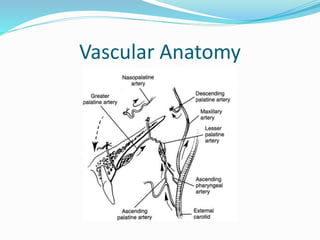
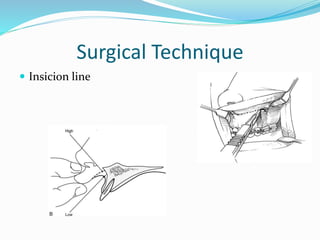
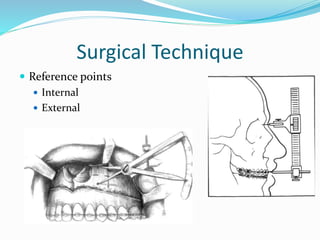
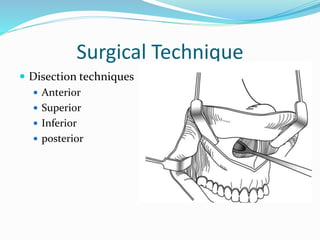
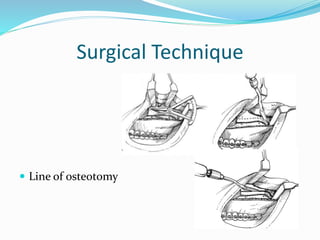
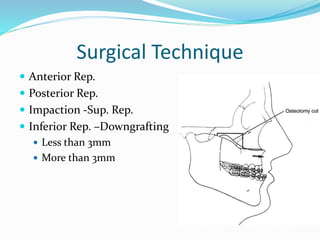
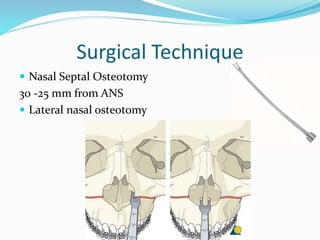
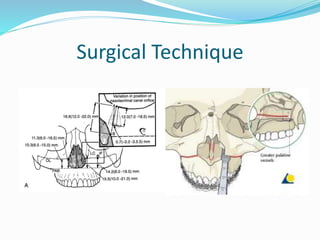
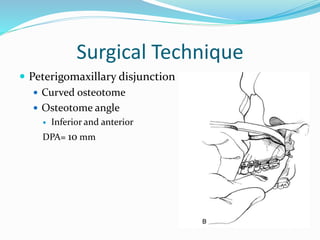
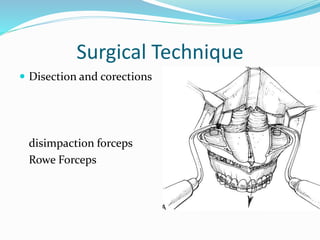
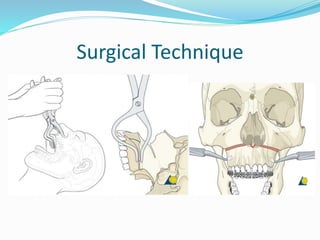
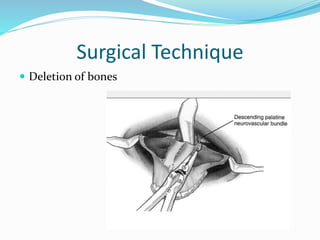
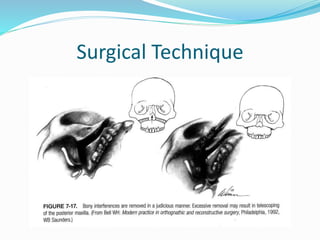
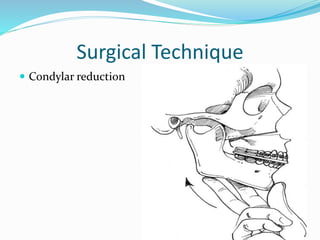
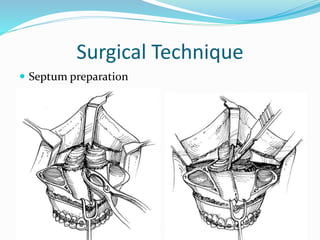
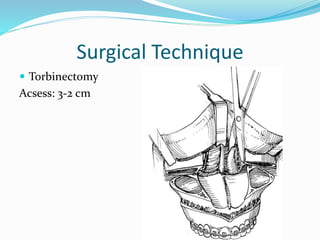
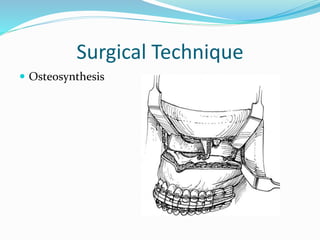
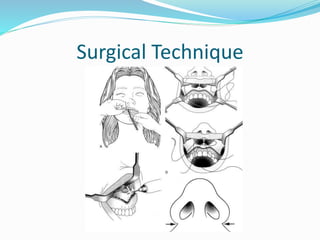
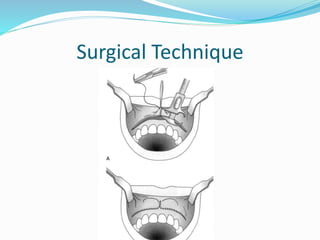
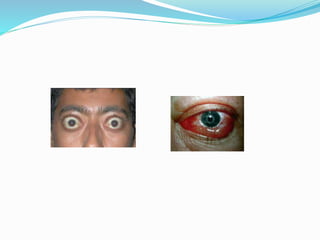
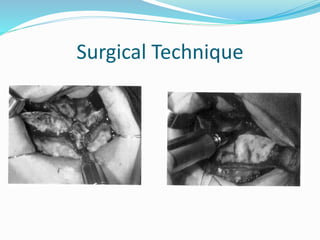
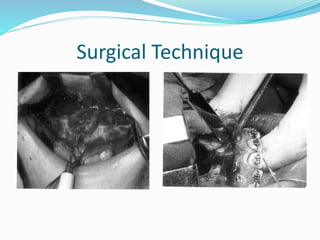
