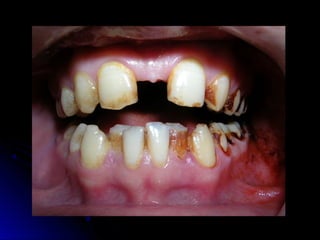
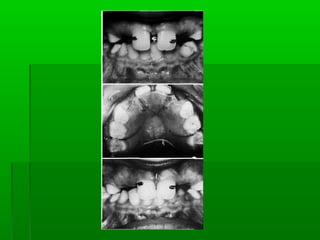
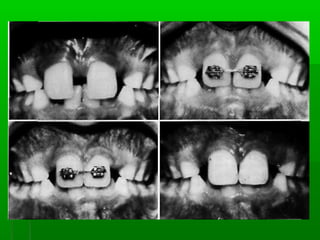
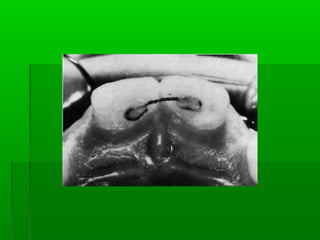
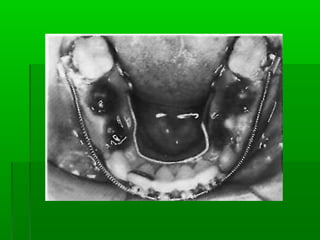
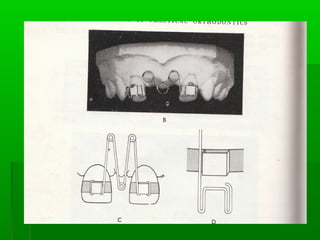
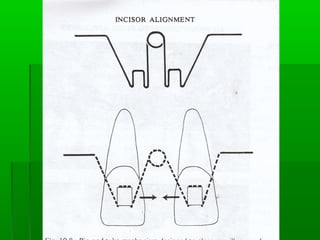
Maxillary median diastema is the presence of a space between the two maxillary incisors. It can be caused by deciduous dentition, abnormal frenal attachments, microdontia, congenitally missing teeth, trauma, abnormal pressure habits, heredity, and racial predisposition. Diagnosis involves measuring tooth sizes and a blanching test. Treatment may include removable appliances, fixed orthodontics, or correcting etiological factors like tongue thrusting. Generalized spacing can be due to small teeth, large arches, macroglossia, or abnormal tongue posture, and is treated through crowns, bridges, or correcting tongue habits.