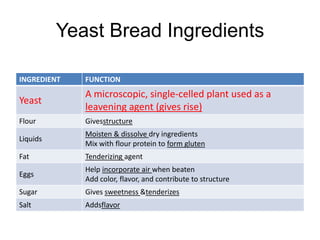
This document provides information about yeast breads, including common types of yeast breads such as sandwich bread, dinner rolls, and bagels. It discusses the key ingredients in yeast breads such as yeast, flour, liquids, fat, eggs, sugar, and salt. It describes the functions of these ingredients and gives tips about using the proper amount of yeast and warm liquid temperature for rising. The document also explains the traditional and one-rise mixing methods as well as kneading and punching down dough.