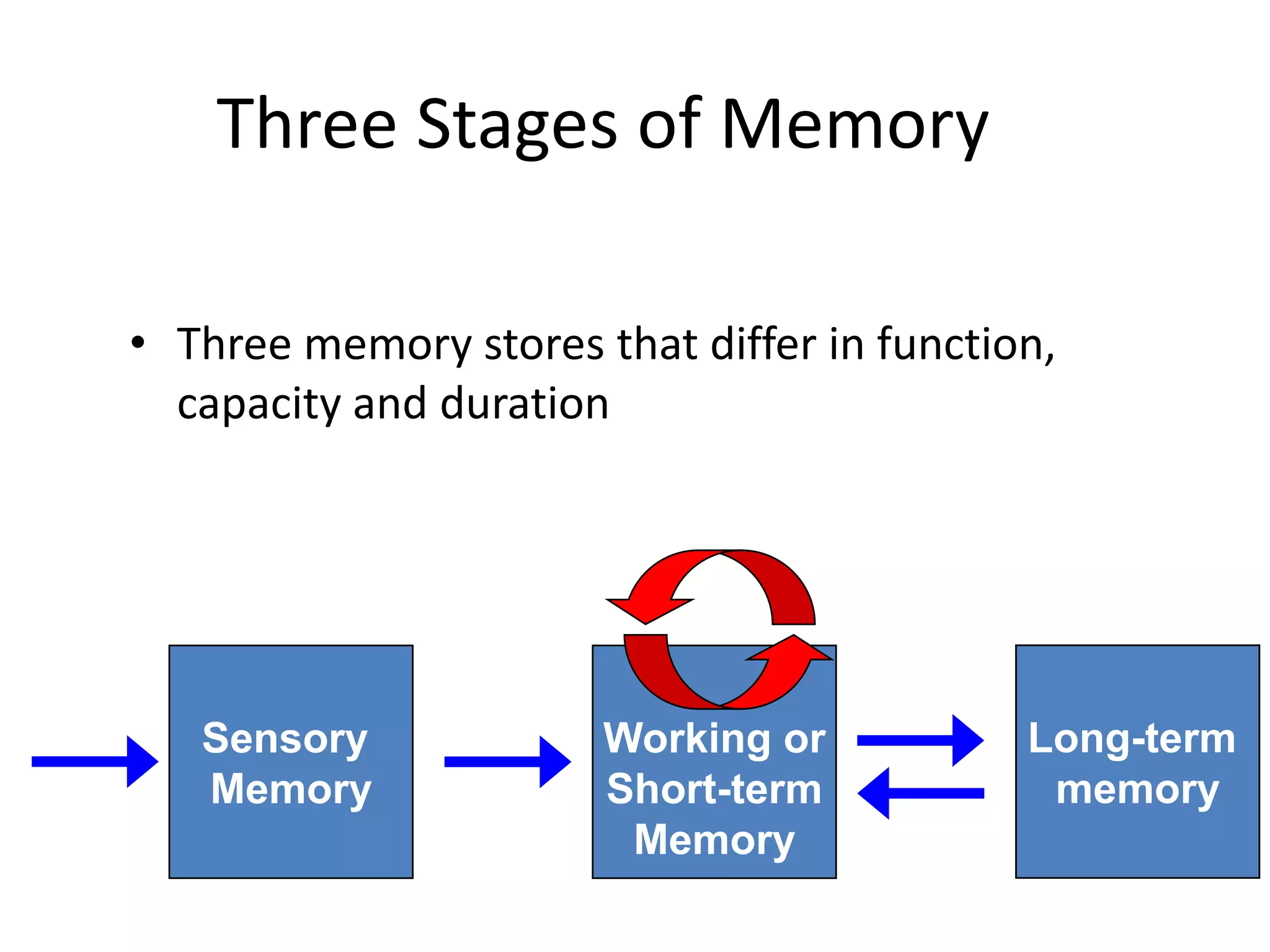
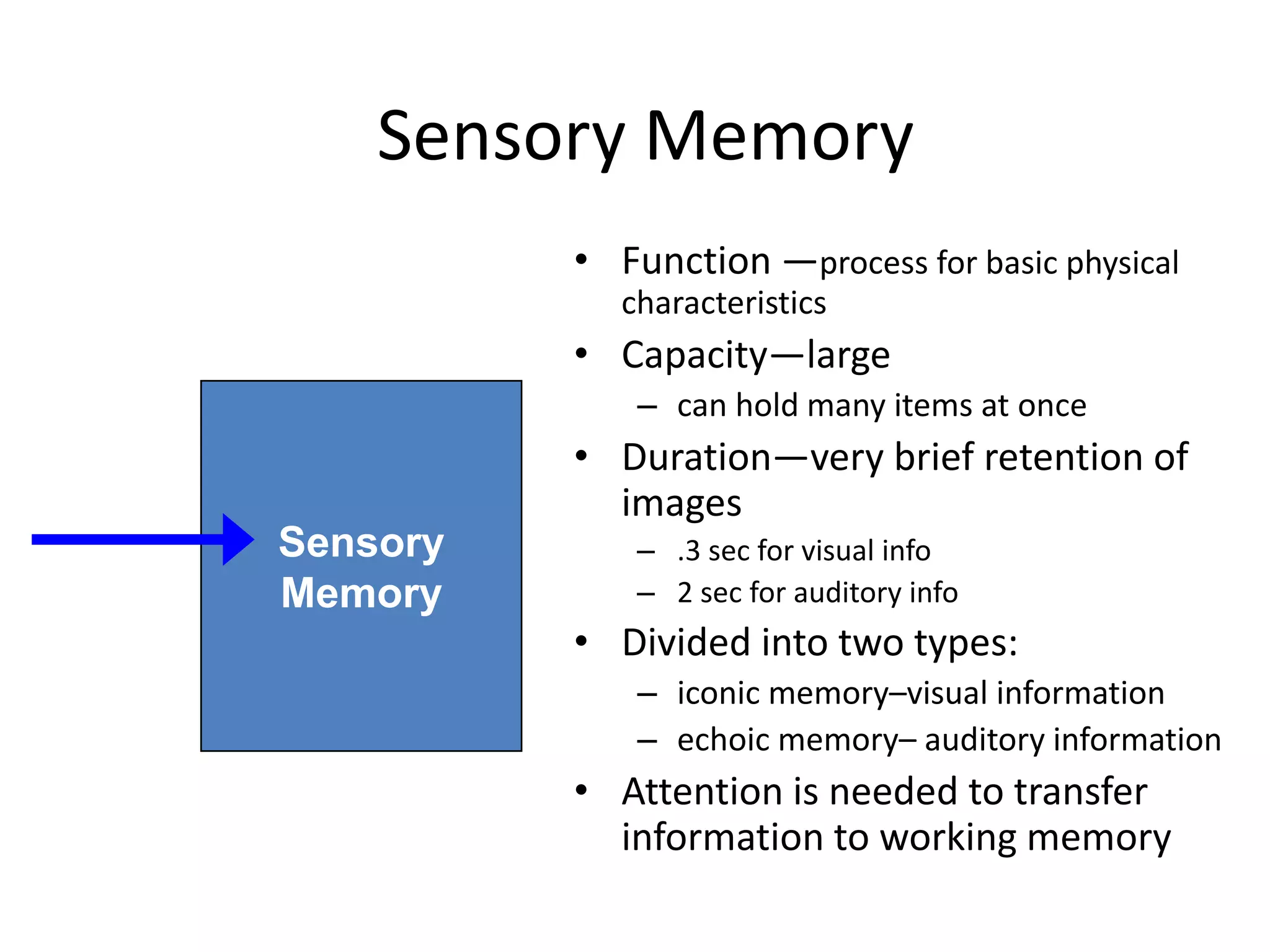
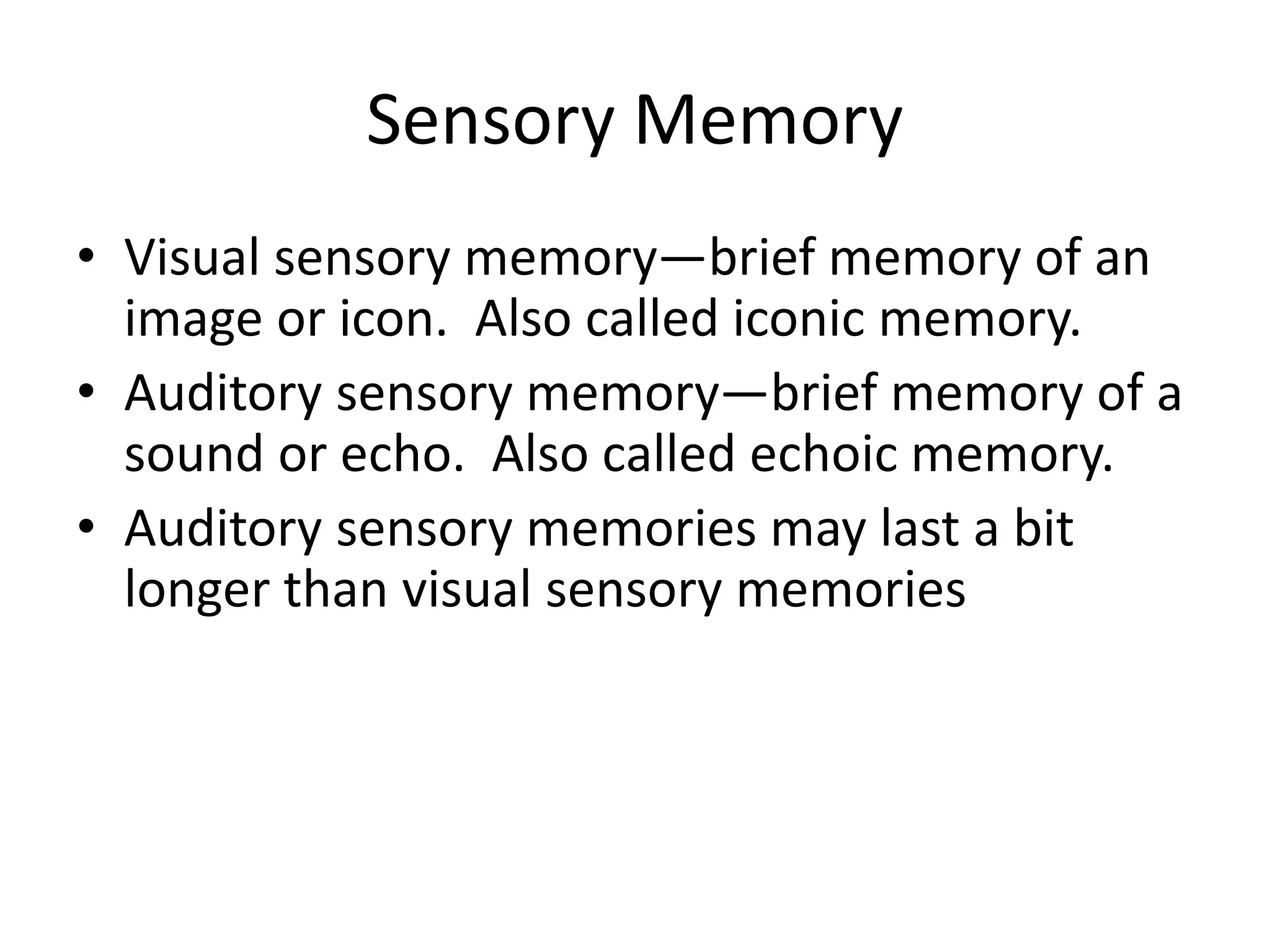
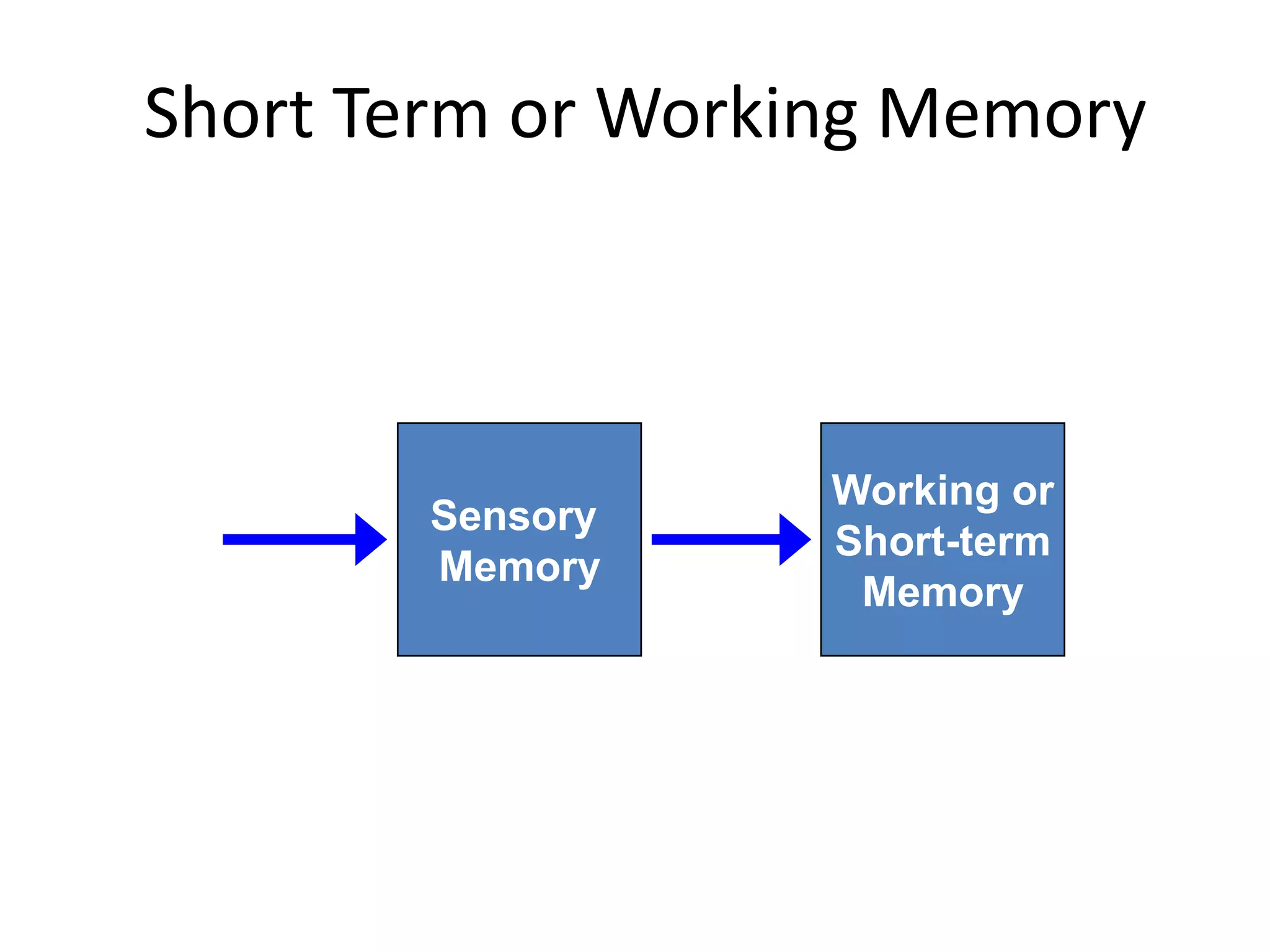
