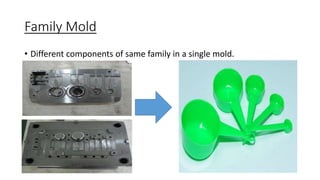
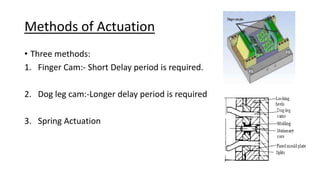
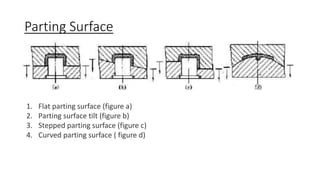
The document provides a comprehensive overview of mold design, detailing the basic concepts, manufacturing and machining processes, types of molds, and the various molding processes including injection molding, compression molding, and blow molding. Additionally, it covers design considerations, part specifications, and software tools like pro/moldesign for simulating and analyzing mold operations. The information serves to educate about the intricacies of mold-making and its applications in producing plastic components.