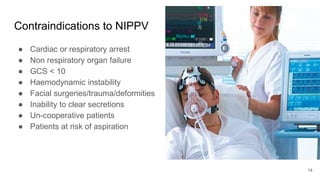
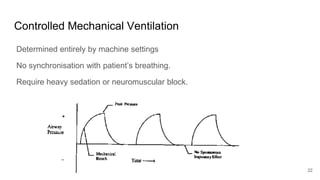
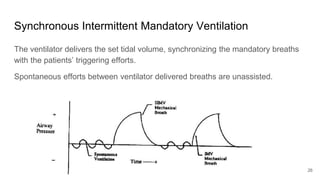
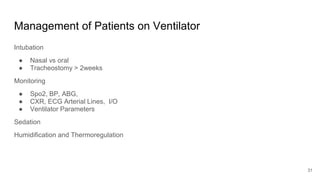
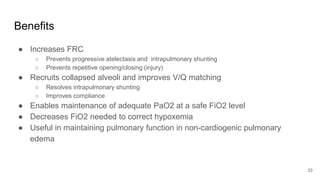
Artificial Ventilation is a method of assisting or replacing spontaneous breathing using a mechanical ventilator. It has a long history dating back to ancient times and was widely used during polio outbreaks. There are two main types - negative pressure ventilation which uses vacuum pressure and positive pressure ventilation which delivers gas via endotracheal tube. Modes include controlled mandatory ventilation where the machine does all breathing, assisted modes where the patient can trigger breaths, and pressure support where the patient determines breathing rate and depth. Key goals are to improve oxygenation and ventilation. Complications can include barotrauma, infections, and ventilator dependence. Proper use and monitoring can greatly impact patient outcomes.