This document provides an introduction to MATLAB programming. It covers topics such as script files, flow control structures, array operations, the EVAL command, functions, variables and workspaces, subfunctions, private functions, and visual debugging. The document consists of 34 pages outlining these MATLAB programming concepts and providing examples to illustrate them.




![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 11
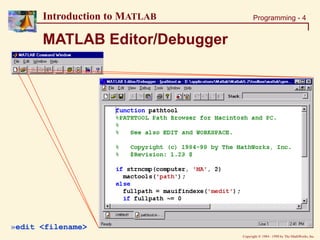
Introduction to MATLAB
Recall: Array Operations
• Using Array Operations:
• Using Loops:
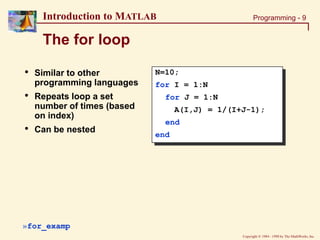
[rows, cols] = size(M);
for I = 1:rows
for J = 1:cols
Density(I,J) = M(I,J)/(L(I,J)*W(I,J)*H(I,J));
end
end
Density = Mass(I,J)/(Length.*Width.*Height);
»array_vs_loops](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 12
Introduction to MATLAB
EVAL Command
% This file creates the first N magic matrices.
% Each matrix is saved as a variable: "magic#".
N = 10;
for I = 1:N
eval(['magic', num2str(I), ' = magic(I)']);
end
»eval_examp
• Evaluates the MATLAB expression specified by
the input string.
• Very useful for inserting indices into strings.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-12-320.jpg)

![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 15
Introduction to MATLAB
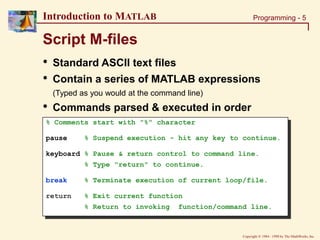
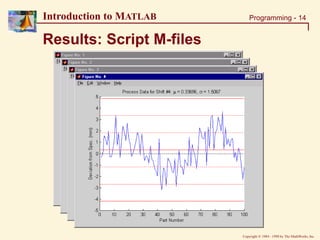
Solution: Script M-files
[parts, shifts]=size(data);
for I=1:shifts
DATA = data(:,I);
MEAN = mean(DATA); % Calculating mean & Std. deviation
STDEV = std(DATA);
figure(I); clf; hold on % Creating plots
plot(1:parts, DATA, 'b');
plot([0 parts], [0 0], 'k:',...
[0 parts], [1 1]*MEAN, 'r-.',...
[0 parts], [1 1]*(MEAN-STDEV), 'r:',...
[0 parts], [1 1]*(MEAN+STDEV), 'r:',...
); % .....etc.
% Writing variables to workspace
eval(['data', num2str(I), '=data(:,I);']);
eval(['mean', num2str(I), '=means(I);']);
eval(['stdev', num2str(I), '=stdev(I);']);
end
»script_soln (uses: script_data.txt)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-15-320.jpg)
![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 17
Introduction to MATLAB
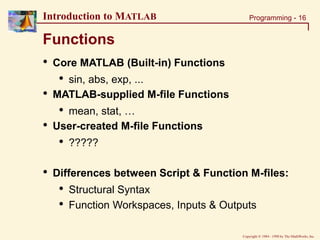
function y = mean(x)
% MEAN Average or mean value.
% For vectors, MEAN(x) returns the mean value.
% For matrices, MEAN(x) is a row vector
% containing the mean value of each column.
[m,n] = size(x);
if m == 1
m = n;
end
y = sum(x)/m;
Structure of a Function M-file
Keyword: function Function Name (same as file name .m)
Output Argument(s) Input Argument(s)
Online Help
MATLAB
Code
»output_value = mean(input_value) Command Line Syntax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-17-320.jpg)
![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 18
Introduction to MATLAB
Multiple Input & Output Arguments
function r = ourrank(X,tol)
% OURRANK Rank of a matrix
s = svd(X);
if (nargin == 1)
tol = max(size(X))*s(1)*eps;
end
r = sum(s > tol); function [mean,stdev] = ourstat(x)
% OURSTAT Mean & std. deviation
[m,n] = size(x);
if m == 1
m = n;
end
mean = sum(x)/m;
stdev = sqrt(sum(x.^2)/m – mean.^2);
Multiple Input
Arguments ( , )
Multiple Output
Arguments [ , ]
»RANK = ourrank(rand(5),0.1);
»[MEAN,STDEV] = ourstat(1:99);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-18-320.jpg)



