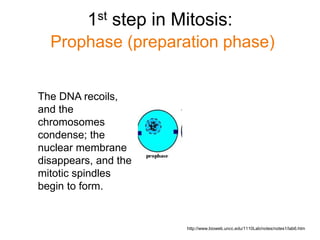
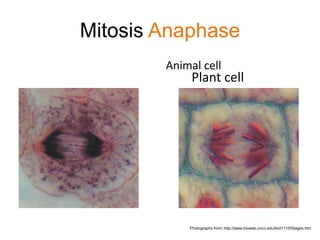
Mitosis and meiosis are cell division processes. Mitosis produces two daughter cells identical to the parent cell and is involved in growth and repair. Meiosis produces gametes for sexual reproduction and results in four cells each with half the number of chromosomes, increasing genetic diversity. The stages of cell division are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.