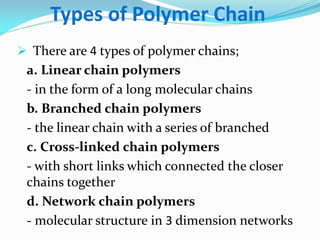
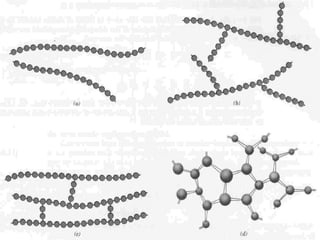
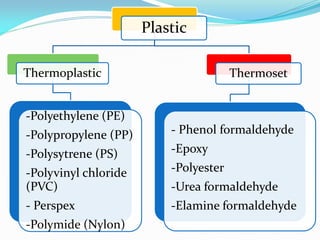
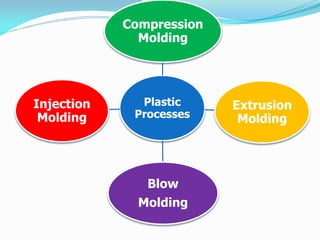
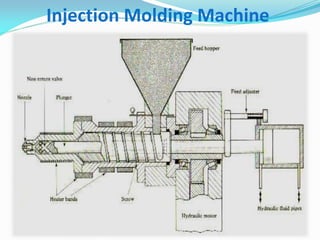
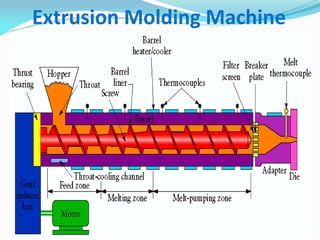
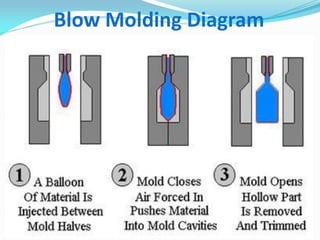
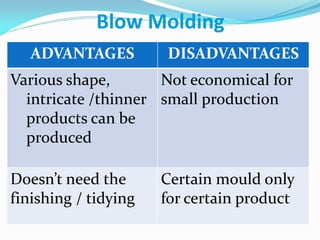
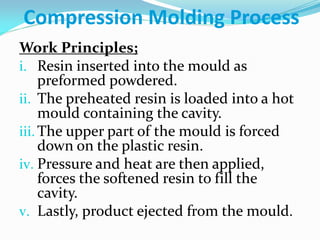
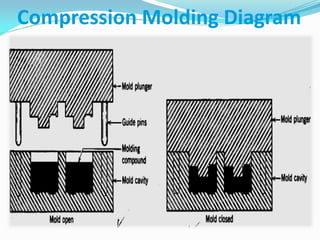
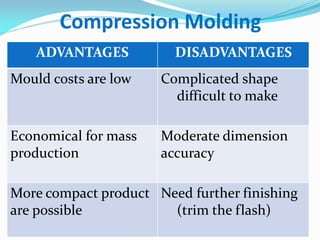
This document defines plastics and their production processes. Plastics are polymers made from monomers and can be thermoplastics or thermosets. Thermoplastics soften when heated and can be remolded, while thermosets set during molding. Common plastics include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyvinyl chloride. Plastics are produced via injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and compression molding. Injection molding uses heated resin that is injected into a mold, while extrusion produces continuous shapes and blow molding uses air to expand parisons in a mold.