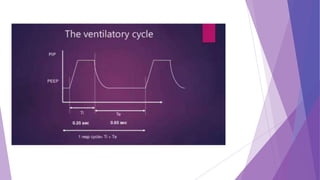
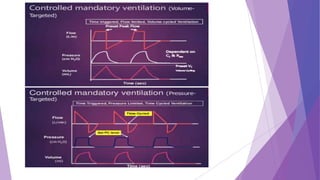
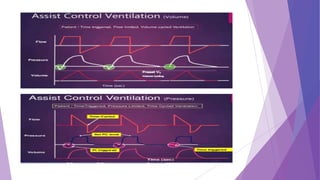
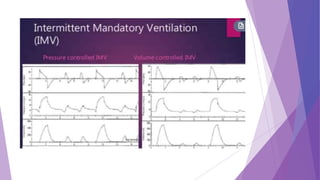
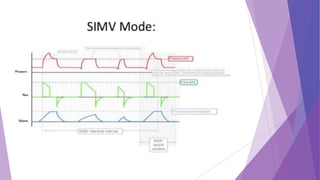
This document discusses invasive and non-invasive mechanical ventilation. It begins by defining key terms like ventilation, ventilator, and the different types of mechanical ventilation. It then covers the indications for mechanical ventilation including acute respiratory failure, prophylactic support, and hyperventilation therapy. The document discusses various ventilator modes like controlled mandatory ventilation, assist-control, intermittent mandatory ventilation, and more. It also covers settings, problems that can arise, and non-invasive ventilation options like CPAP, BiPAP, and pressure support ventilation.