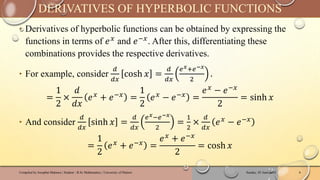
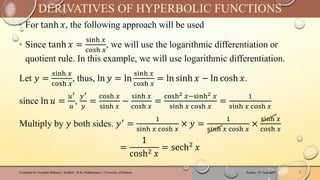
The document discusses hyperbolic functions, which are formed from exponential functions, specifically sinh(x) and cosh(x), and includes their definitions, identities, derivatives, integrals, and inverses. Key identities and differentiations are provided using logarithmic forms and implicit differentiation. Additionally, practice problems are included to reinforce understanding of hyperbolic and inverse hyperbolic functions.