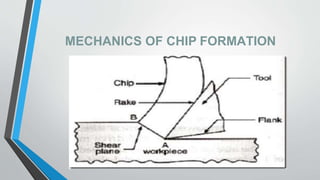
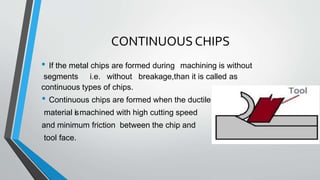
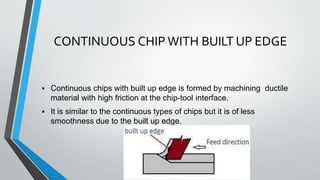
This document discusses chip formation during metal cutting processes. It begins with an introduction to metal cutting and chip formation. It then describes the mechanics of chip formation, including how shear deformation causes material to be removed from the workpiece in the form of chips. It discusses factors that influence chip type, such as the material properties, cutting conditions, and tool properties. Finally, it describes the different types of chips that can be formed, including continuous chips, discontinuous chips, and continuous chips with built up edges.