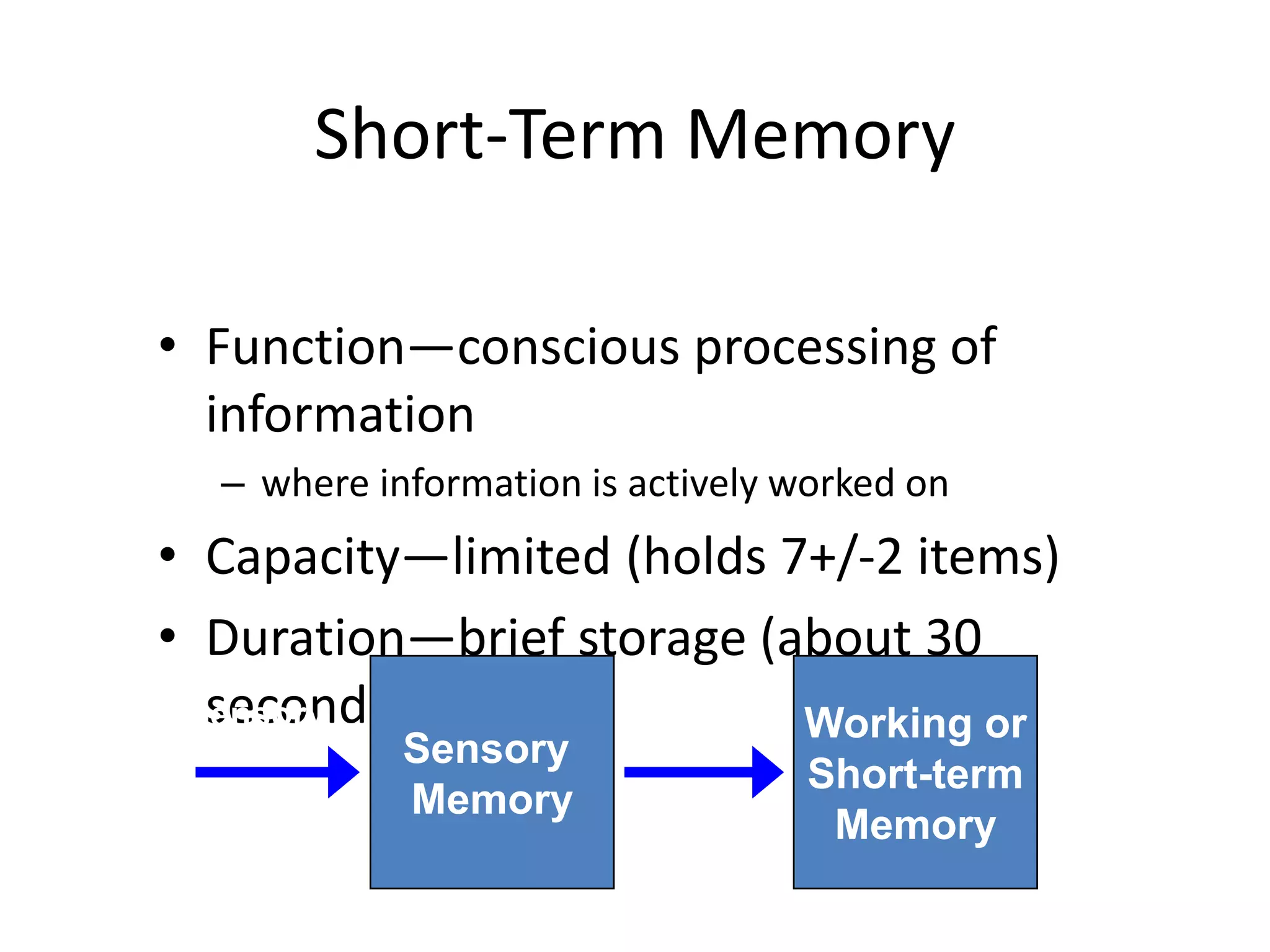
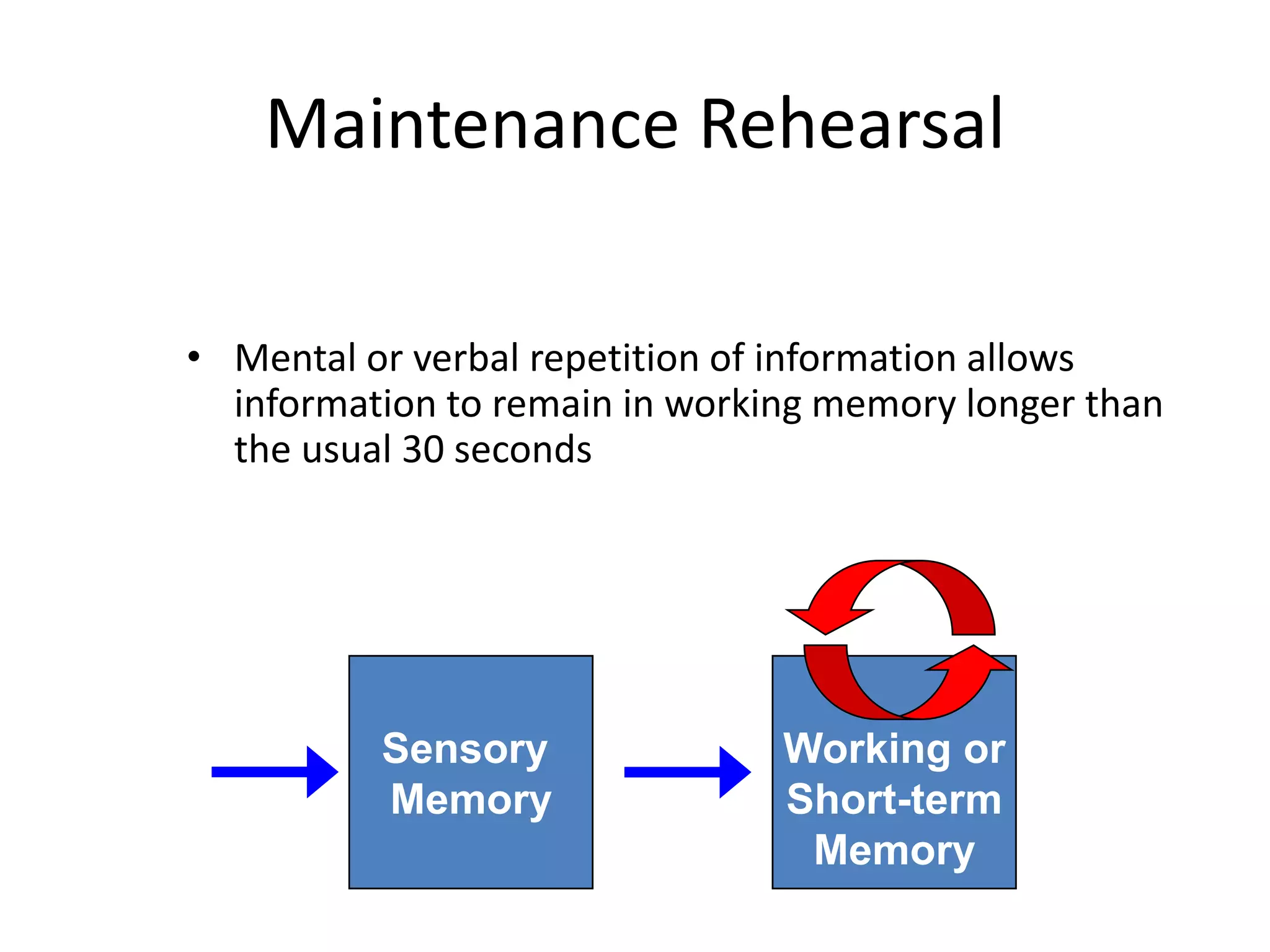
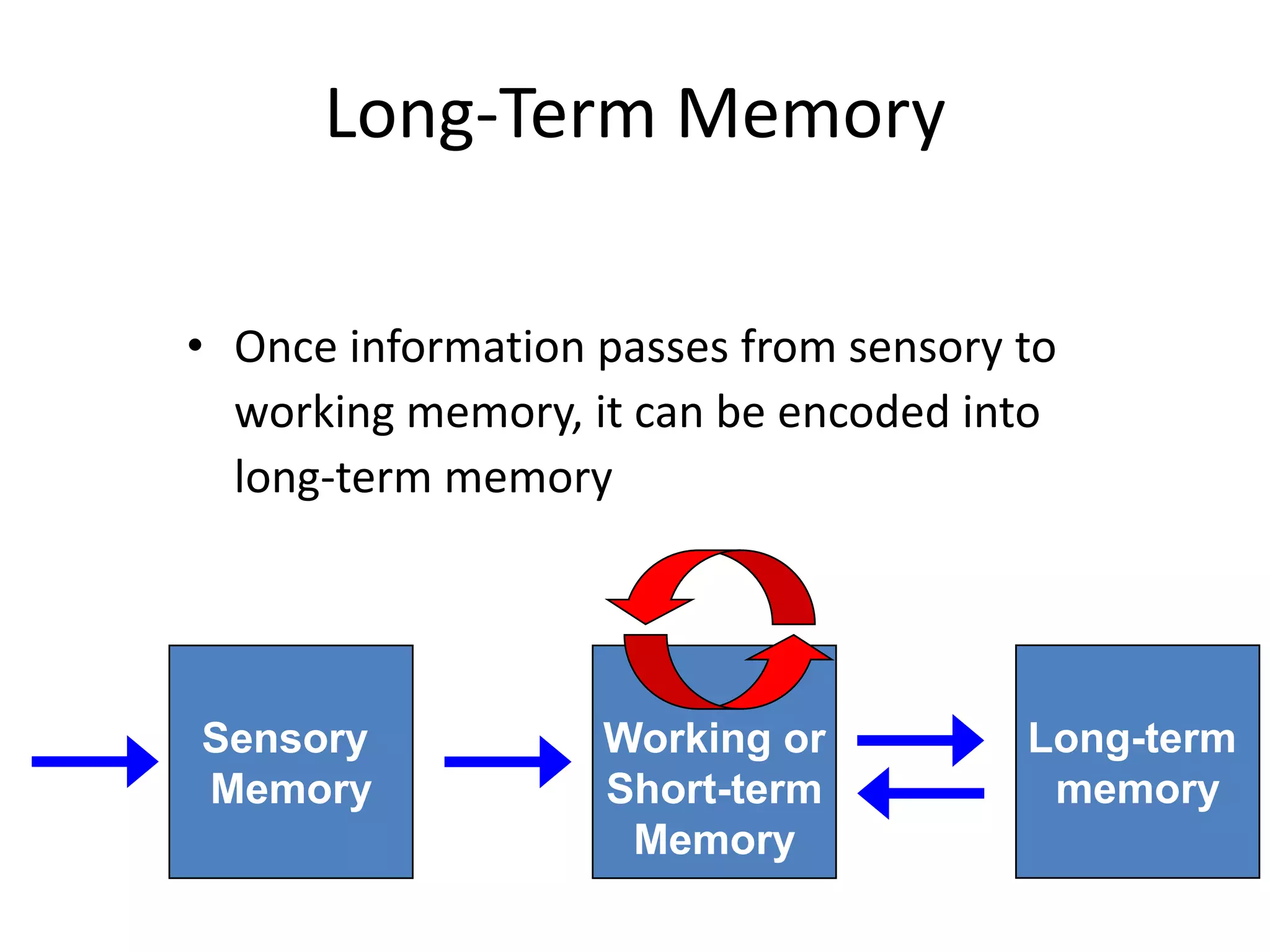
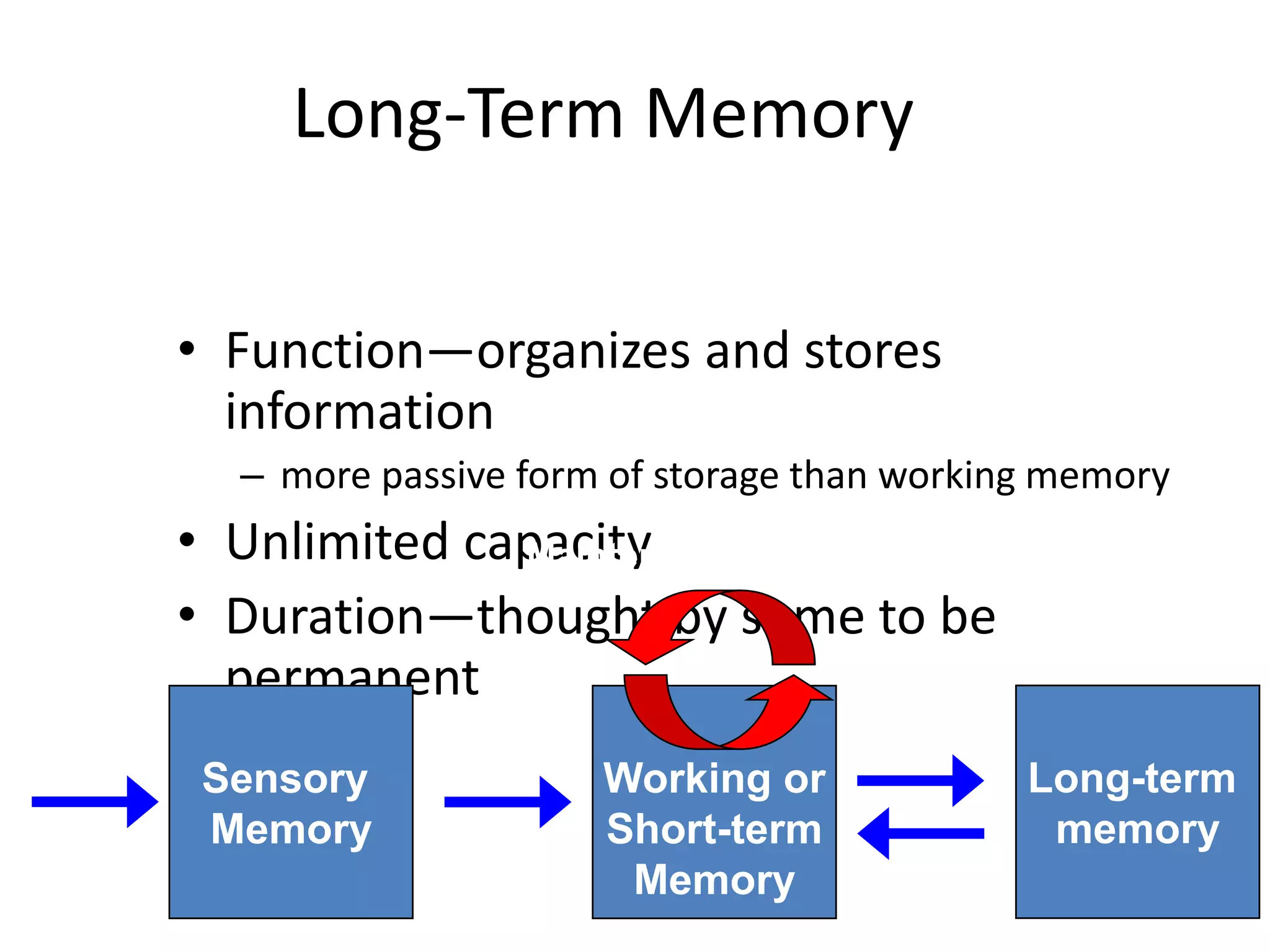
