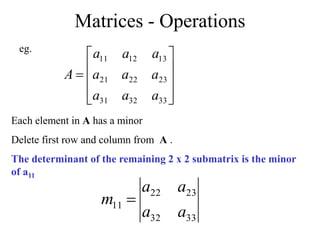
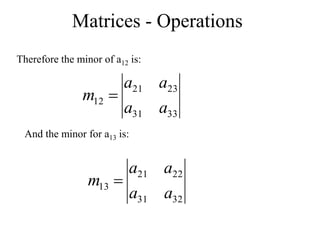
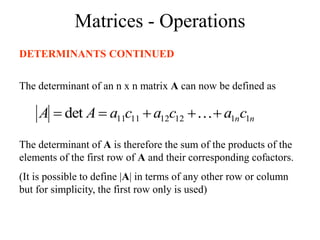
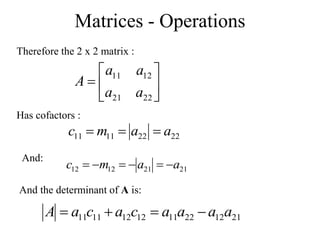
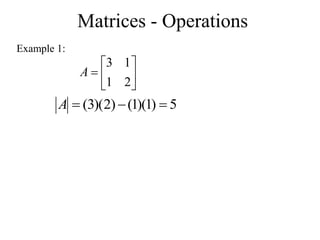
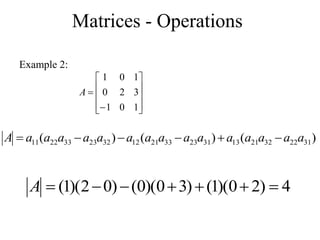
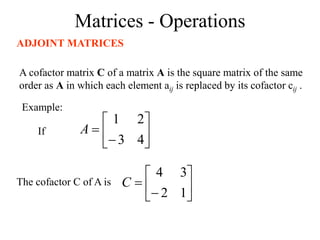
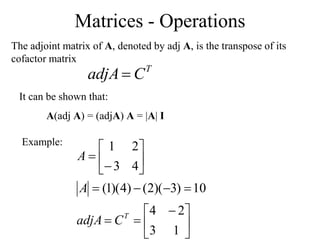
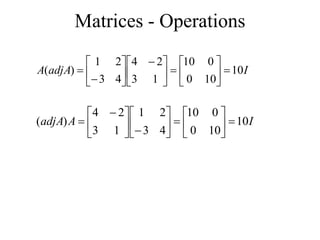
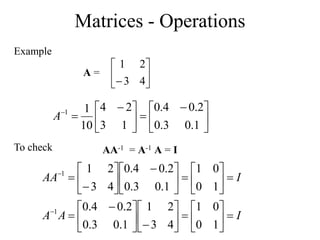
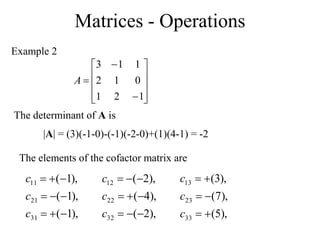
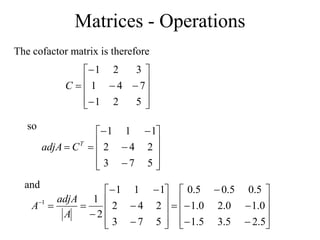
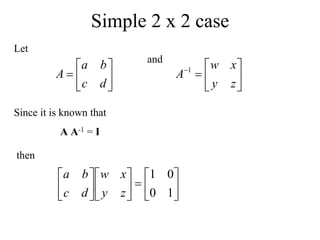
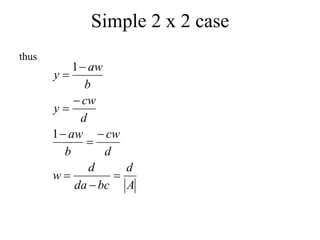
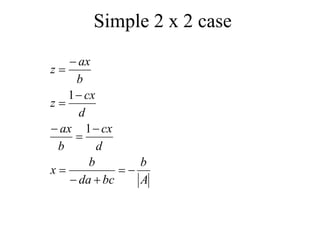
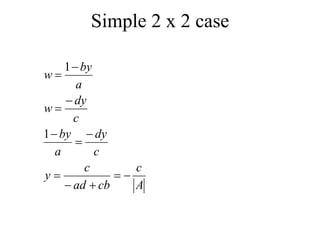
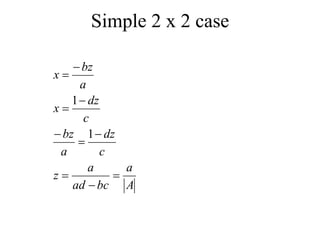
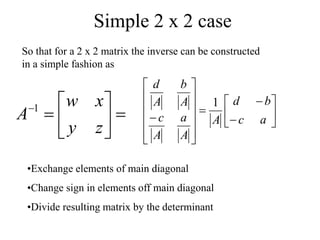
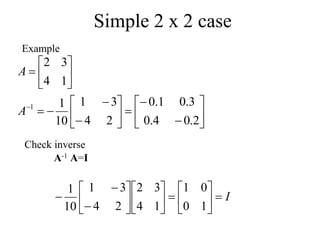
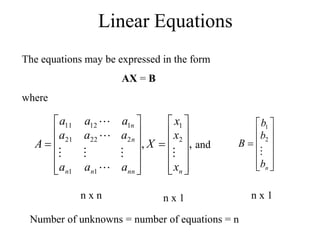
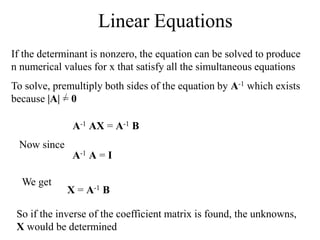
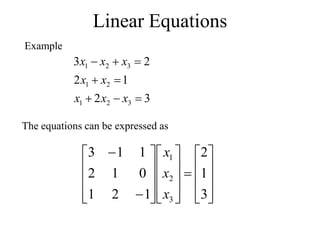
