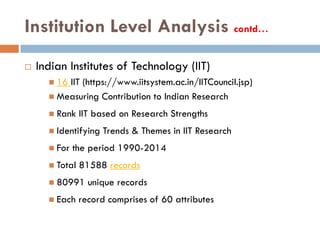
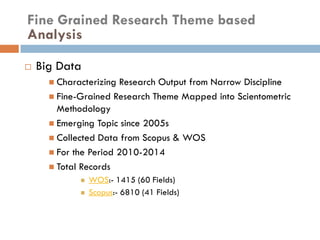
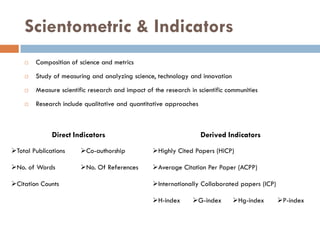
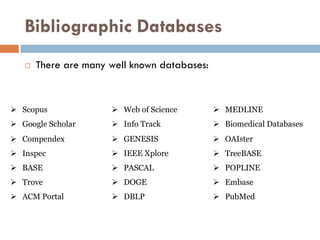
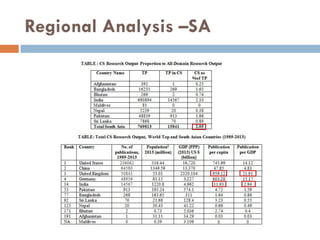
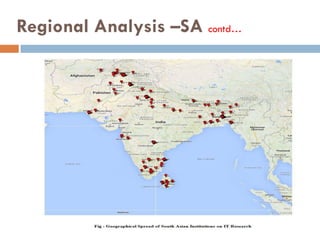
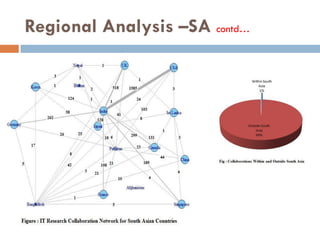
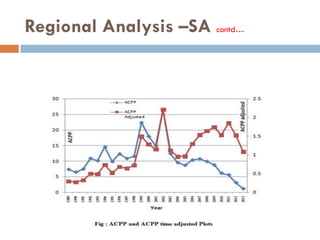
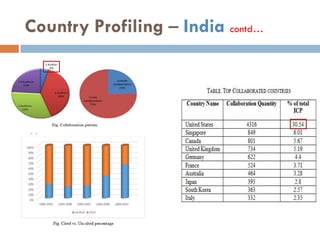
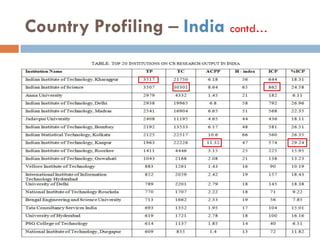
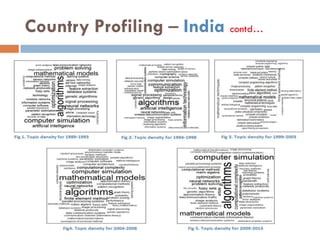
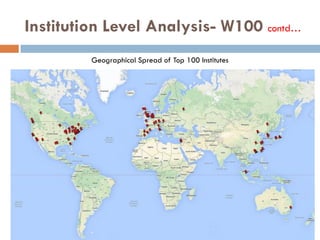
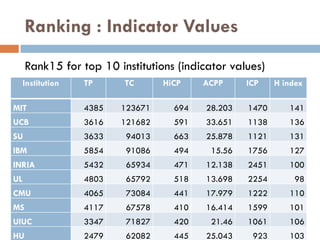
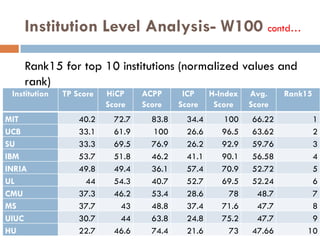
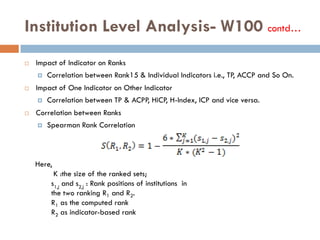
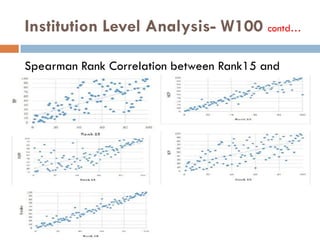
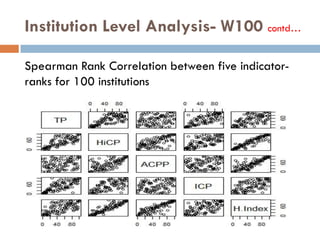
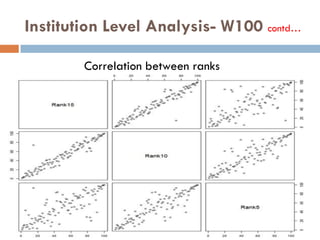
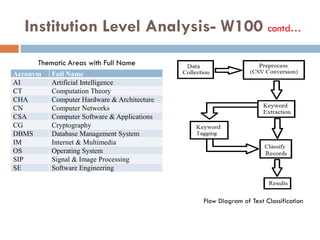