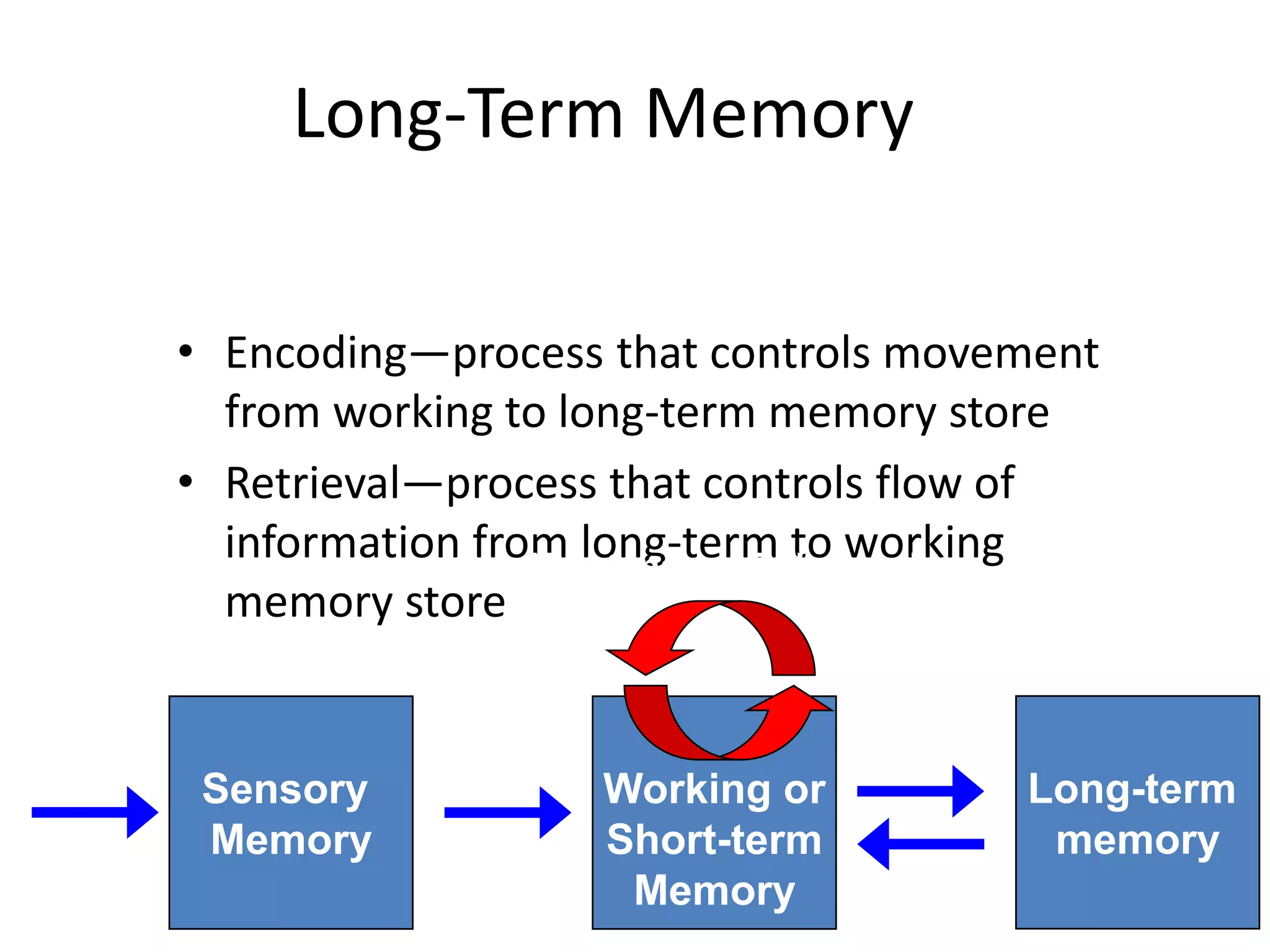
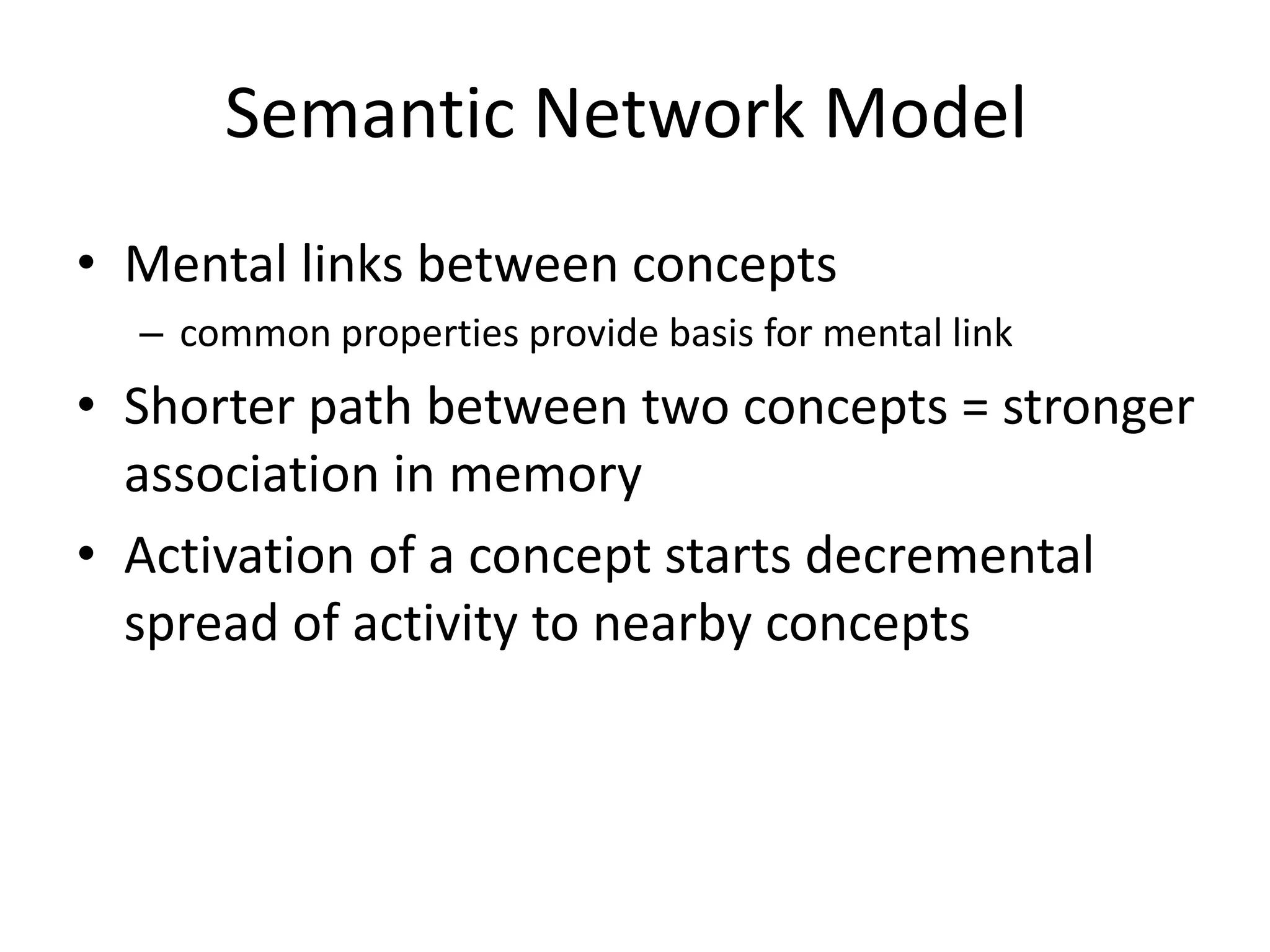
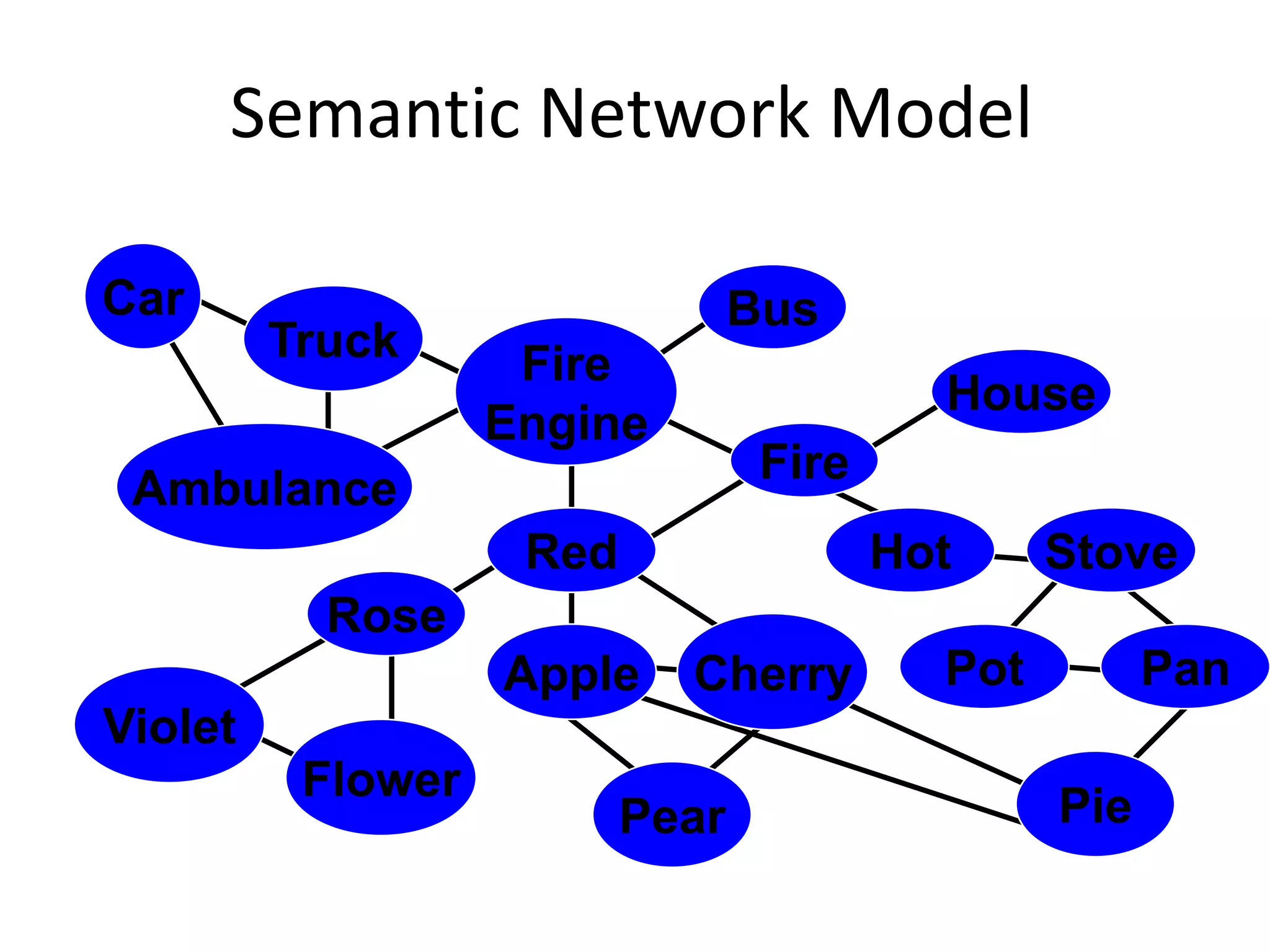
