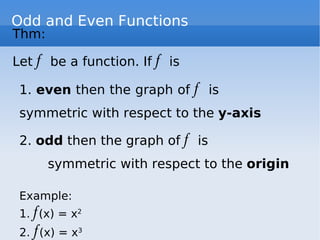
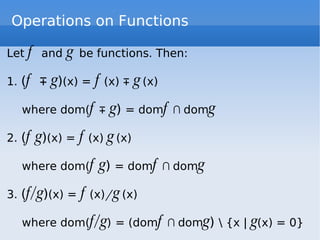
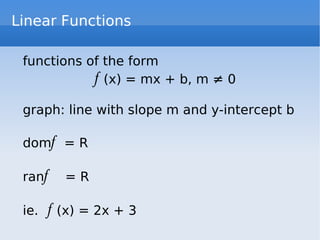
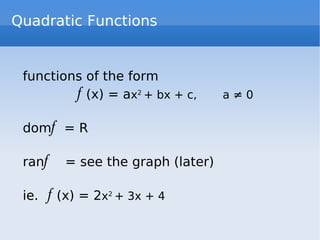
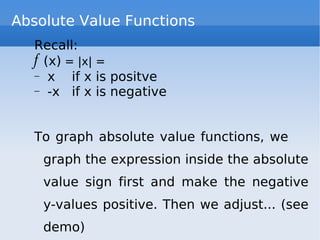
El documento trata sobre las gráficas de funciones y sus propiedades, incluyendo la definición de una función y el test de la línea vertical. Se discuten funciones pares e impares, así como operaciones con funciones, y se presentan ejemplos de funciones constantes, lineales y cuadráticas, junto con sus gráficos. También se explican las funciones de valor absoluto y las funciones por tramos.