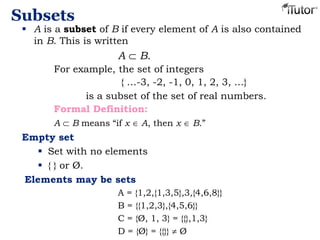
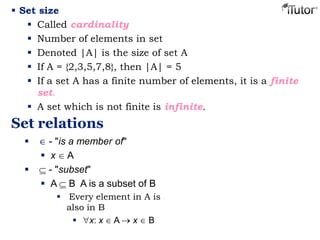
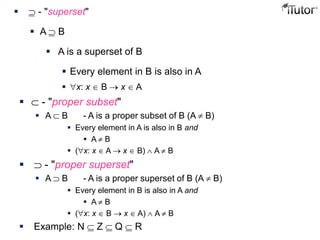
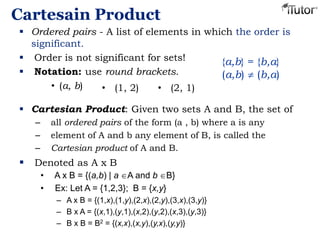
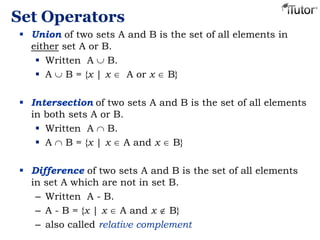
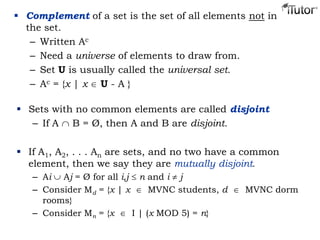
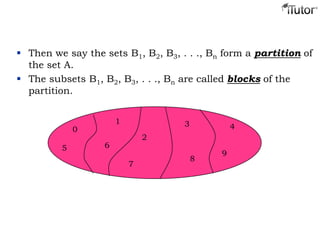
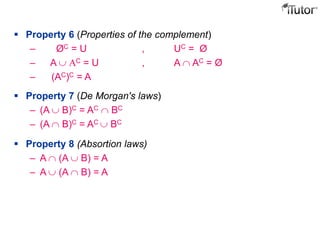
This document provides an overview of set theory, including definitions and concepts. It begins by defining a set as a collection of distinct objects, called elements or members. It describes how sets are denoted and provides examples. Key concepts covered include subsets, the empty set, set operations like union and intersection, and properties of sets. The document also discusses topics like the power set, Cartesian products, partitions, and the universal set. Overall, it serves as a comprehensive introduction to the basic ideas and terminology of set theory.