![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 24
Introduction to MATLAB
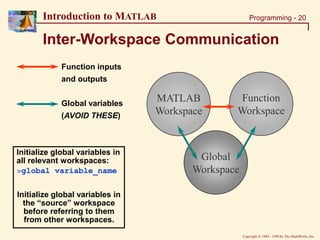
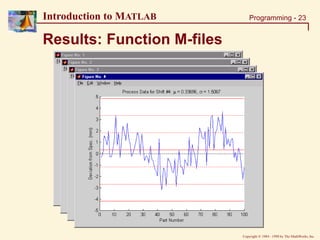
Solution: Function M-files (1)
% Modified Script file
% ====================
% This solution sets the figure#, overwrites the title, &
% writes the workspace variables outside the function.
shifts=size(data,2);
for I=1:shifts
DATA = data(:,I);
figure(I)
% Function Call
[MEAN, STDEV] = func_plot(DATA);
% Writing variables to workspace
eval(['data', num2str(I), '=DATA;']);
eval(['mean', num2str(I), '=MEAN;']);
eval(['stdev', num2str(I), '=STDEV;']);
end
»func_soln (uses: func_plot & script_data.txt)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-24-320.jpg)
![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 25
Introduction to MATLAB
Solution: Function M-files (2)
function [MEAN, STDEV] = func_plot(data)
% FUNC_PLOT Calculates mean & std. deviation & plots data
DATA = data(:);
parts= length(DATA);
MEAN = mean(DATA); % Calculating mean & Std. deviation
STDEV = std(DATA);
clf; hold on % Creating plots
plot(1:parts, DATA, 'b');
plot([0 parts], [0 0], 'k:',...
[0 parts], [1 1]*MEAN, 'r-.',...
[0 parts], [1 1]*(MEAN-STDEV), 'r:',...
[0 parts], [1 1]*(MEAN+STDEV), 'r:',...
); % .....etc.
xlabel('Part Number');
ylabel('Deviation from Spec. (mm)');
»func_soln (uses: func_plot & script_data.txt)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-25-320.jpg)
![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 27
Introduction to MATLAB
Example: Subfunctions
function [totalsum,average] = subfunc (input_vector)
% SUBFUNC Calculates cumulative total & average
totalsum = sum(input_vector);
average = ourmean(input_vector); %Call to subfunction
function y = ourmean(x)
% (OURMEAN) Calculates average
[m,n] = size(x);
if m == 1
m = n;
end
y = sum(x)/m;
»[SUM, MEAN] = subfunc(rand(1,50))
Primary
Function
Sub-
Function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-27-320.jpg)

![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 30
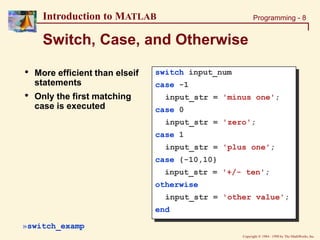
Introduction to MATLAB
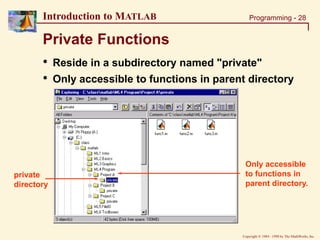
Visual Debugging
Set Breakpoint
Clear Breaks
Step In
Single Step
Continue
Quit Debugging
»[SUM, MEAN] = subfunc(rand(1,50))
Select
Workspace
Set Auto-
Breakpoints](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-30-320.jpg)
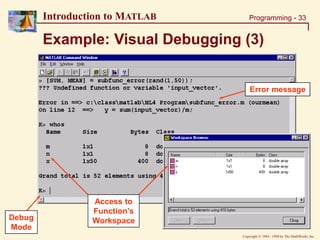
![Copyright 1984 - 1998 by The MathWorks, Inc.
Programming - 31
Introduction to MATLAB
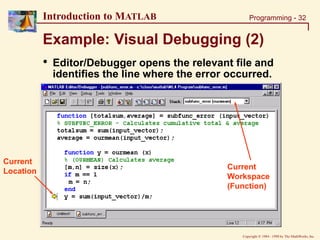
Example: Visual Debugging
• Set up your debugger to stop if an error occurs
• Then run: »[SUM, MEAN] = subfunc_error(rand(1,50))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconceptofmatlab-230209185247-605ba616/85/Basic-concept-of-MATLAB-ppt-31-320.jpg)