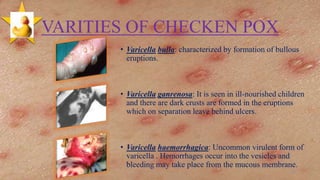
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus and causes a characteristic itchy vesicular rash. It is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets. The rash progresses rapidly from macules to papules to vesicles and crusts over within 4-7 days. Complications can occur in immunosuppressed individuals and include pneumonia and encephalitis. Vaccination with the live attenuated varicella vaccine provides effective protection.