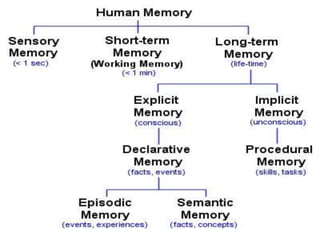
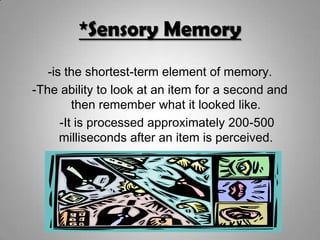
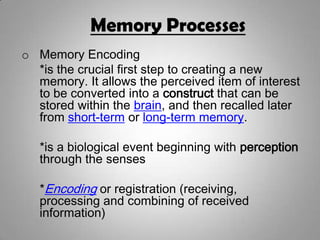
Sensory memory briefly stores perceptions and passes them to short-term memory. Short-term memory stores recently acquired information through working memory. Long-term memory securely stores information for long periods through explicit (declarative) memory of facts and episodic memory of experiences, and implicit (procedural) memory of skills. The three processes of memory are encoding, which converts information into a storable form; storage, where information resides in the brain over time; and retrieval, where the brain recalls previously learned information.