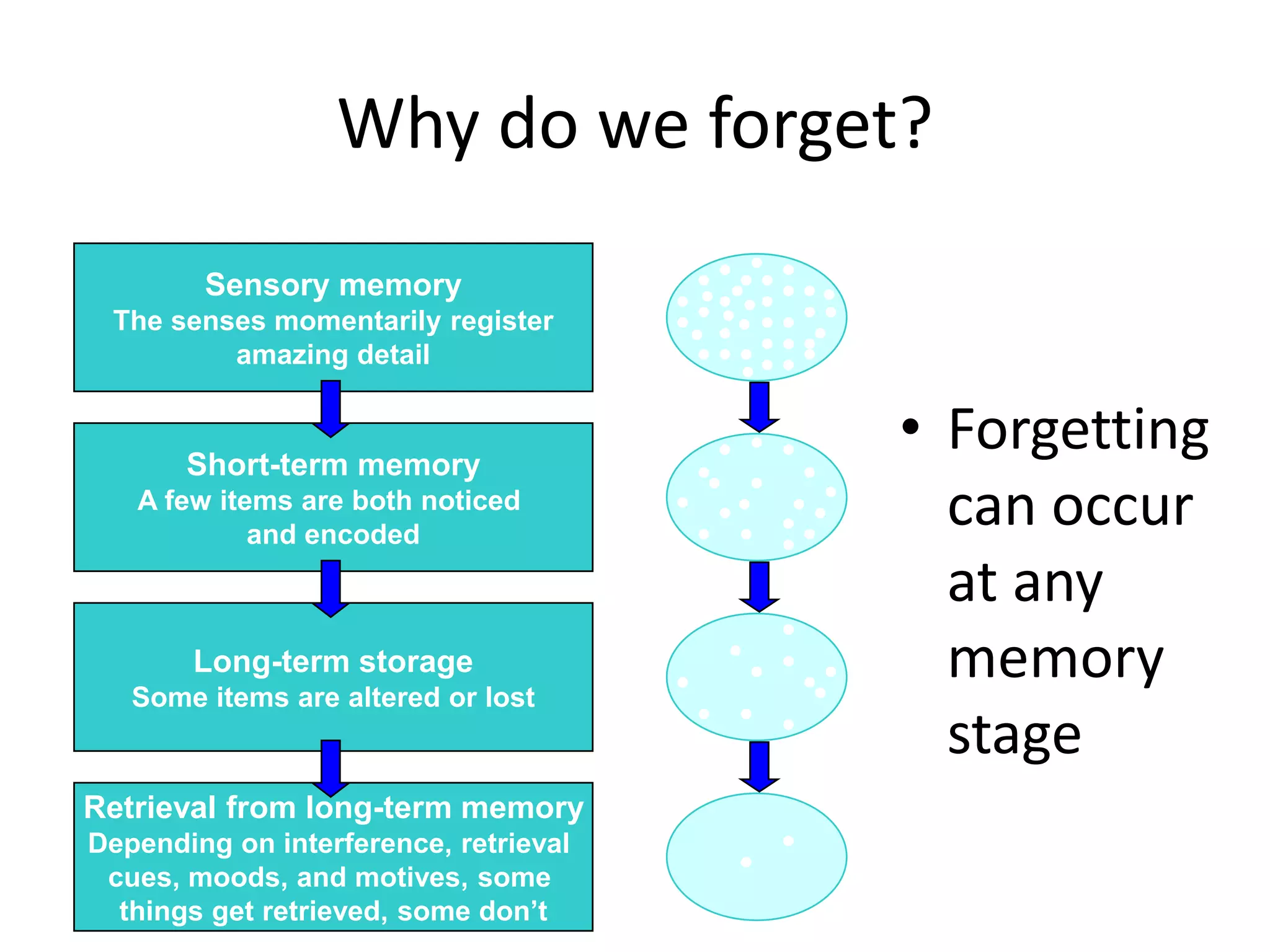
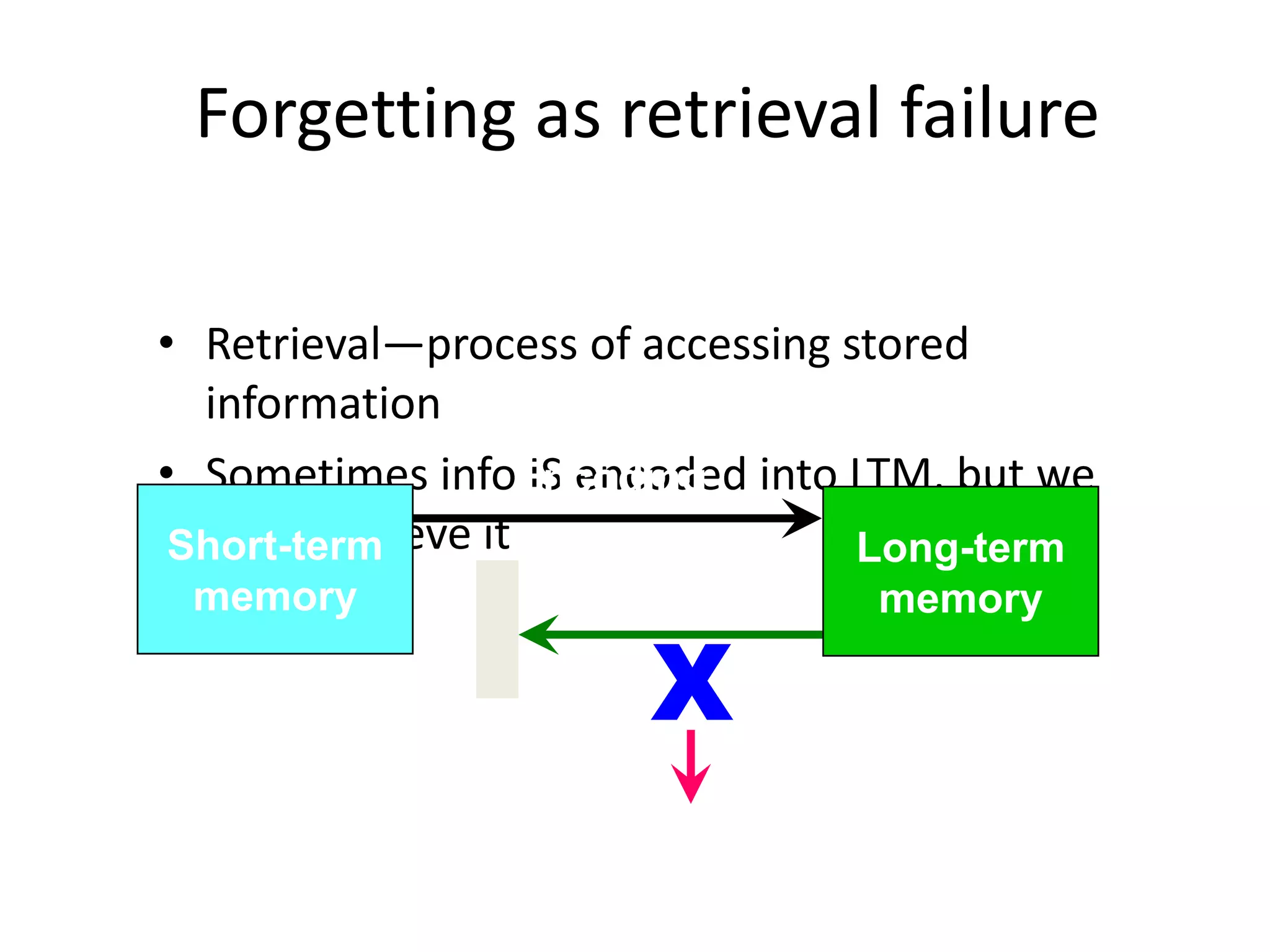
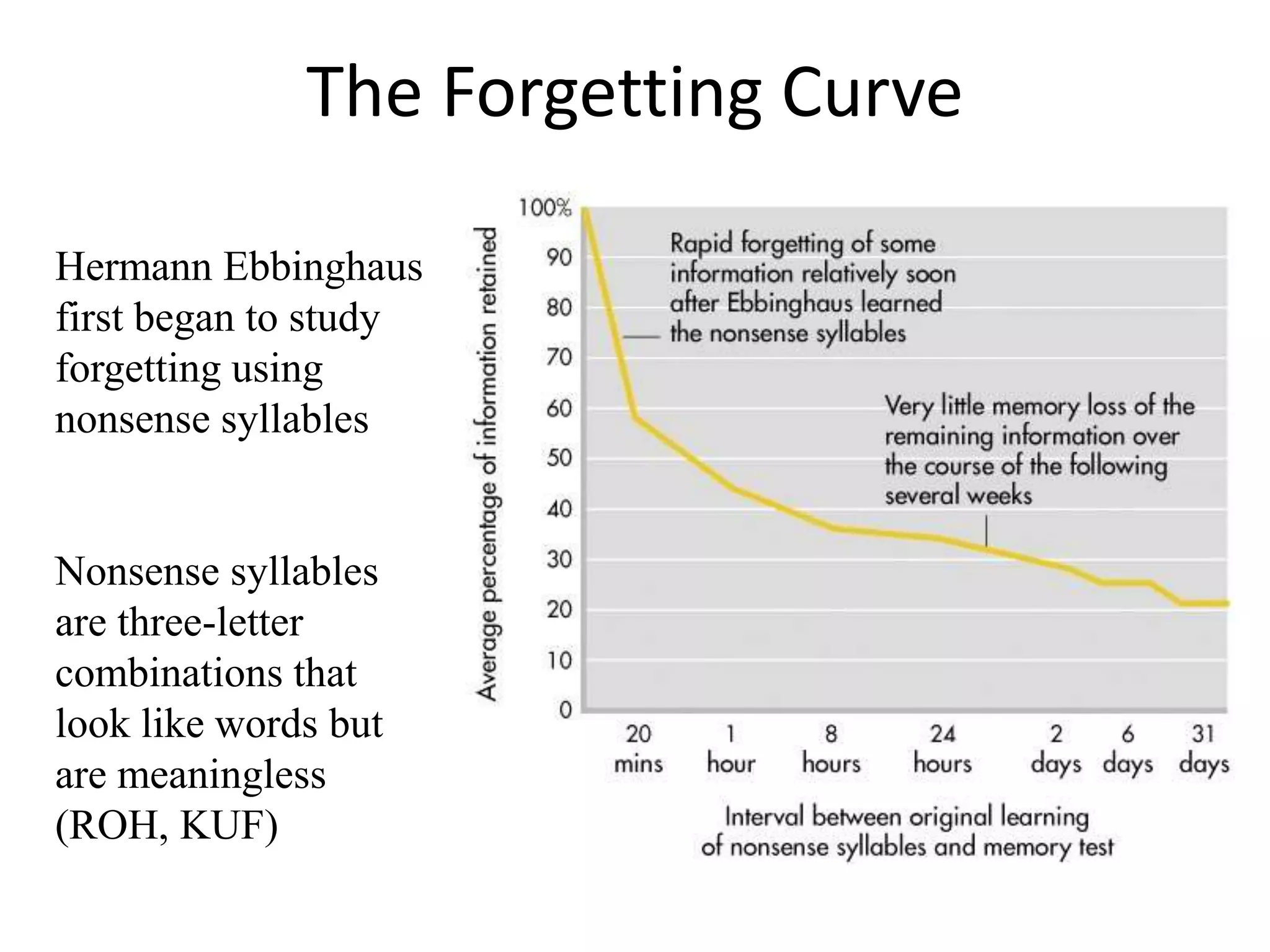
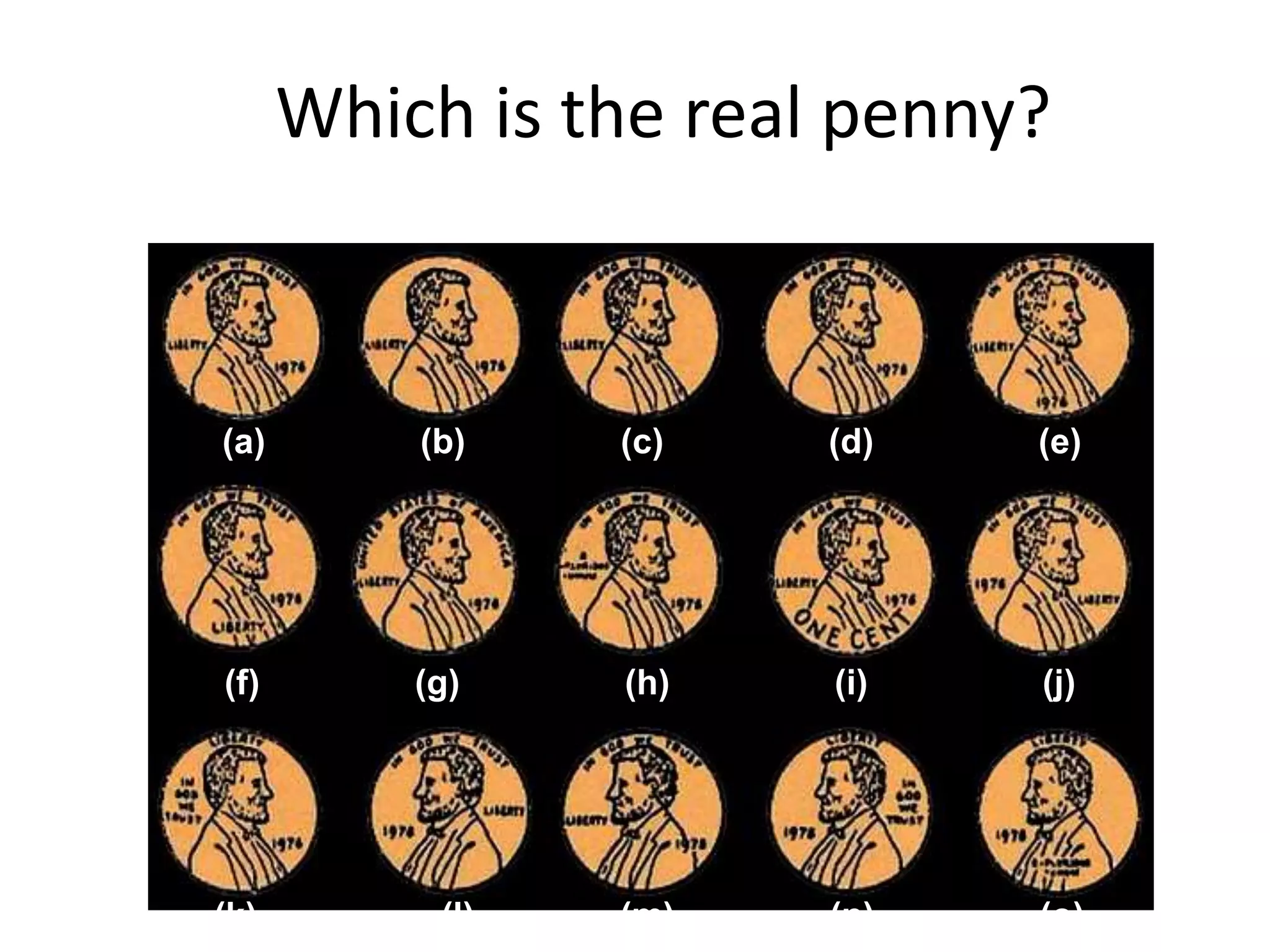
