Embed presentation
Download to read offline
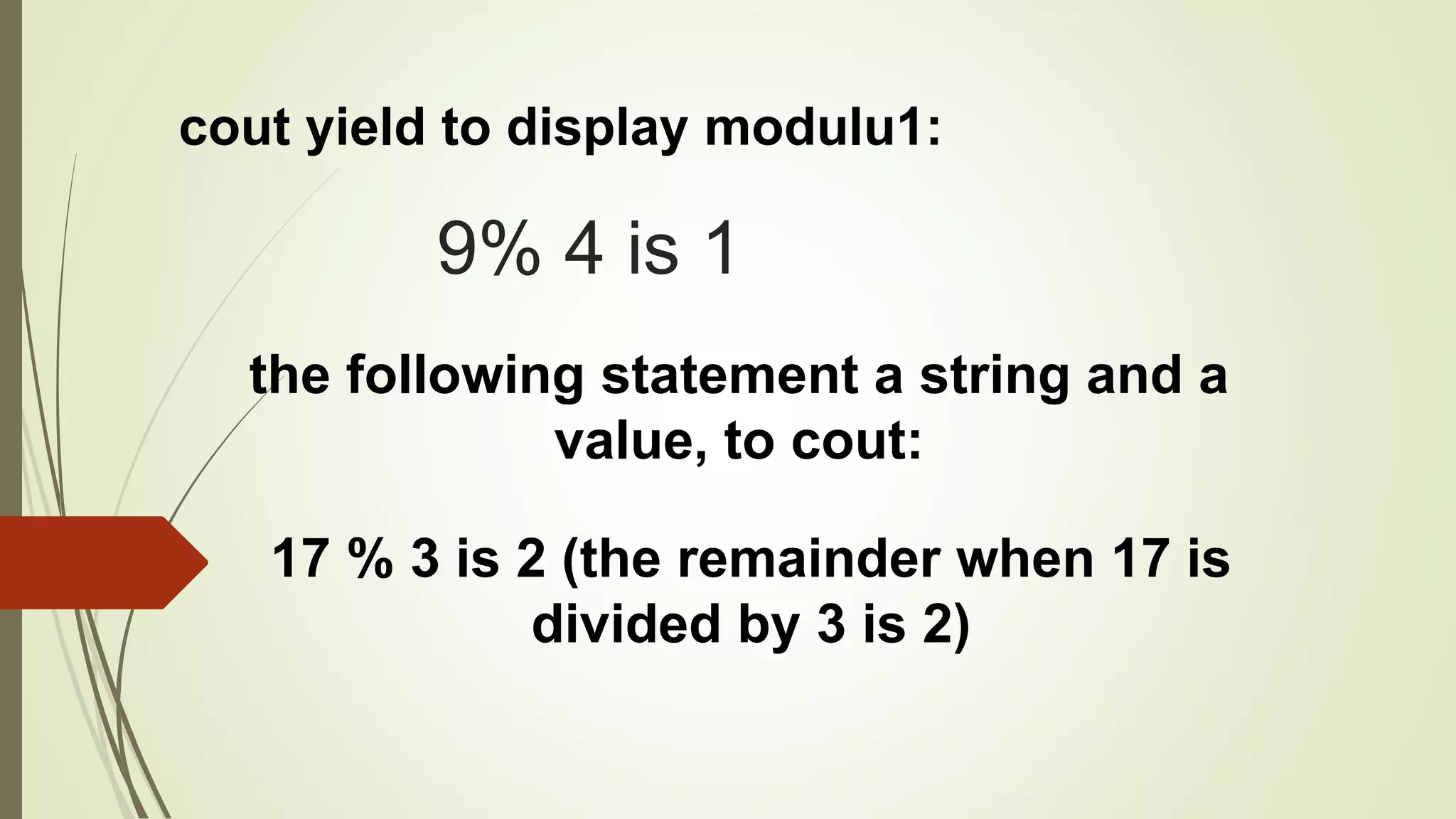



Integer division in C++ truncates any fractional part of the result. The modulus operator (%) returns the remainder of an integer division. For example, 17 % 3 is 2, because the remainder of 17 divided by 3 is 2. The modulus operator allows retaining the remainder instead of dropping it during integer division.