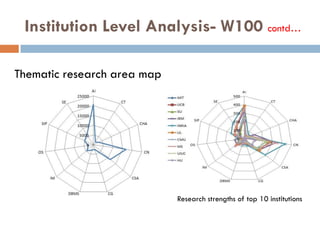
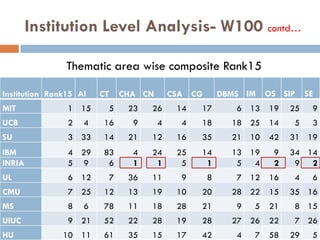
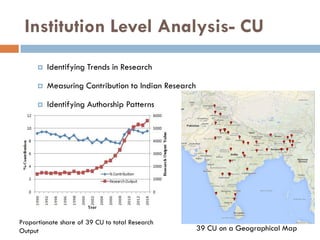
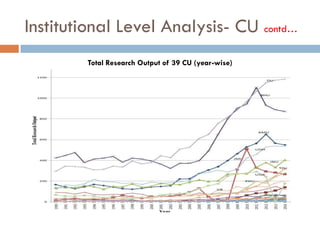
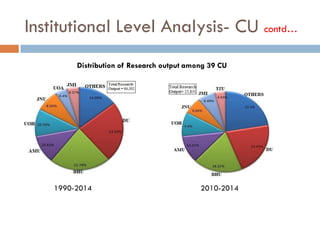
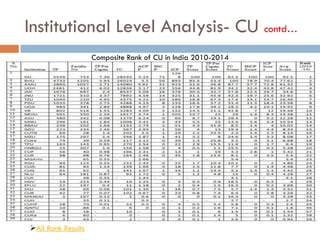
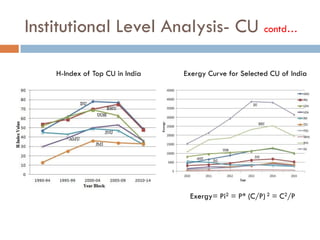
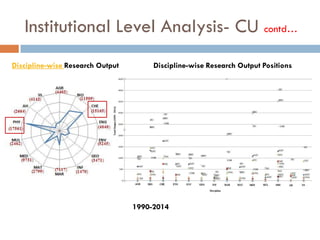
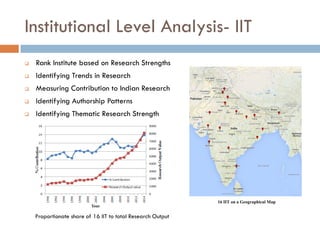
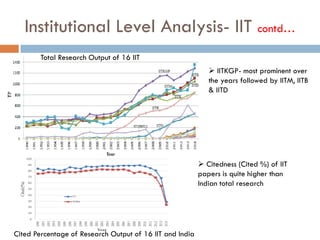
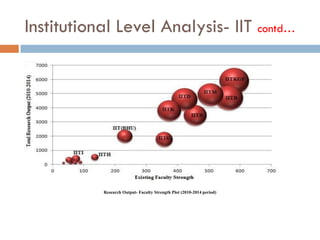
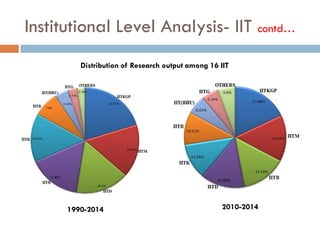
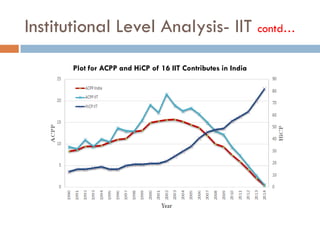
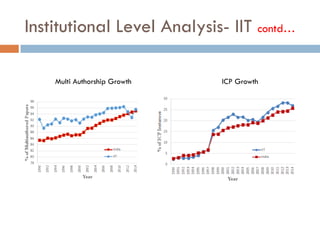
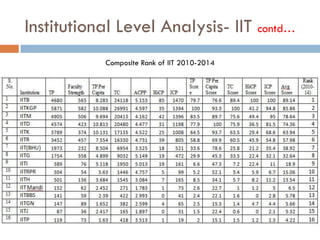
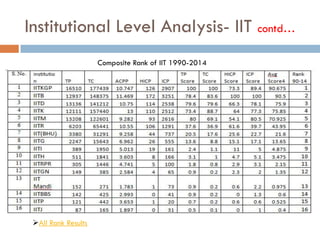
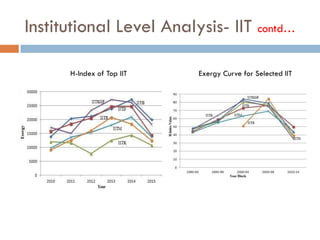
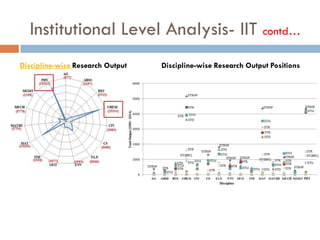