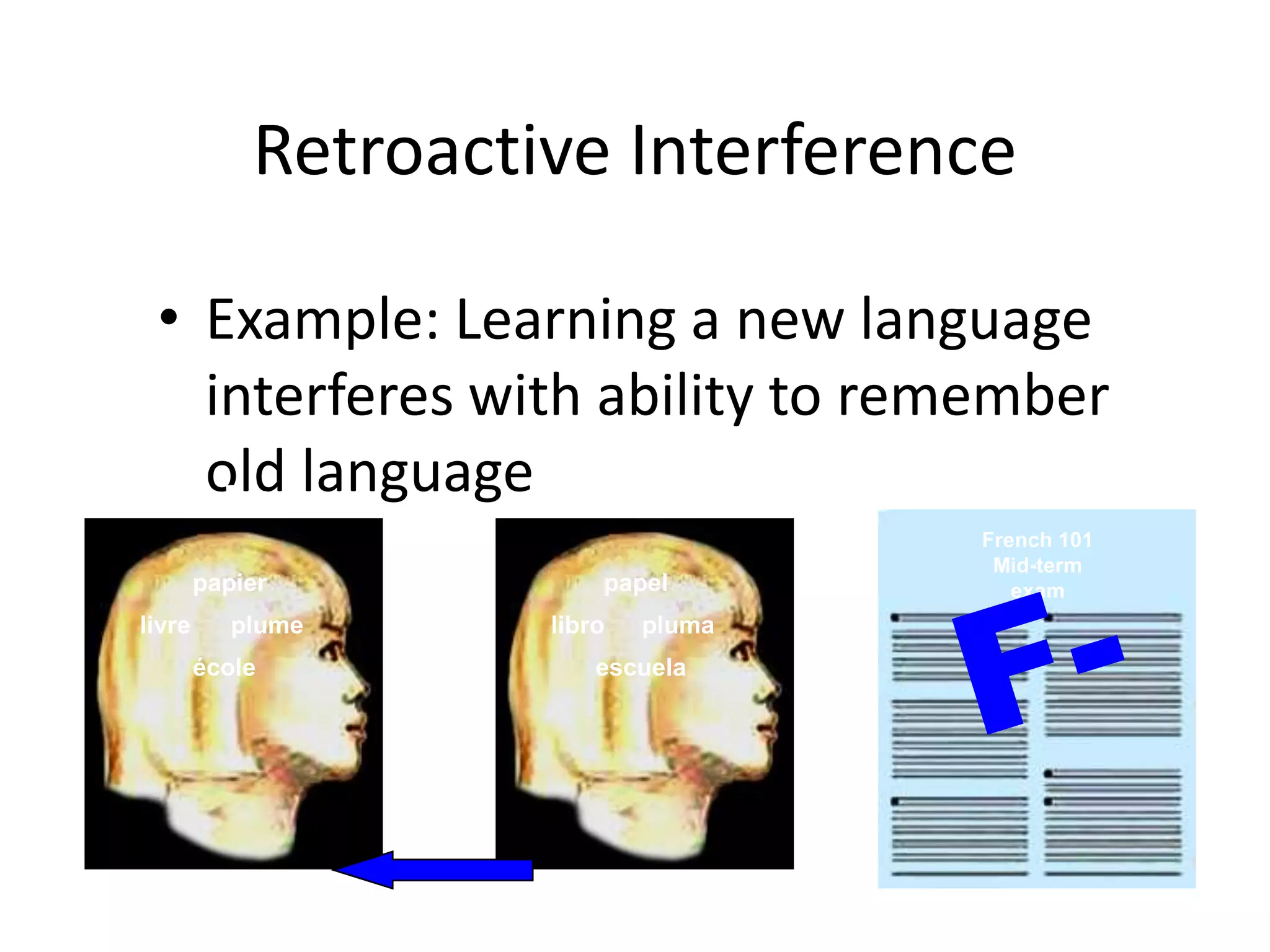
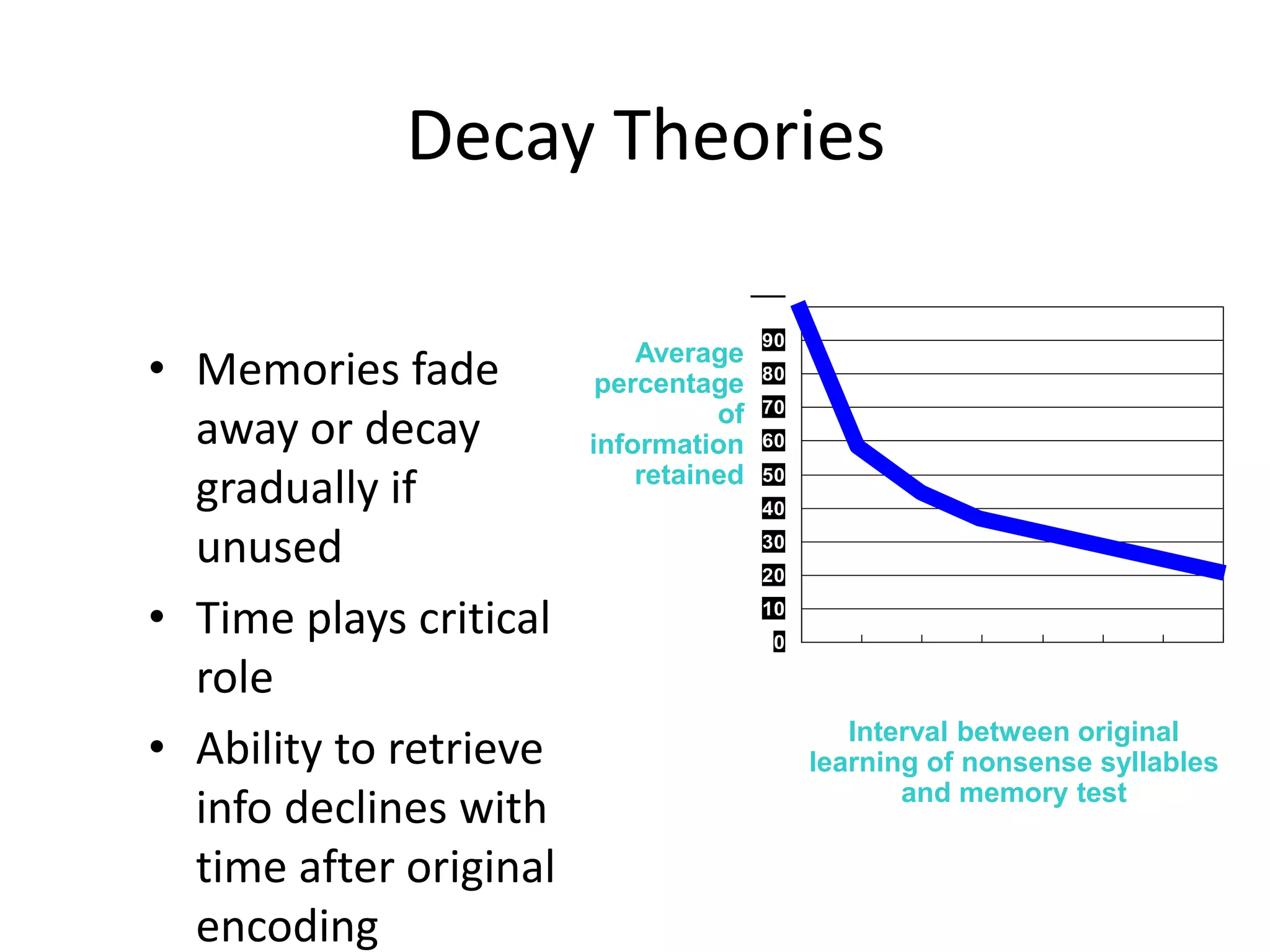
The document summarizes key concepts about human memory processes. It describes the three main stages of memory as sensory memory, short-term/working memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory briefly stores images and sounds, while working memory actively processes information over short periods. Long-term memory passively stores unlimited information for long durations. The document also discusses encoding, storage, retrieval, forgetting through interference and failure to encode, and theories of memory organization and decay.