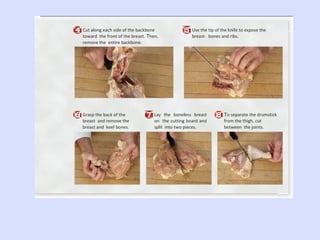
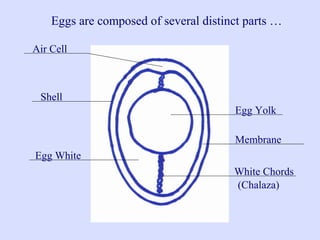
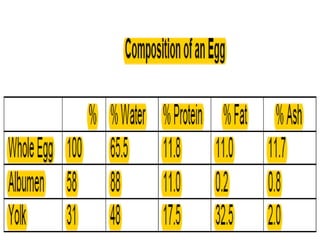
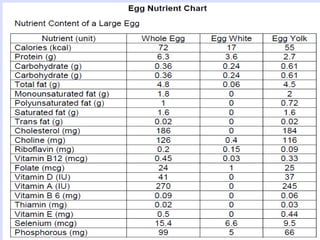
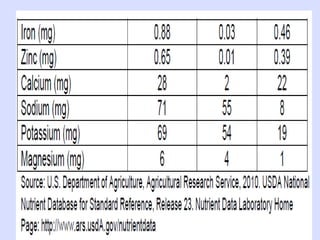
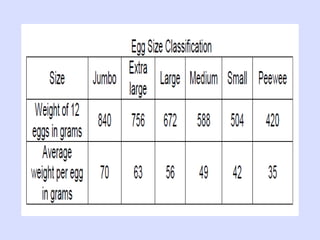
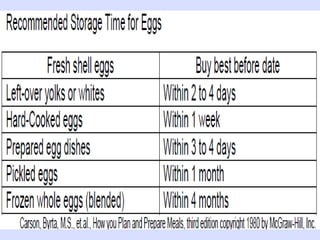
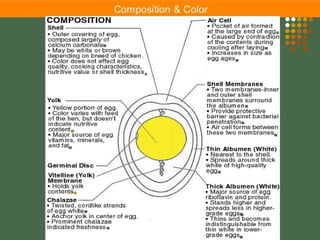
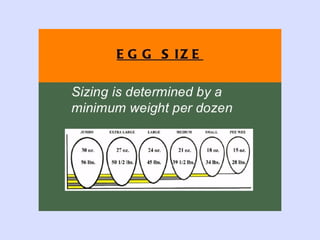
This document provides information about poultry and eggs. It defines different types of poultry like chicken, turkey, duck and goose. It describes how poultry is classified based on age and gender. Key points about poultry nutrition, purchasing, handling and cooking are covered. Eggs are also discussed, including nutrition facts, grades, storage and different cooking methods. Common egg dishes are listed at the end.