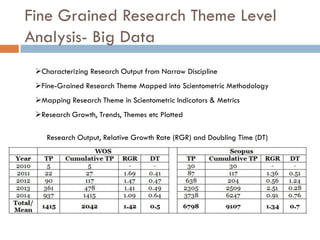
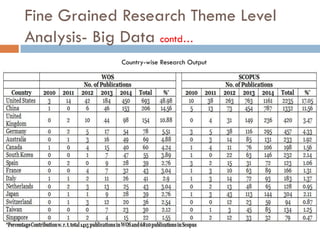
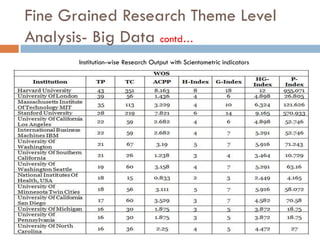
This document outlines a scientometric analysis of research competitiveness at the country, institution, and subject level. It discusses analyzing the research output of countries in South Asia, as well as Bangladesh and India individually. It also describes characterizing the top 100 world research institutions, analyzing the contribution and rankings of central universities and Indian Institutes of Technology in India. Finally, it discusses a fine-grained analysis of the research theme of big data. Key aspects covered include bibliographic databases used, scientometric indicators, methodology, and findings at each level of analysis.