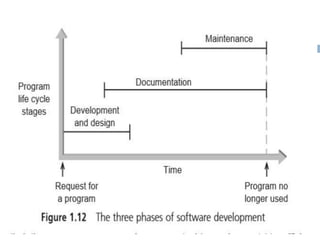
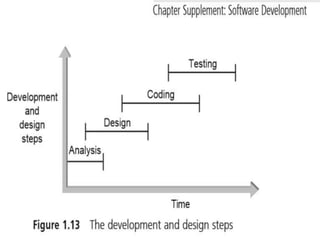
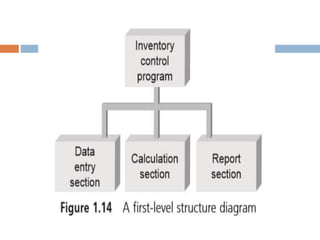
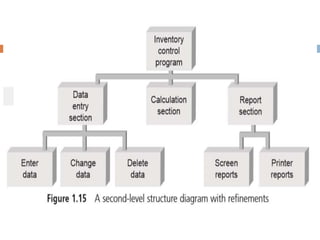
The document discusses the phases and steps of the software development process. It begins with defining a program and explaining that writing a program is the last step after determining the problem and solution method. There are typically three phases: development and design, documentation, and maintenance. The development and design phase consists of four steps - analyzing the problem, developing a solution algorithm, coding the solution, and testing and correcting the program. The goal of software engineering is to create programs and systems that are readable, efficient, reliable, and maintainable.