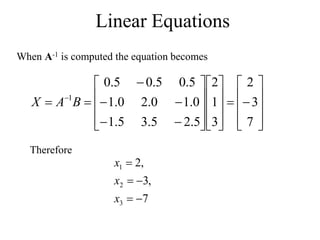
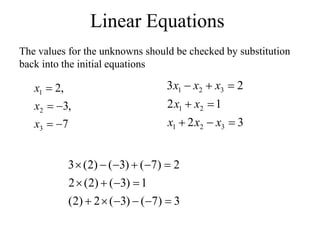
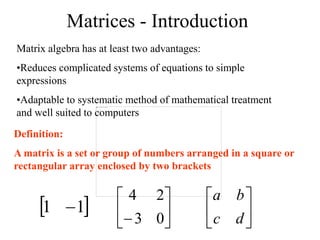
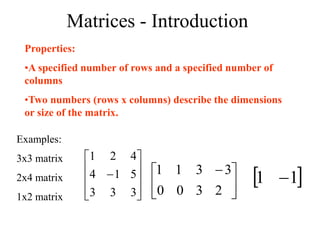
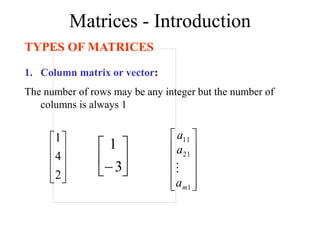
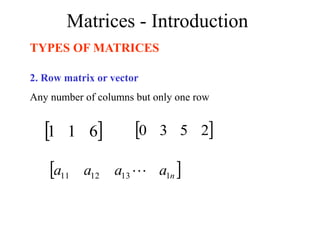
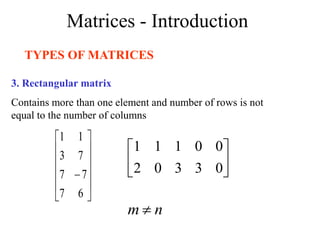
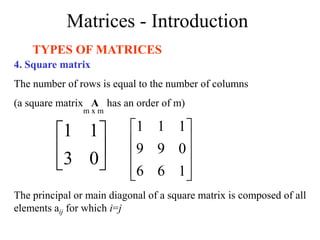
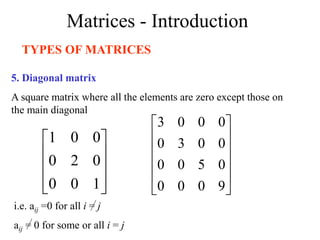
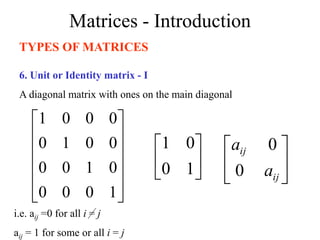
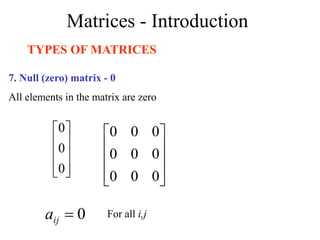
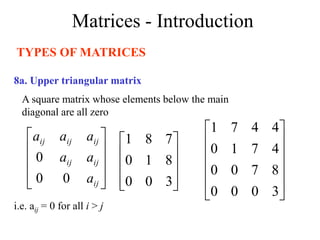
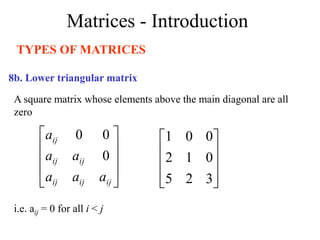
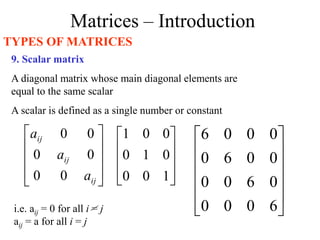
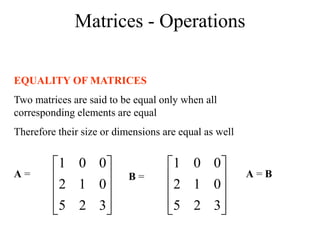
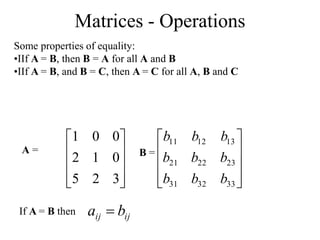
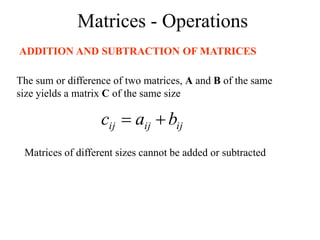
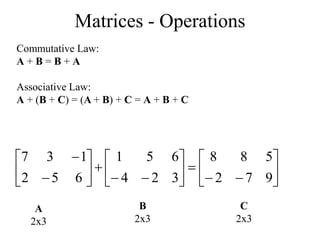
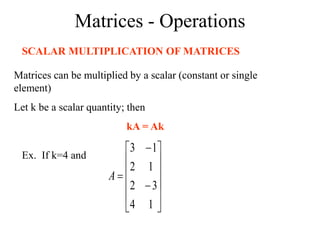
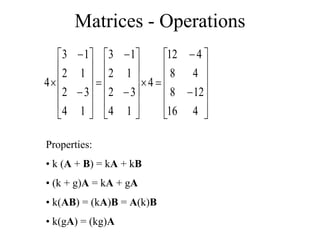
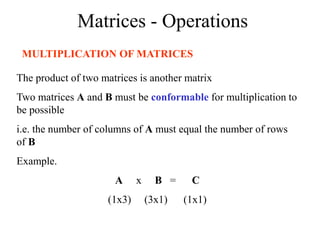
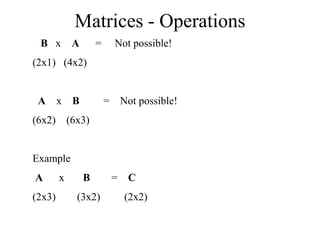
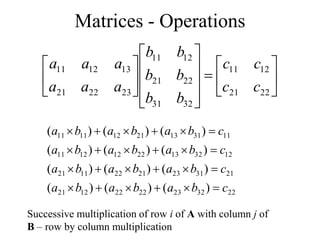
