The document discusses measles, including:
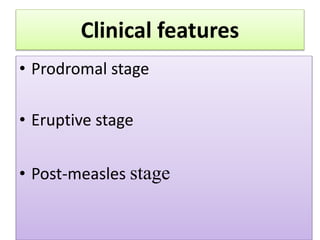
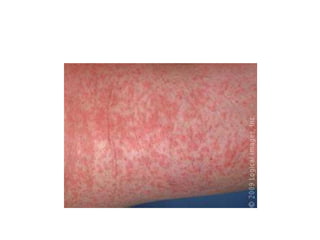
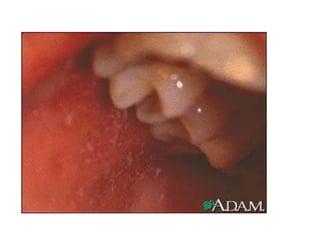
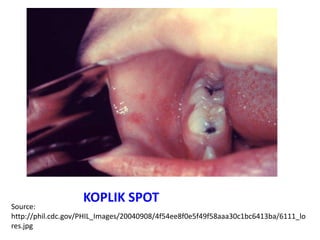
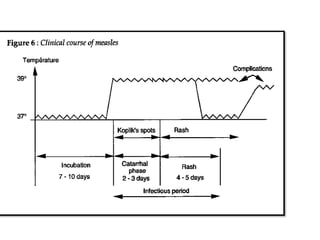
1. Measles is a highly infectious disease caused by a virus that affects virtually all children in developing countries where environmental conditions are poor.
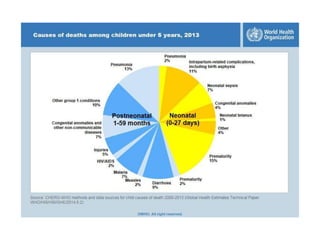
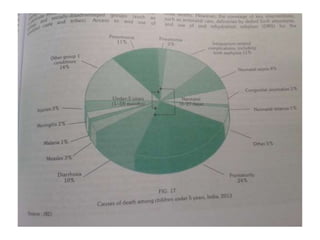
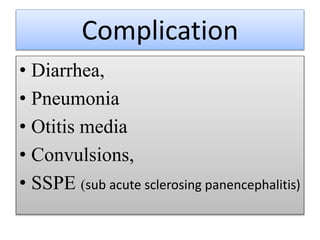
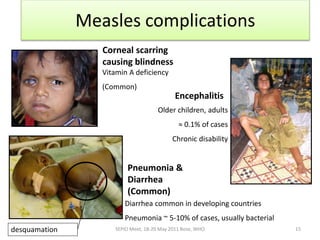
2. While most cases are not serious, measles can cause complications like pneumonia, encephalitis, and death. It can also weaken the immune system and cause malnutrition.
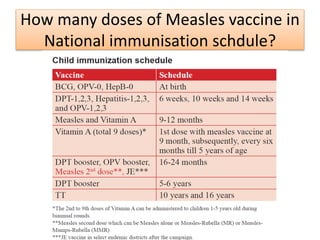
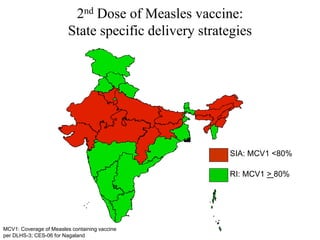
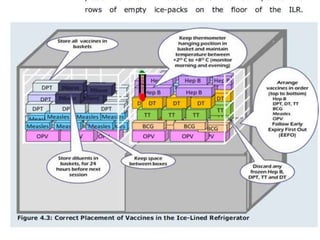
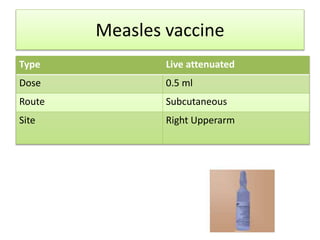
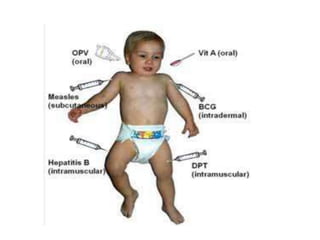
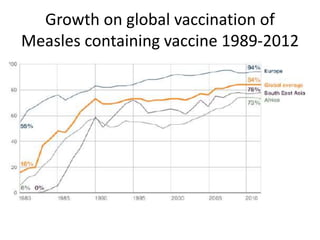
3. Measles can be eliminated through high vaccination coverage with effective measles vaccines via routine immunization programs and supplemental immunization activities like catch-up campaigns for children. Maintaining high coverage is important to prevent outbreaks.