This document provides information about inverse functions including:
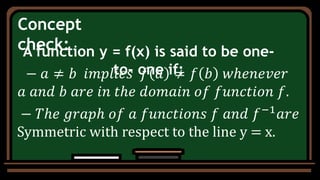
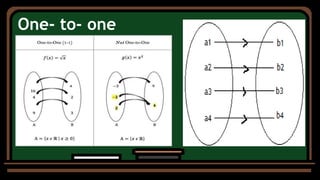
- The inverse of a function is formed by reversing the coordinates of each ordered pair. A function has an inverse only if it is one-to-one.
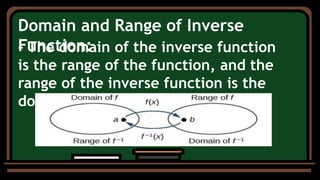
- The domain of the inverse function is the range of the original function, and the range of the inverse is the domain of the original.
- To find the inverse of a one-to-one function, replace f(x) with y, interchange x and y, then solve for y in terms of x and replace y with f^-1(x).
- Several examples are provided to demonstrate finding the inverse of different one-to-one functions by following the given steps.