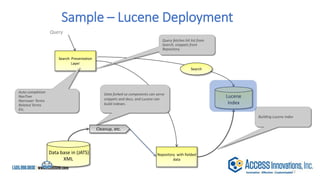
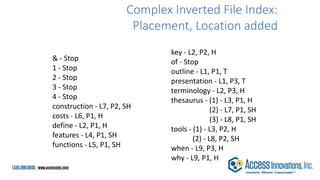
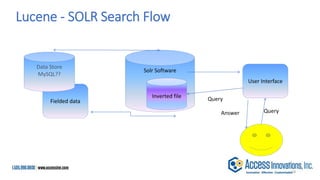
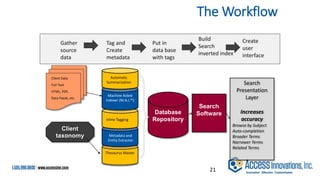
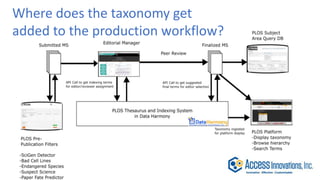
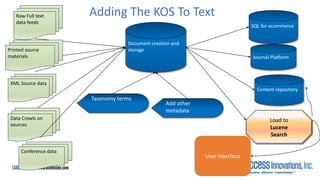
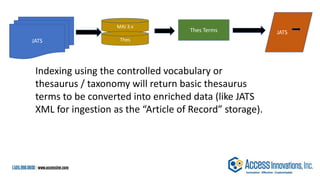
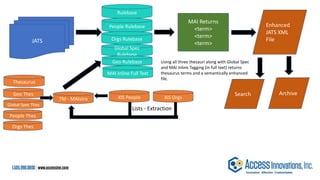
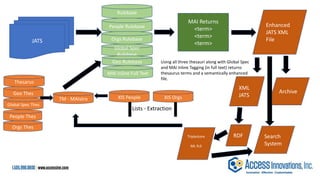
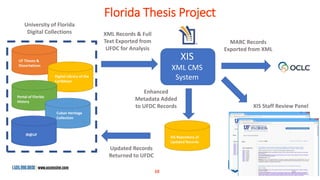
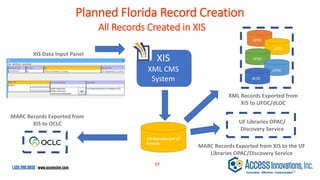
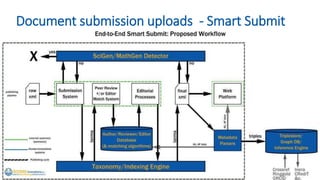
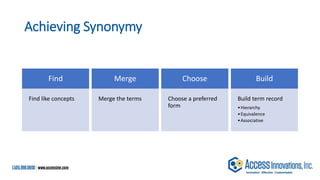
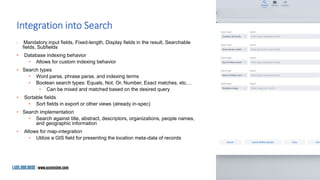
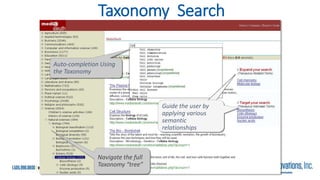
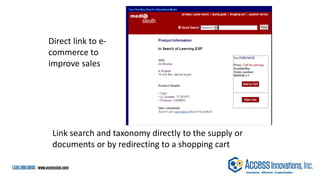
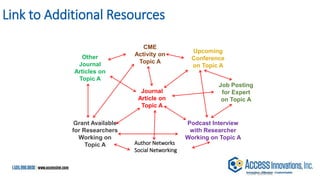
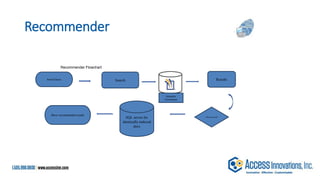
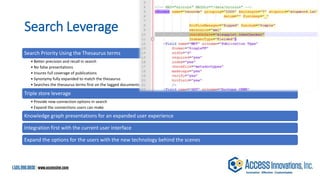
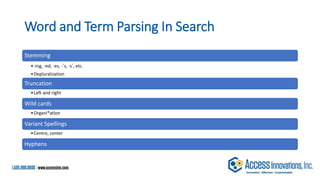
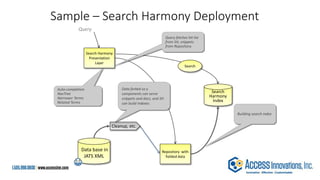
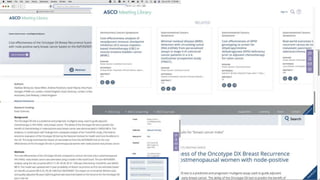
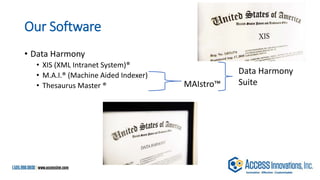
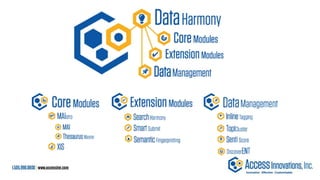
The document is a presentation by Marjorie M. K. Hlava on the role of taxonomies in enhancing search functionality across e-commerce and information systems. It discusses the challenges of search relevance and discoverability, advocating for the use of taxonomies to provide structured and efficient information retrieval. Key components such as search algorithms, content layers, and user interface design are emphasized for improved user experience and search outcomes.