The rational root theorem states that if P/Q is a rational root of a polynomial equation with integer coefficients, then P must be a factor of the leading coefficient and Q must be a factor of the constant term.
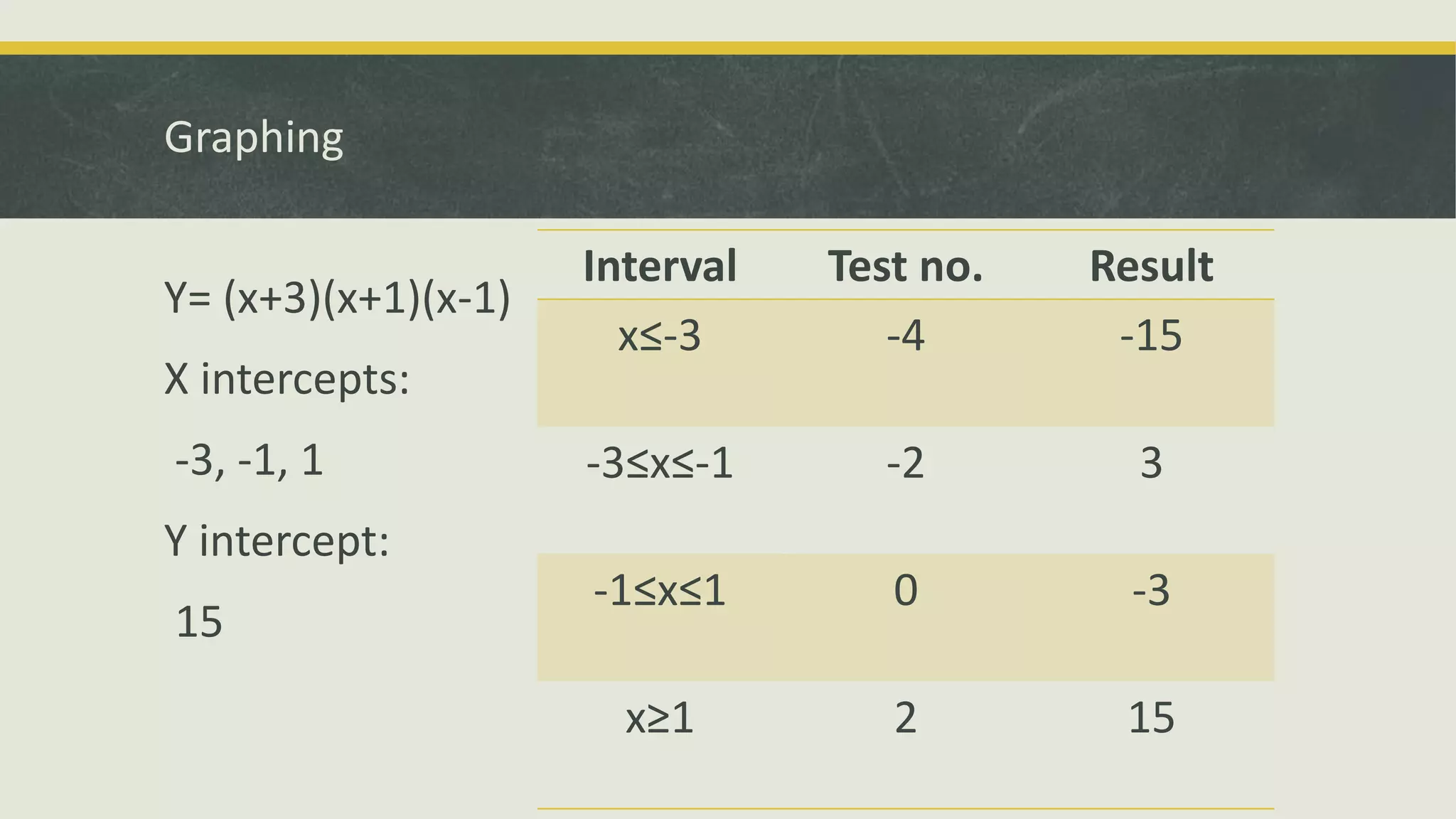
The document also discusses using the interval test and graphing polynomials to determine where a polynomial is positive or negative. It provides examples of sketching graphs of polynomials based on their degree and characteristics at roots, such as whether the graph will cross or bounce at roots depending on if the root's multiplicity is odd or even.