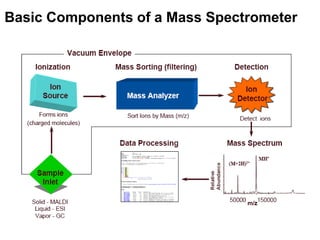
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that provides qualitative and quantitative information about molecules and atoms in samples, including their mass and molecular structure. It works by ionizing analyte molecules, separating the resulting ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio, and detecting them. Common applications include protein identification, characterization of biological molecules, and analysis of organic and inorganic compounds. Key components include methods for ionization, mass analyzers for separation of ions, and detectors.


























![Importance of the Matrix
• Matrix is necessary to dilute and disperse the analyte
• It functions as energy mediator for ionising the analyte itself or other neutral molecules
• It forms an activated state produced by photo ionisation.
•Maldi forms predominantly singly charged ions like [M+H]+ or adducts: sodium [M+Na]+
or potassium [M+K]+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-bat-mass-spec-heena-1-230414103333-a344af1b/85/05-BAT-Mass-Spec-Heena-1-pdf-28-320.jpg)











![Types of Ions Formed
• Electrospray can operate in either positive or negative mode.
• Positive mode:
– Best suited to basic molecules that form a stable HCl salt.
• [M+H]+ is the primary ion formed
• [M+nH]n+ and [M+Na+]+ can also be formed.
• Negative mode:
– Best suited to acidic molecules that form stable Na salts.
• [M-H]-, [M-nH]n- and [M+I-]-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-bat-mass-spec-heena-1-230414103333-a344af1b/85/05-BAT-Mass-Spec-Heena-1-pdf-40-320.jpg)

![1. Electrospray is a soft ionization technique generally producing [M+H]+ ions
in positive mode.
2. Most analytes that form an HCl salt will be analyzable by positive mode
electrospray.
3. Volatile buffers and mobile phases will increase generally ionization
efficiency.
4. Good chromatography producing concentrated bands of analyte at the
nebulizer tip will increase ionization efficiency.
5. Poor clean-up can lead to significant ion suppression usually at the
beginning of the LC run.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-bat-mass-spec-heena-1-230414103333-a344af1b/85/05-BAT-Mass-Spec-Heena-1-pdf-42-320.jpg)







![• Some of the analyte molecules can be indirectly ionized with the help of the
solvent molecules.
• The photons also excite the solvent molecules which are much more in
number than the analyte molecules.
• Since the molecules are at atmospheric pressure, there are billions of
molecular collisions per second.
•For a small fraction of these collisions, the result is a chemical reaction in
which the solvent molecule donates a proton (depicted by an H below) to the
analyte molecule (protonation).
• The process and outcome depends on the particular solvent used, but
generally this solvent-assisted chemical ionization can be represented as:
M + S + h → [M + H]+ + [S - H]- (solvent dependent)
Dopant Assisted APPI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-bat-mass-spec-heena-1-230414103333-a344af1b/85/05-BAT-Mass-Spec-Heena-1-pdf-50-320.jpg)
![• By this process we get two types of ions:
(M+• and [M + H]+) from one compound.
• These then proceed to the MS to be analyzed.
• This technique has been found to give much enhanced ionization for
some substances, as compared to atmospheric pressure chemical
ionization.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-bat-mass-spec-heena-1-230414103333-a344af1b/85/05-BAT-Mass-Spec-Heena-1-pdf-51-320.jpg)