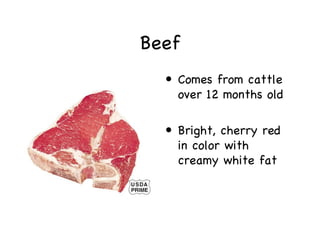
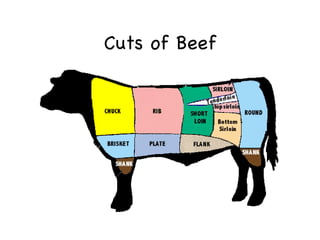
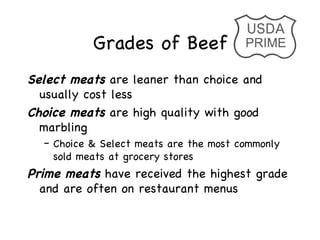
The document provides information on meat and poultry including recommended servings, cuts of beef and pork, types of poultry, safe cooking temperatures, and storage guidelines. It discusses the importance of protein for the body and recommends removing skin from poultry and using cooking methods like broiling or grilling to reduce fat. Grading systems for beef and poultry are explained to indicate quality.