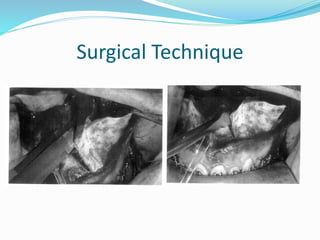
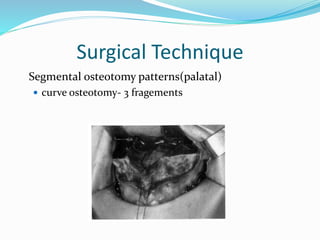
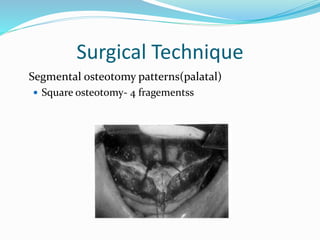
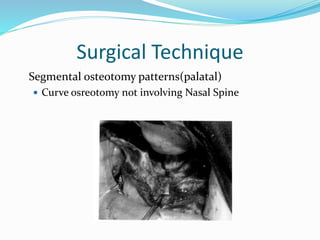
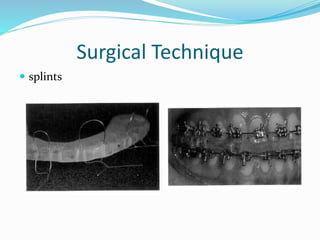
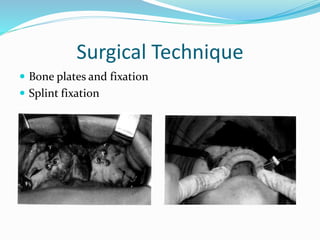
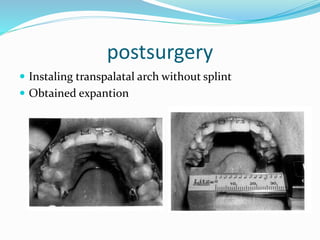
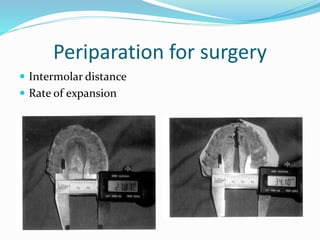
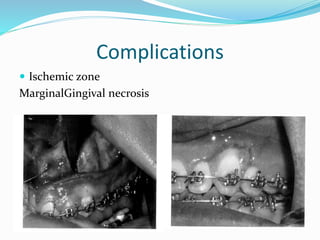
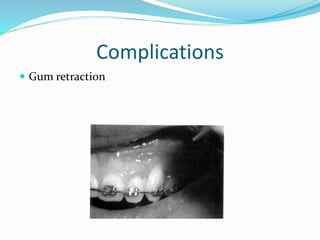
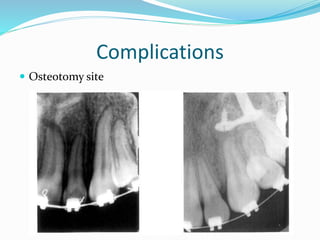
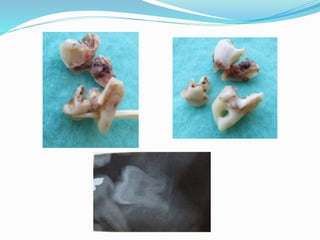
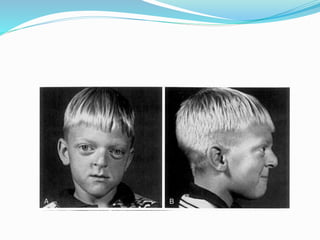
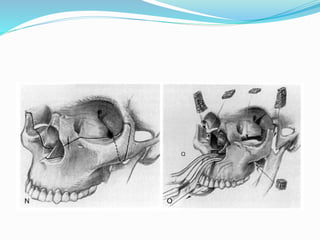
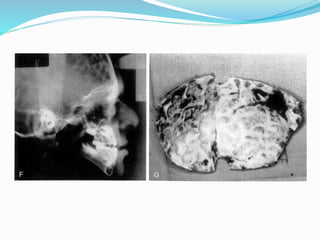
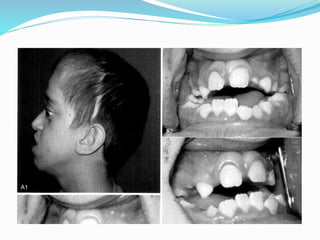
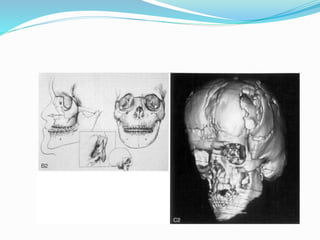
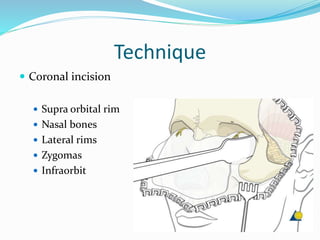
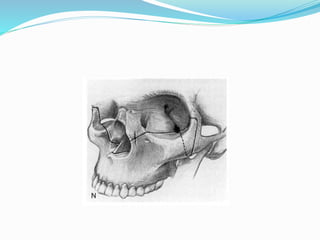
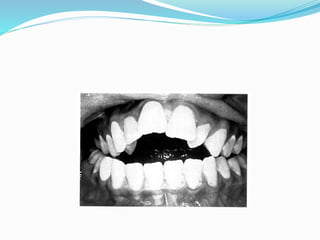
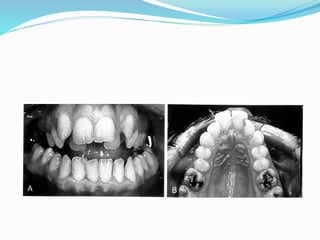
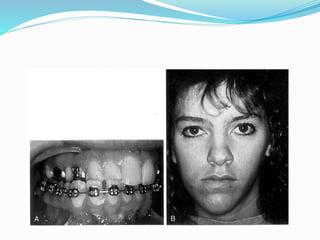
