This document provides an introduction and overview of MATLAB. It discusses:
- What MATLAB is, its history of being created in 1984 by Cleve Moler as a numerical computing environment and programming language.
- Why MATLAB is useful for matrix manipulation, plotting functions and data, implementing algorithms, and creating GUIs.
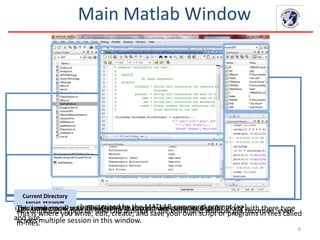
- The main components of the MATLAB structure including the command window, editor window, workspace, command history and current directory.