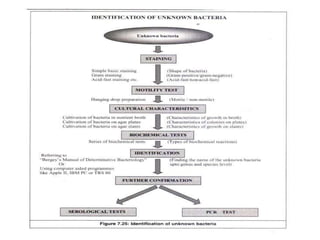
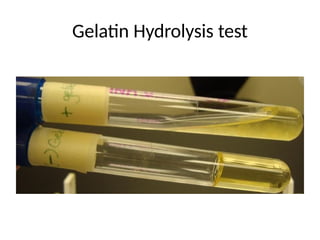
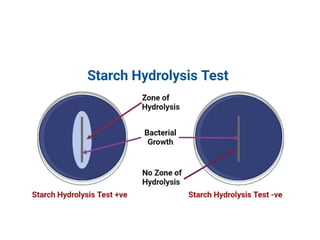
The document describes various biochemical tests used to differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including the indole, methyl red, voges proskauer, citrate, triple sugar iron, urease, gelatin hydrolysis, catalase, coagulase, oxidase, and starch hydrolysis tests. Each test evaluates specific metabolic capabilities of bacteria, such as fermentation and enzyme production, aiding in the identification of pathogenic species. Important examples include staphylococcus aureus, mycobacterium species, and various enteric bacteria, which play significant roles in human health and disease.