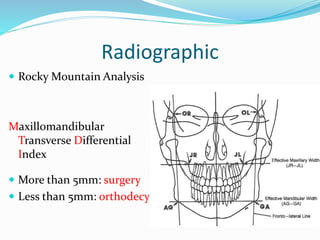
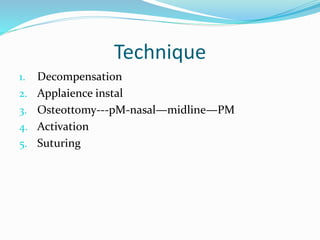
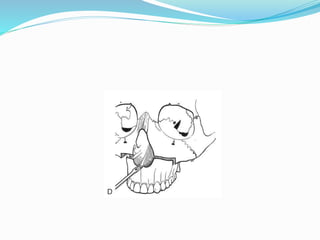
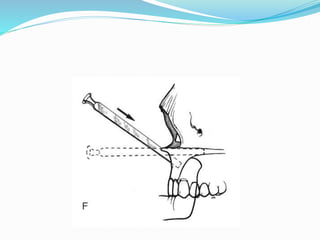
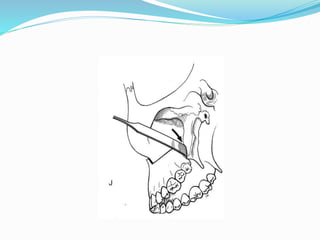
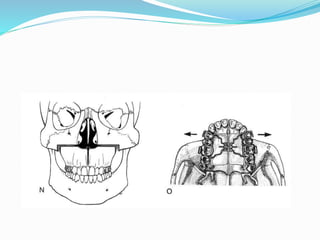
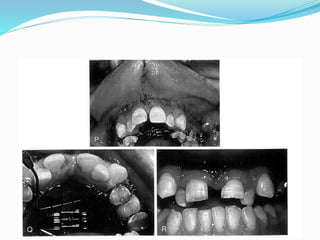
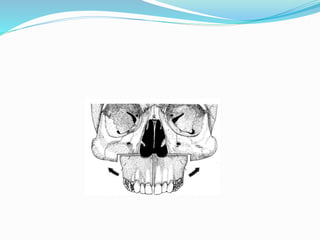
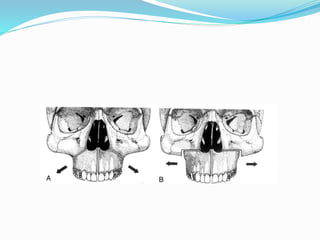
This document summarizes various techniques for maxillary osteotomies. It discusses Lefort 1 osteotomy, Lefort 1 segmental osteotomy, Lefort 3 osteotomy, subcranial Lefort 3 osteotomy, modified Lefort 3 osteotomy, and transverse maxillary distraction osteogenesis. For each technique, it provides information on history, indications, surgical anatomy, technique, complications, and modifications when applicable. The document is a guide for orthognathic surgeons on different maxillary osteotomy procedures.