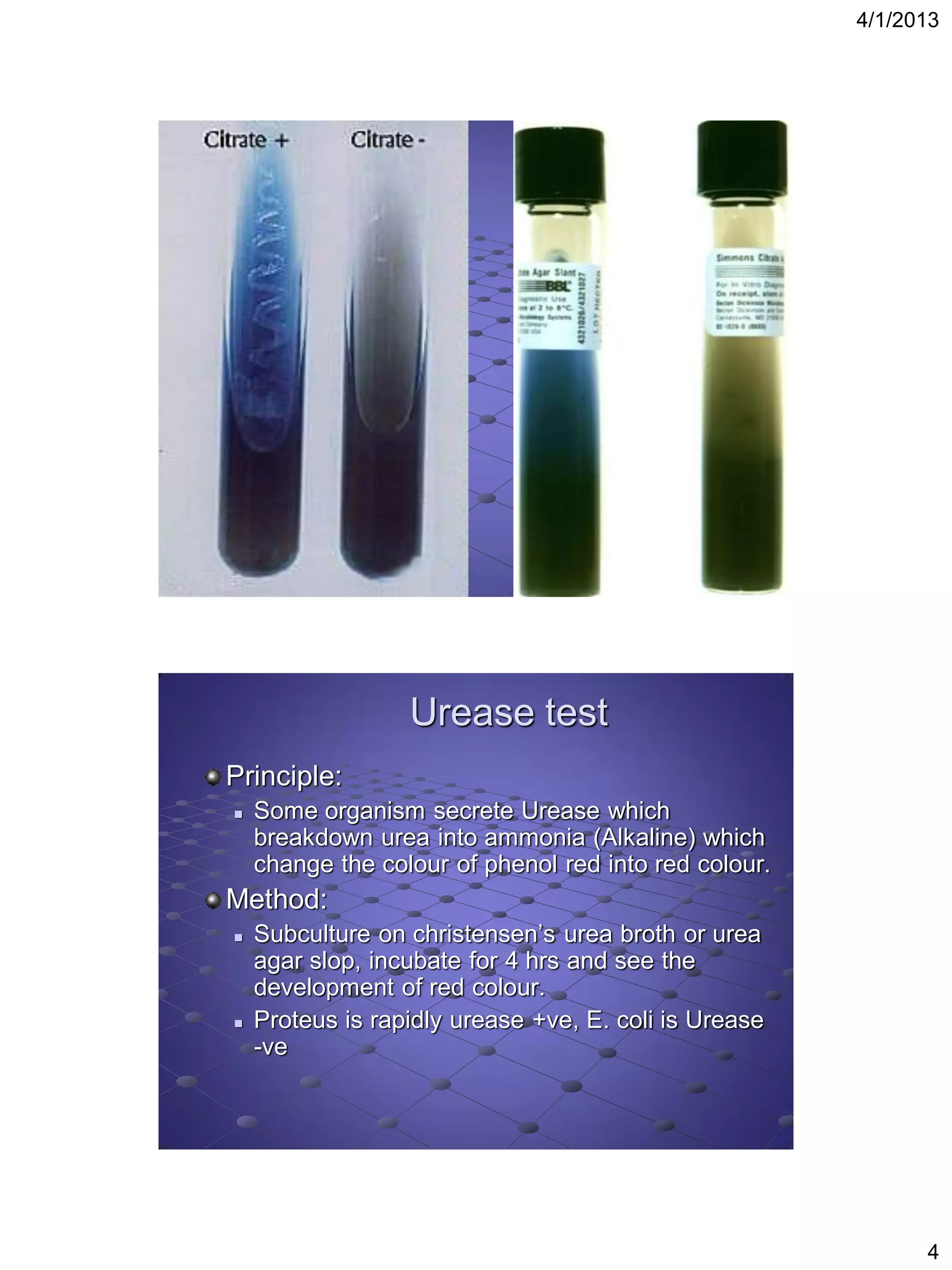
This document provides instructions for several biochemical tests used to identify Gram-negative bacteria, including the indole test, methyl red test, Voges-Proskauer test, citrate utilization test, urease test, oxidase test, H2S production test, motility test, Kligler iron agar test, sugar fermentation test, ONPG test, oxidation fermentation test, and phenyl pyruvic acid test. For each test, the document explains the principle, media or reagents used, and method for performing and interpreting the test results.