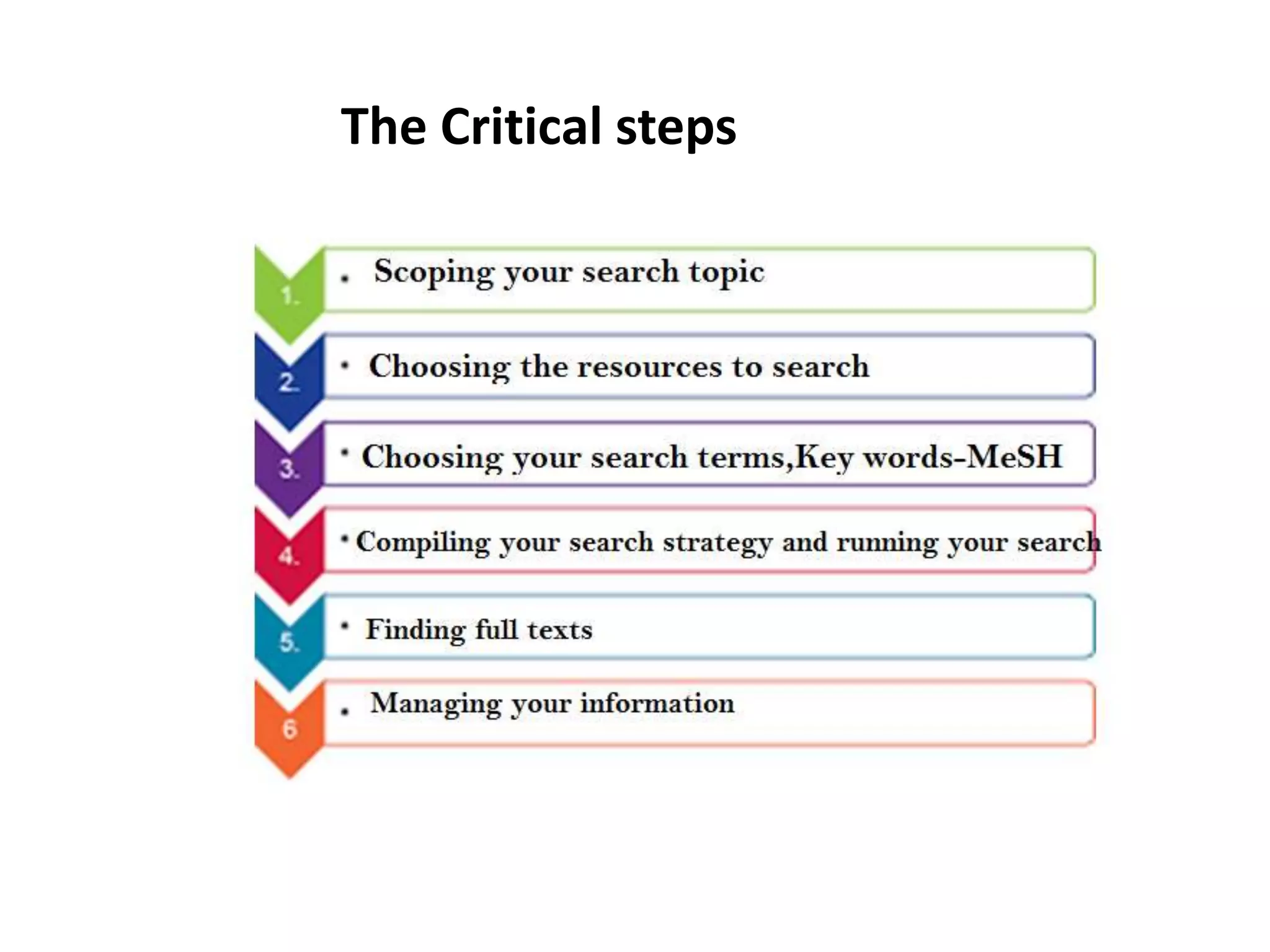
Dr. Bhaskar Borgohain discusses strategies for conducting an effective literature search. He emphasizes defining a clear research question, brainstorming keywords, using appropriate search techniques like Boolean operators and filters, and keeping detailed records of the search process. Maintaining a search diary and using a citation manager are important for reproducing and organizing search results.














![Search techniques:-
Refine your searches
Use of Filter to define Limit
• Age - children
• Time - last 5 years
• Language - English
• Article type - RCT, Metanalysis
• Subject - tumors
• [mh] to search a MeSH heading
• [majr] to search a MeSH heading that is a major topic of an
article](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/literaturesearchijokol-copy-191006062803/75/How-to-do-a-Literature-search-for-your-research-and-scientific-publication-16-2048.jpg)






![Example:
• If you type eye [mh] it will retrieve citations
indexed to:
Eye
Eyebrows
Eyelids
Eyelashes
Eyelids etc
Search techniques](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/literaturesearchijokol-copy-191006062803/75/How-to-do-a-Literature-search-for-your-research-and-scientific-publication-23-2048.jpg)
![Field tag
Type [au] for Author
e.g. John (au)
Type [ti] to search for Title of the paper
Type [ta] for search for the journal- but will not pick up ebooks
hypertension [ta]- to search for the Journal only
Note: this will find the journal named HYPERTENSION but not pick up the keyword
“hypertension”
Type [dp] for date of publication- period
blood[au] AND hypertension[ta] AND 2005[dp]
Search techniques](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/literaturesearchijokol-copy-191006062803/75/How-to-do-a-Literature-search-for-your-research-and-scientific-publication-24-2048.jpg)