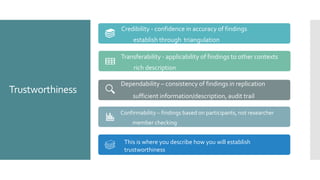
The document provides a comprehensive overview of qualitative methodology for dissertations, including research design, the role of the researcher, data collection techniques, and approaches such as case study, phenomenology, and grounded theory. It emphasizes the importance of trustworthiness, ethics, and effective recruitment and data analysis strategies. Additionally, it offers support resources for students seeking assistance with their dissertation projects.