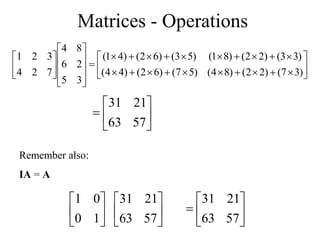
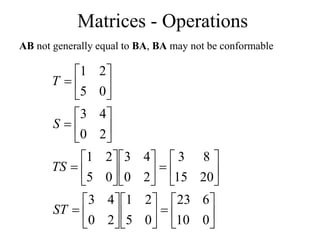
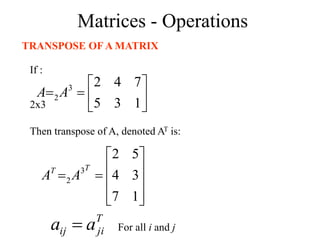
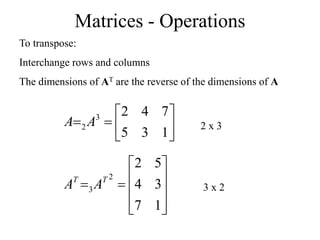
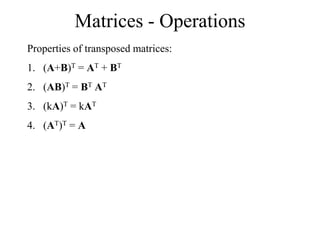
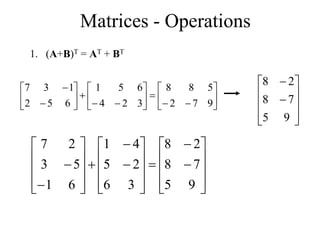
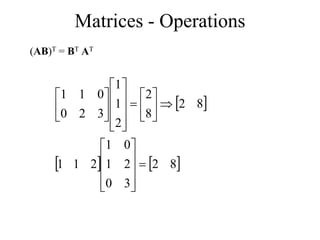
Matrices can be represented as arrays of numbers arranged in rows and columns. A matrix is defined by its dimensions (number of rows and columns). There are several types of matrices including square, rectangular, diagonal, identity, null, triangular, and scalar matrices. Operations on matrices include addition, subtraction, and multiplication. For matrices to be added or subtracted, they must be the same size. Matrices can be multiplied by a scalar value. Matrix multiplication results in another matrix, and the number of columns of the first matrix must equal the number of rows of the second matrix.

![Matrices - Introduction
A matrix is denoted by a bold capital letter and the elements
within the matrix are denoted by lower case letters
e.g. matrix [A] with elements aij
mn
ij
m
m
n
ij
in
ij
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
2
1
2
22
21
12
11
...
...
i goes from 1 to m
j goes from 1 to n
Amxn=
mAn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alliedmathematics-iunitiiimatrices-240213052955-e2d8a649/85/ALLIED-MATHEMATICS-I-UNIT-III-MATRICES-ppt-4-320.jpg)







![Matrices - Operations
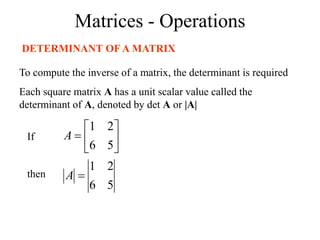
If A = [A] is a single element (1x1), then the determinant is
defined as the value of the element
Then |A| =det A = a11
If A is (n x n), its determinant may be defined in terms of order
(n-1) or less.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alliedmathematics-iunitiiimatrices-240213052955-e2d8a649/85/ALLIED-MATHEMATICS-I-UNIT-III-MATRICES-ppt-42-320.jpg)