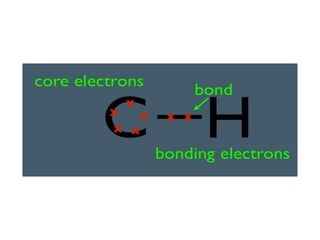
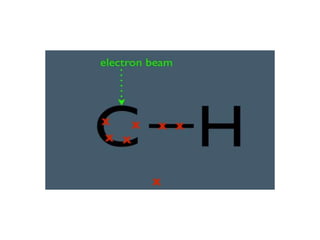
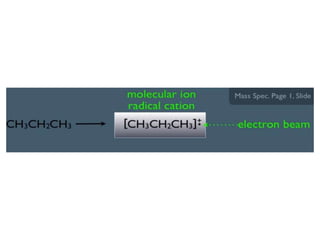
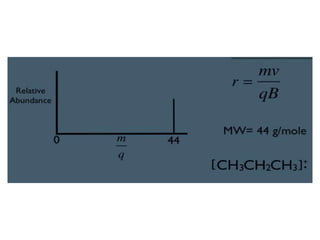
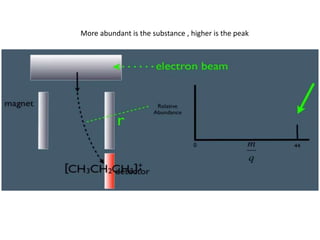
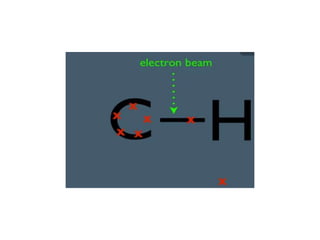
Mass spectrometry is a technique that identifies unknown substances based on the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It works by ionizing analyte molecules and separating the resulting ions in an electric or magnetic field based on their m/z ratio. Different ionization techniques like electron ionization, chemical ionization, electrospray ionization, and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization are used depending on the sample's physical state and properties. Mass analyzers like quadrupoles and time-of-flight instruments then measure the m/z of ionized molecules to generate mass spectra for analysis.